Mechanism of mechanical strength degradation and microstructure evolution of anthracite induced by supercritical carbon dioxide
-
摘要:
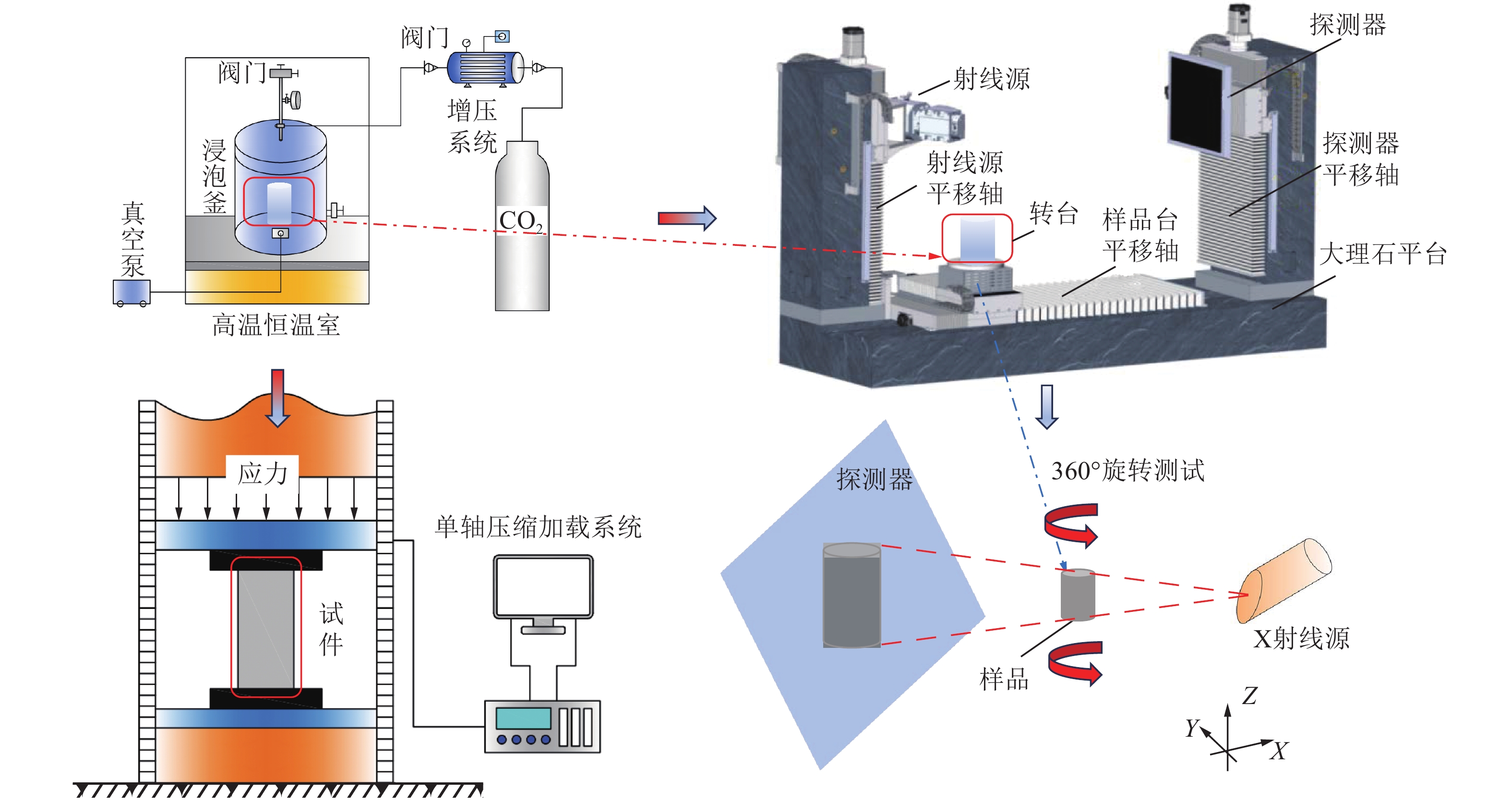
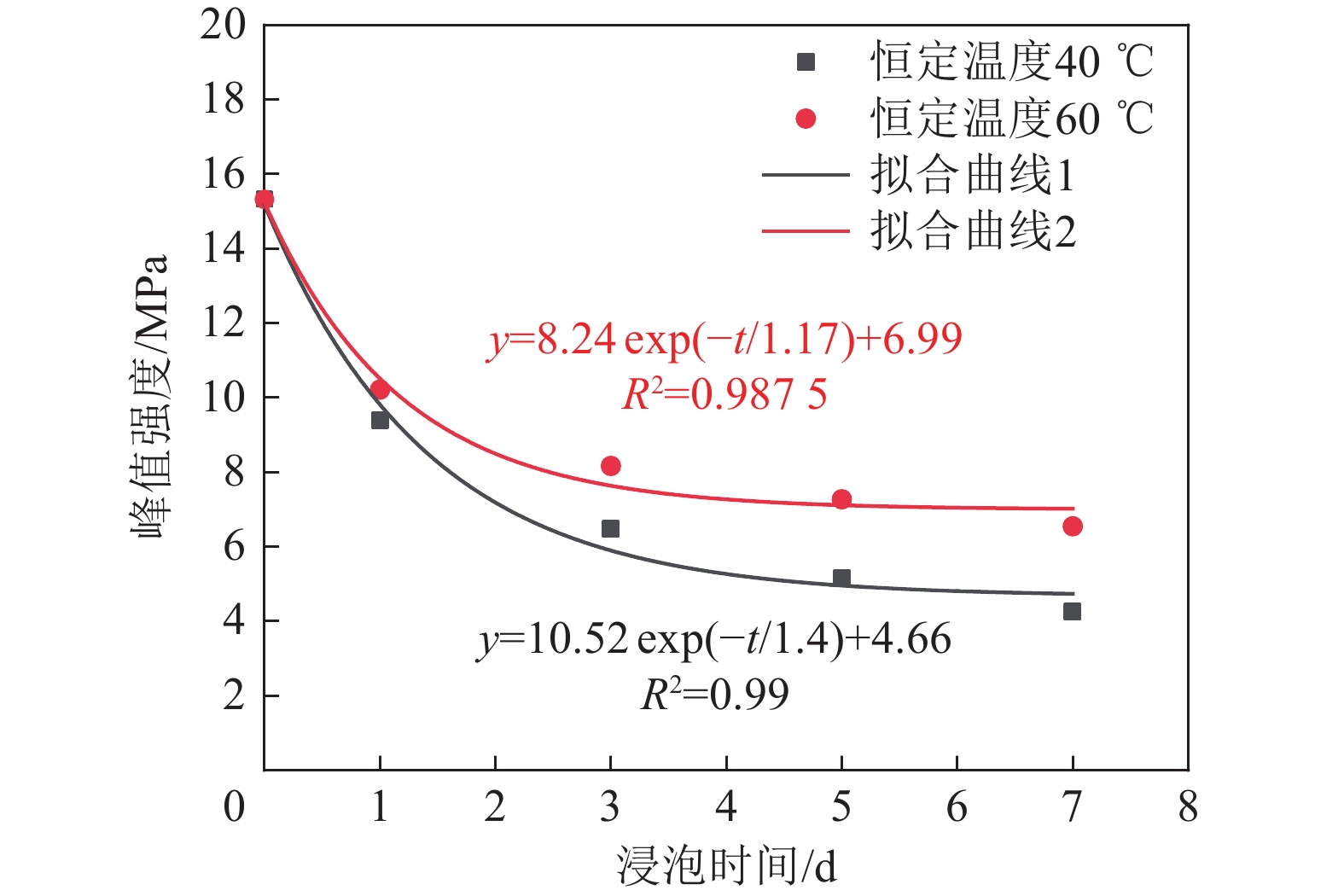
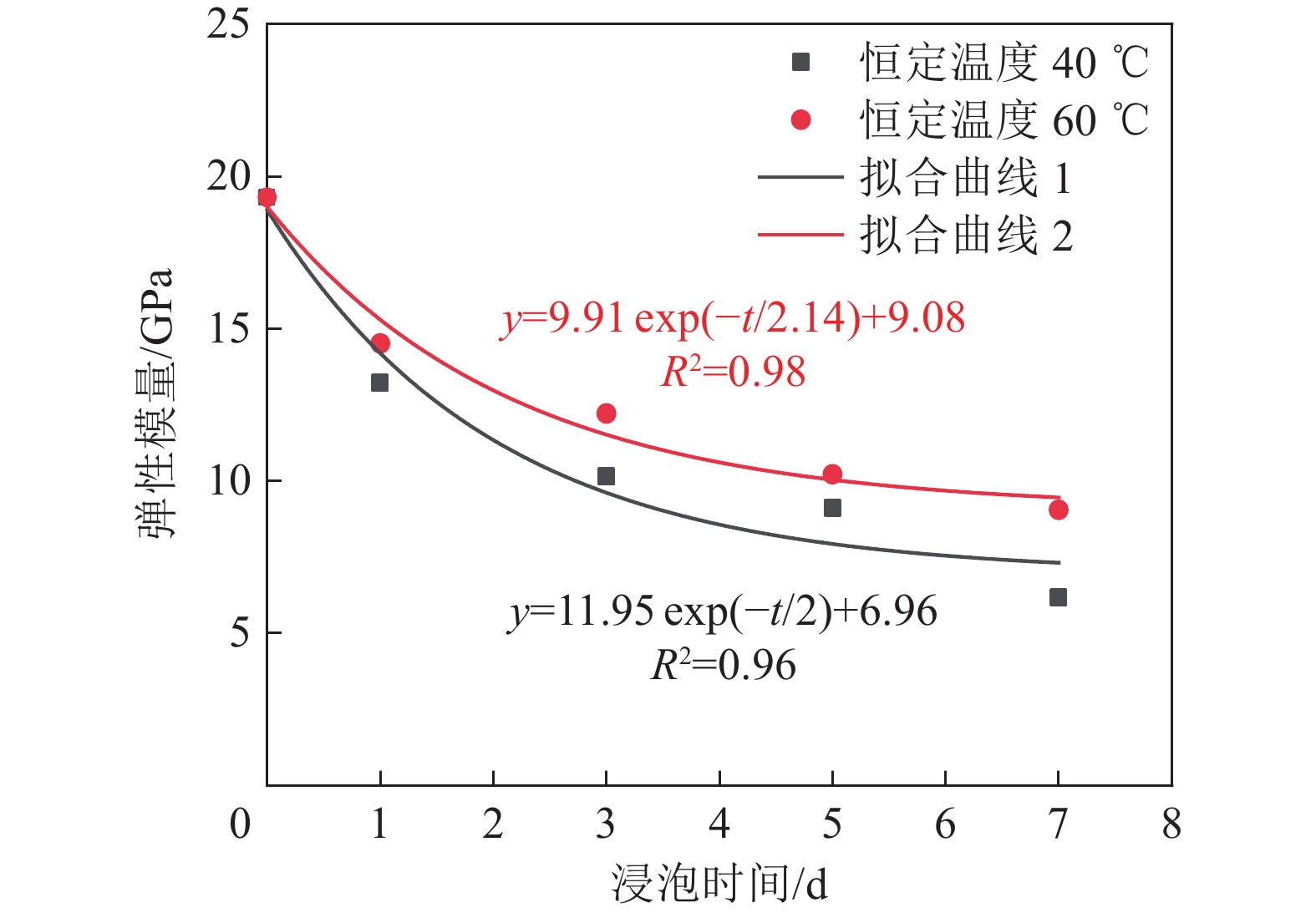
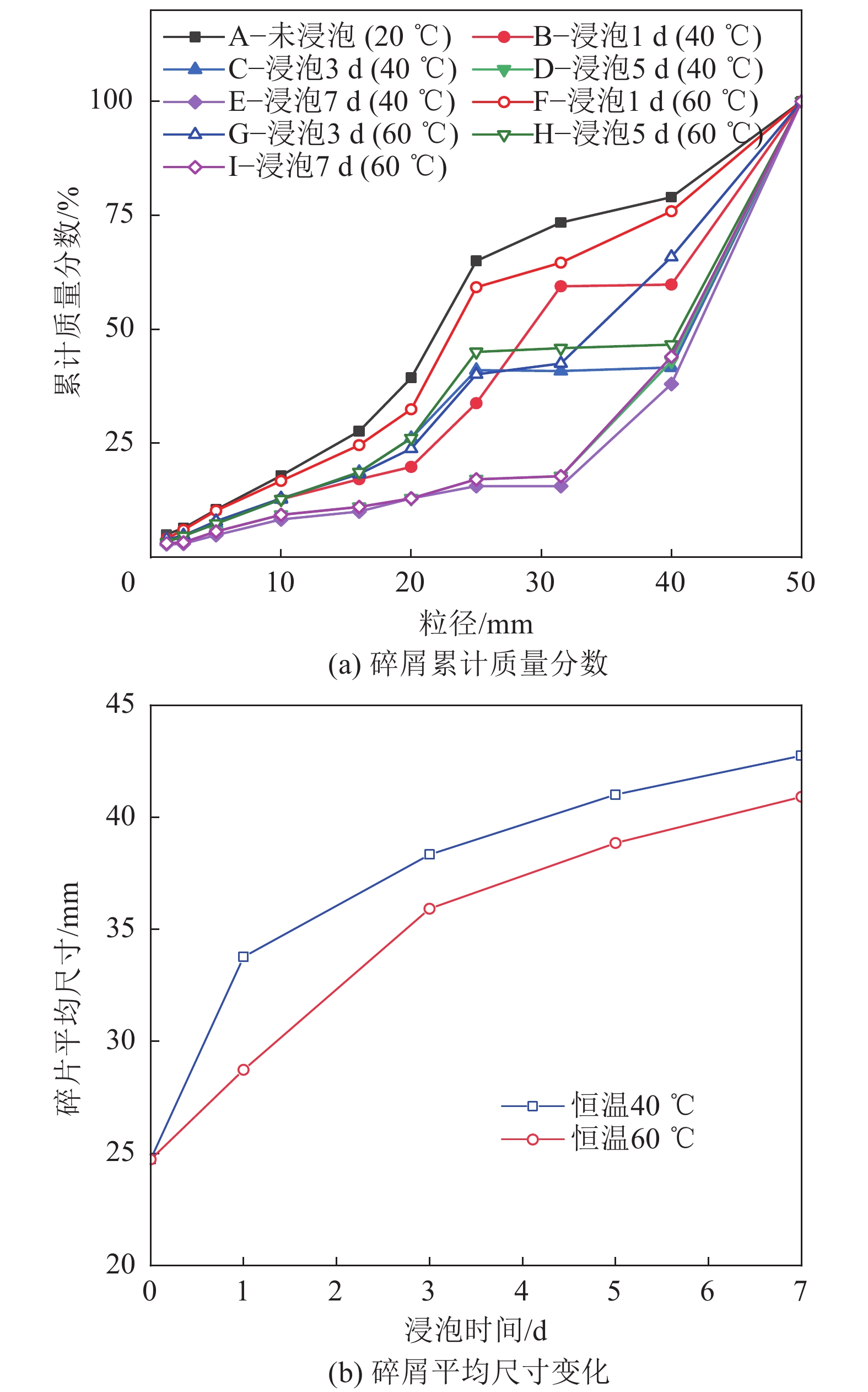
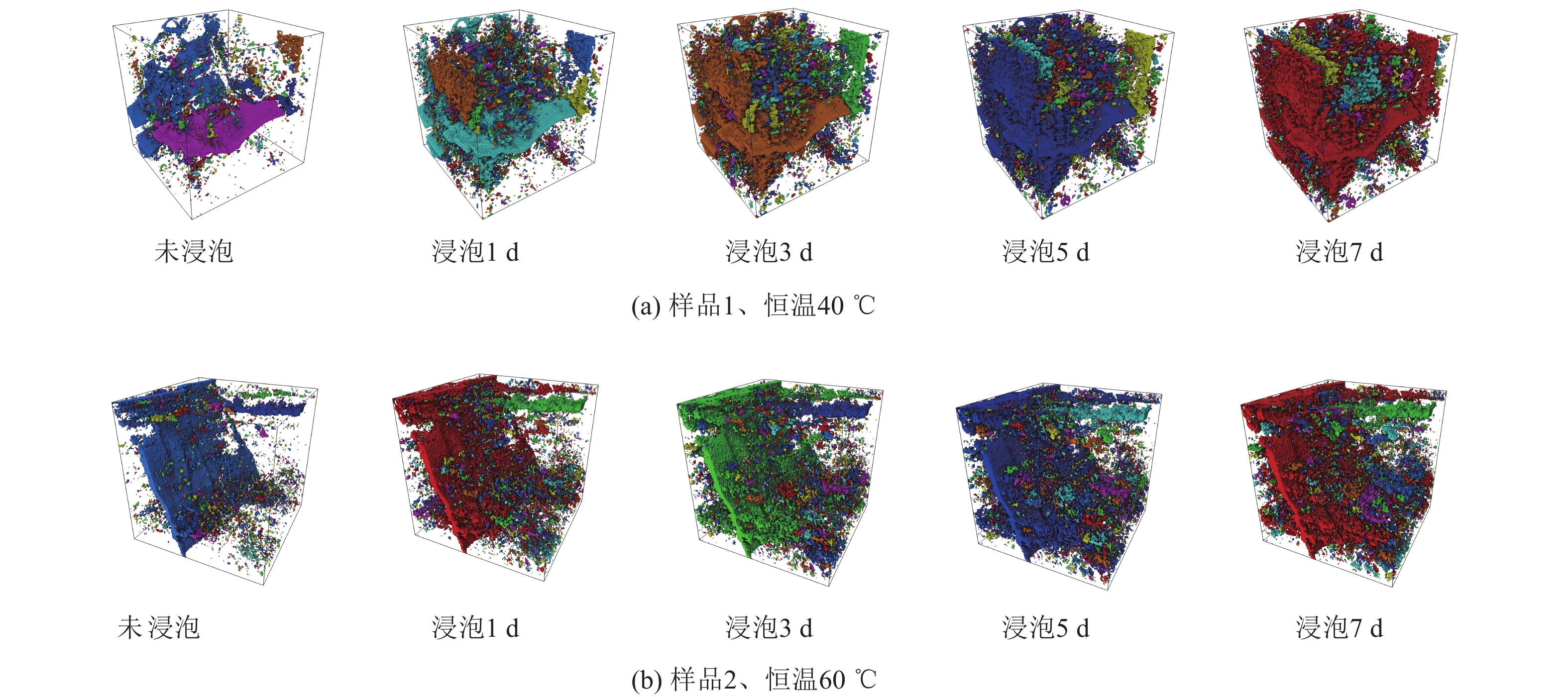
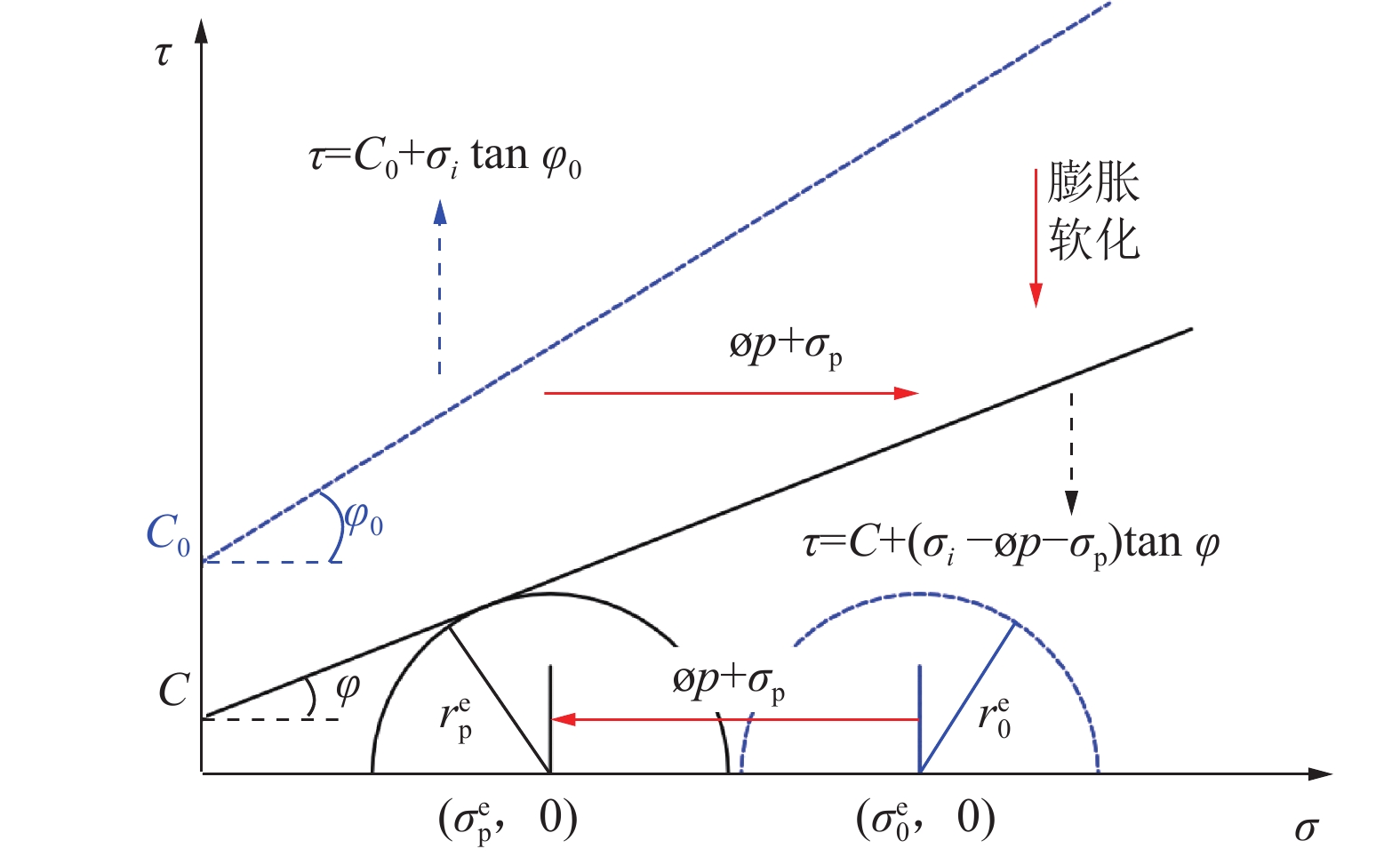
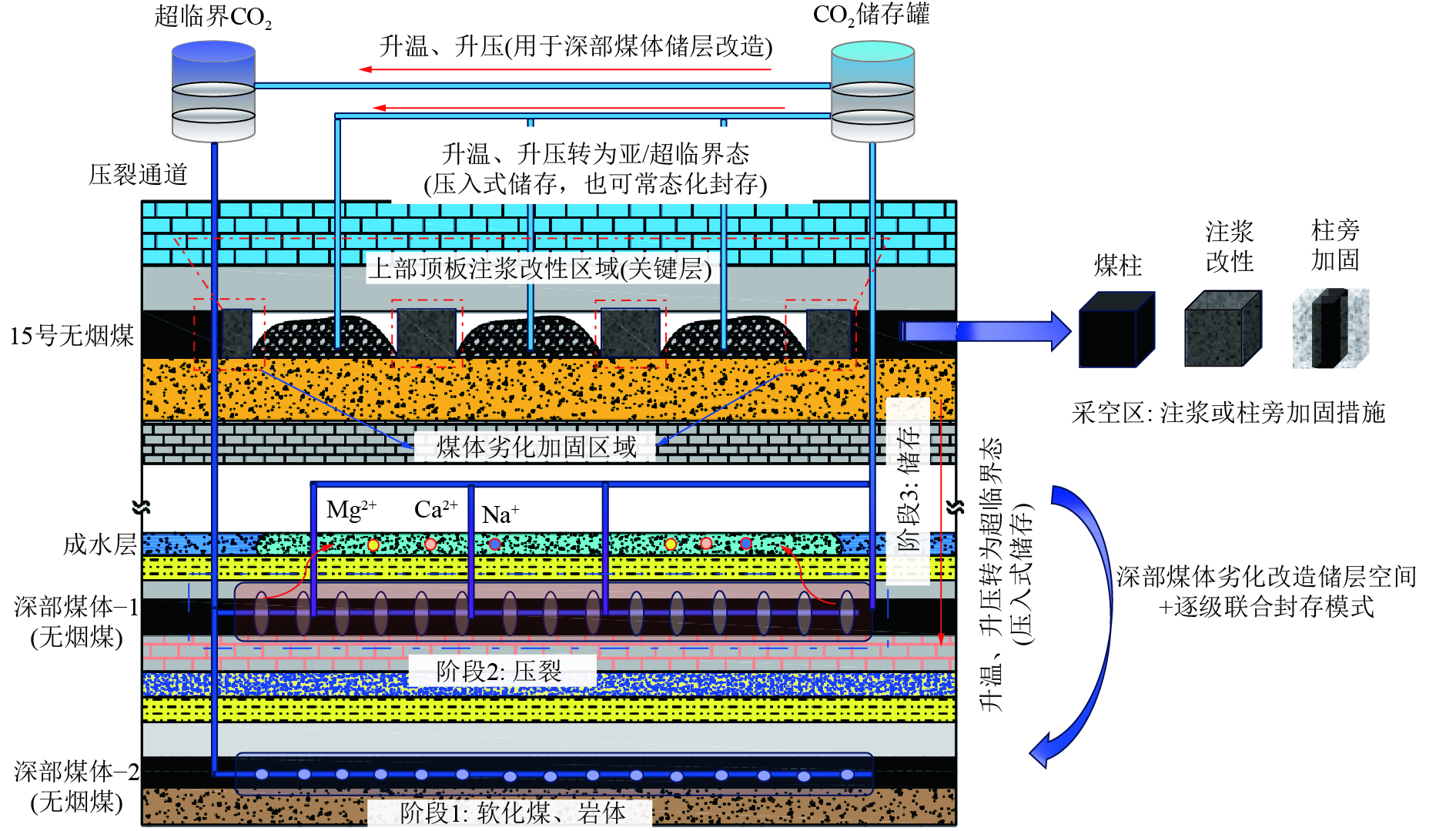
为揭示深部煤层注入CO2过程中,超临界CO2对无烟煤力学强度与微观结构的影响规律,以无烟煤为研究对象,对2种恒定温度(40、60 ℃)条件下超临界CO2对煤体劣化特性进行探究,利用自主研制的超临界CO2浸泡设备搭配煤体单轴加载装置对其力学强度进行初步测定,借助CT扫描系统表征孔裂隙等结构,通过分析不同浸泡时间(0、1、3、5、7 d)对孔裂隙的物化效应,揭示超临界CO2浸泡后无烟煤宏观强度损失与微观结构演变的内在联系。结果表明:超临界CO2对无烟煤宏观强度的劣化具有一定的时间效应,伴随着浸泡时间的增加,劣化效应逐渐减弱,逐渐趋于某一定值,其劣化主要时期为浸泡0~5 d,同时破坏模式改变,破坏颗粒的平均尺寸逐渐增大。同比恒温60 ℃,恒温40 ℃状态下的超临界CO2对煤体劣化作用较为明显;借助CT 扫描系统发现,经超临界CO2浸泡后白色矿物质消失,“溶蚀孔洞”逐渐扩大,新生孔裂纹不断发育,裂隙开度增加。煤样内部孔裂隙在0~5 d迅速发育成较为连续的孔隙团,此后内部孔裂隙缓慢发育,逐渐趋于稳定;超临界CO2侵入煤体内部,其通过萃取煤基质中的有机物与溶蚀碳酸盐矿物组分,形成“溶蚀孔洞”,破坏晶体结构,导致内部孔隙团逐渐发育。伴随着比表面积的增大,煤体吸附能力增加,其“溶胀效应”进一步增加孔裂隙发育,最终导致宏观力学强度的改变;由宏观强度损失数学模型分析得到,煤体经过超临界CO2浸泡后,强度包络线向右偏移,摩尔应力圆向左偏移,内摩擦角与黏聚力均变小,最终导致煤体宏观强度的损失。
Abstract:In order to reveal the effect of supercritical carbon dioxide on the mechanical strength and microstructure of anthracite in the process of CO2 injection into deep coal seams, takes anthracite as the research object, the degradation characteristics of coal by supercritical carbon dioxide under two constant temperatures (40 ℃ and 60 ℃) were investigated. The self-developed supercritical carbon dioxide immersion equipment combined with coal uniaxial loading device was used to preliminarily determine its mechanical strength. The structures such as pores and cracks were characterized by CT scanning system, and the physicochemical effects of different soaking days (0, 1, 3, 5, 7 d) on pores and cracks were analyzed. The intrinsic relationship between macroscopic strength loss and microstructure evolution of anthracite after supercritical carbon dioxide immersion was revealed. The results show that supercritical carbon dioxide has a certain time effect on the deterioration of the macroscopic strength of anthracite. With the increase of soaking time, the deterioration effect gradually weakens and gradually reaches a certain value. The main period of the deterioration is within 0−5 days of soaking, and the average size of the damaged particles gradually increases with the change of failure mode. Compared with the constant temperature of 60 ℃, the supercritical carbon dioxide under constant temperature of 40 ℃ has a more obvious degradation effect on coal. With the help of CT scanning system, it was found that after the supercritical carbon dioxide immersion, the white minerals disappeared, the “solution holes” gradually expanded, the cracks in the new holes continued to develop, and the crack opening increased. The internal pore and fissure of the coal sample developed rapidly into a relatively continuous pore group within 0−5 days, and then the internal pore and fissure developed slowly and gradually became stable. The supercritical carbon dioxide intrudes into the coal, and by extracting organic matter in the coal matrix and dissolution of carbonate mineral components, it forms “dissolution pores”, destroys the crystal structure, and leads to the gradual development of internal pore groups. With the increase of specific surface area, the adsorption capacity of coal increases, and the“swelling effect”further increases the development of pore and fracture, and finally leads to the change of macroscopic mechanical strength. According to the analysis of the macroscopic strength loss mathematical model, after the coal is soaked in supercritical CO2, the strength envelope shifts to the right, the molar stress circle shifts to the left, and the internal friction Angle and cohesion become smaller, resulting in the macroscopic strength loss of the coal.
-
-
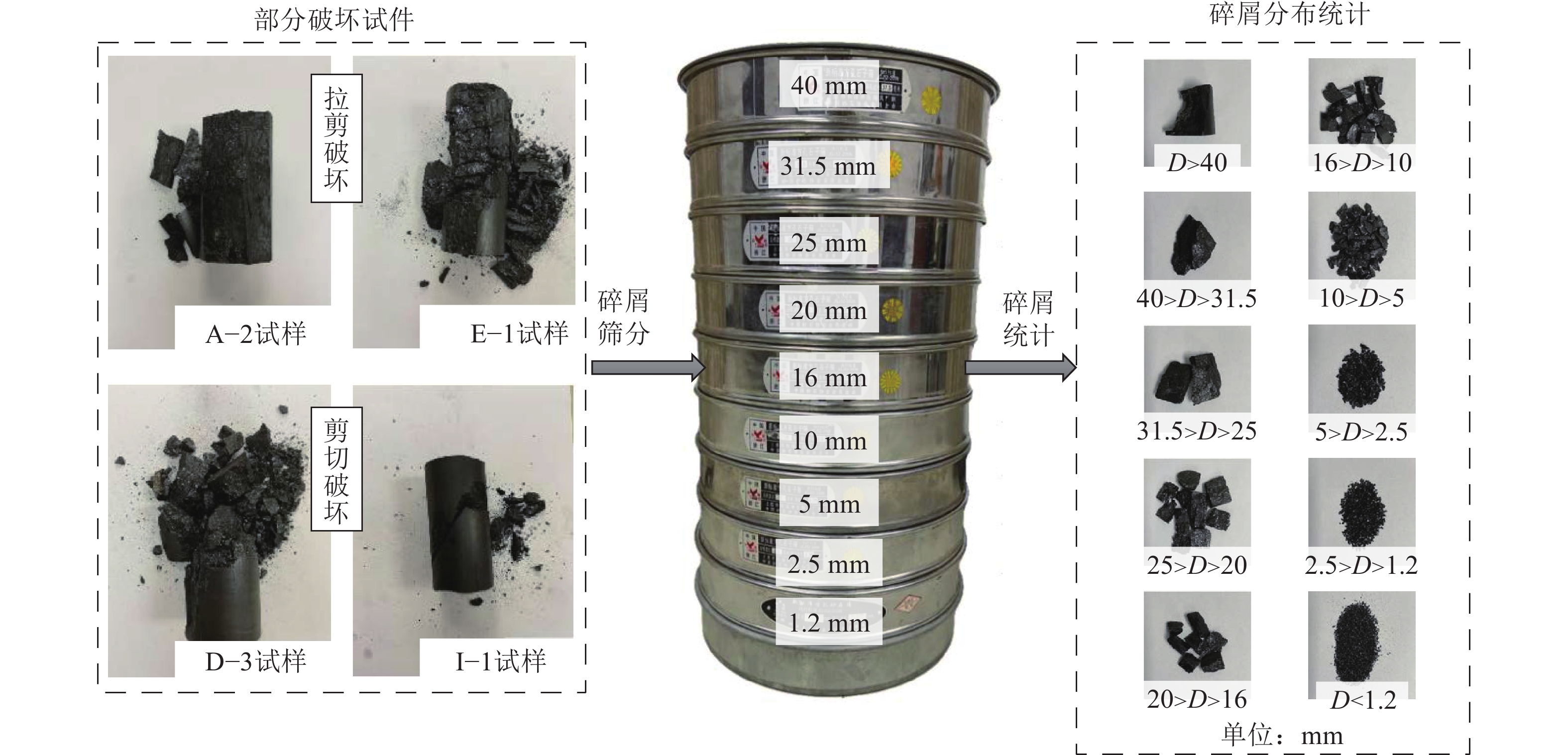
表 1 浸泡实验方案
Table 1 Immersion experiment scheme
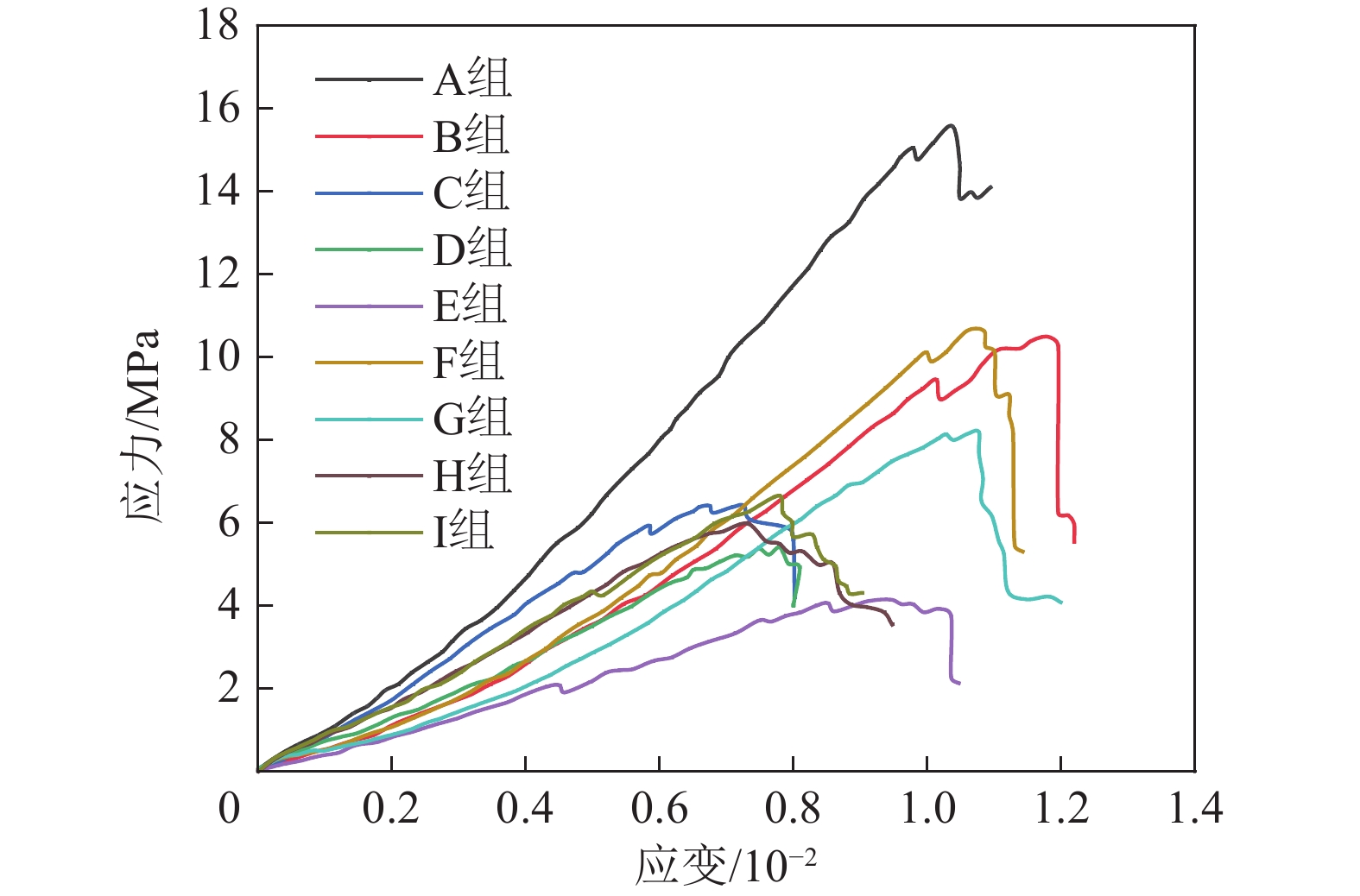
组号 温度/℃ 浸泡时间/d A 20(室温) 0 B,C,D,E 40 1,3,5,7 F,G,H,I 60 1,3,5,7 表 2 煤样试件在不同实验条件下的峰值强度及劣化程度
Table 2 Peak strength and deterioration degree of coal samples under different experimental conditions
浸泡时间/d 恒定温度40 ℃ 恒定温度60 ℃ 抗压强度/MPa 总劣化度/% 阶段劣化度/% 抗压强度/MPa 总劣化度/% 阶段劣化度/% 0 15.321 0 0 15.321 0 0 1 9.391 38.71 38.71 10.214 33.33 33.33 3 6.467 57.79 19.08 8.164 46.71 13.38 5 5.154 66.36 8.59 7.268 52.56 5.85 7 4.247 72.28 5.92 6.543 57.29 4.73 表 3 煤样试件在不同实验条件下的破坏特征
Table 3 Failure characteristics of coal samples under different experimental conditions
组号 恒定温度/℃ 浸泡时间/d 破坏特征 失稳类型 A 20 0 拉剪破坏 突发失稳 B 40 1 拉剪破坏 突发失稳 C 40 3 拉剪破坏 突发失稳 D 40 5 剪切破坏 准突发失稳 E 40 7 剪切破坏 渐进失稳 F 60 1 拉剪破坏 突发失稳 G 60 3 拉剪破坏 突发失稳 H 60 5 拉剪破坏 渐进失稳 I 60 7 剪切破坏 渐进失稳 表 4 不同ScCO2浸泡时间CT扫描图像切片
Table 4 CT scan image sections for different supercritical CO2 soaking days
CT扫描 浸泡时间/d 0 1 3 5 7 第1层 
第2层 
第3层 
第4层 
第5层 
第6层 
表 5 不同ScCO2浸泡时间试件内部孔裂隙分布
Table 5 Distribution of internal pore cracks in specimens with different supercritical CO2 soaking days
样品 恒定温度/℃ 浸泡时间/d 孔裂隙数量/条 孔隙率/% 样品1 20(室温) 0 10019 3.275 40 1 23048 8.972 40 3 35328 10.882 40 5 39751 12.633 40 7 42623 13.784 样品2 20(室温) 0 10325 3.395 60 1 21642 8.021 60 3 30912 9.181 60 5 36142 11.883 60 7 38956 12.386 -
[1] 桑树勋,牛庆合,曹丽文,等. 深部煤层CO2注入煤岩力学响应特征及机理研究进展[J]. 地球科学,2022,47(5):1849−1864. doi: 10.3321/j.issn.1000-2383.2022.5.dqkx202205022 SANG Shuxun,NIU Qinghe,CAO Liwen,et al. Mechanical response characteristics and mechanism of coal-rock with CO2 injection in deep coal seam:A review[J]. Earth Science,2022,47(5):1849−1864. doi: 10.3321/j.issn.1000-2383.2022.5.dqkx202205022
[2] 张鸿翔,李小春,魏宁. 二氧化碳捕获与封存的主要技术环节与问题分析[J]. 地球科学进展,2010,25(3):335−340. ZHANG Hongxiang,LI Xiaochun,WEI Ning. The major technology track and analysis about carbon dioxide capture and storage[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2010,25(3):335−340.
[3] 桑树勋,袁亮,刘世奇,等. 碳中和地质技术及其煤炭低碳化应用前瞻[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(4):1430−1451. SANG Shuxun,YUAN Liang,LIU Shiqi,et al. Geological technology for carbon neutrality and its application prospect for low carbon coal exploitation and utilization[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2022,47(4):1430−1451.
[4] 李宁,金之钧,张士诚,等. 水/超临界二氧化碳作用下的页岩微观力学特性[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2023,50(4):872−882. doi: 10.11698/PED.20220710 LI Ning,JIN Zhijun,ZHANG Shicheng,et al. Micro-mechanical properties of shale due to water/supercritical carbon dioxide-rock interaction[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2023,50(4):872−882. doi: 10.11698/PED.20220710
[5] 梁卫国,张倍宁,韩俊杰,等. 超临界CO2驱替煤层CH4装置及试验研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2014,39(8):1511−1520. LIANG Weiguo,ZHANG Beining,HAN Junjie,et al. Experimental study on coal bed methane displacement and recovery by super critical carbon dioxide injection[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2014,39(8):1511−1520.
[6] 张俊超. 模拟超临界CO2注入高阶煤体积应变及力学性质变化特征研究[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2016. ZHANG Junchao. Study on the volume strain and mechanical property variation with simulation of supercritical CO2 injection into the high rank coal[D]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology,2017.
[7] 牛庆合. 超临界CO2注入无烟煤力学响应机理与可注性试验研究[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2020. NIU Qinghe. Experimental study on the mechanical response mechanism and injectivity with supercritical CO2 injection in anthracite cite[D]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology,2020.
[8] 贺伟,梁卫国,张倍宁,等. 不同煤阶煤体吸附储存CO2膨胀变形特性试验研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2018,43(5):1408−1415. HE Wei,LIANG Weiguo,ZHANG Beining,et al. Experimental study on swelling characteristics of CO2 adsorption and storage in different coal rank[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2018,43(5):1408−1415.
[9] VIETE D R,RANJITH P G. The effect of CO2 on the geomechanical and permeability behaviour of brown coal:Implications for coal seam CO2 sequestration[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology,2006,66(3):204−216. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2005.09.002
[10] SAMPATH K H S M,PERERA M S A,LI D Y,et al. Characterization of dynamic mechanical alterations of supercritical CO2-interacted coal through gamma-ray attenuation,ultrasonic and X-ray computed tomography techniques[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2019,174:268−280. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2018.11.044
[11] PIRZADA M A,ZOORABADI M,LAMEI RAMANDI H,et al. CO2 sorption induced damage in coals in unconfined and confined stress states:a micrometer to core scale investigation[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology,2018,198:167−176. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2018.09.009
[12] 白冰,李小春,刘延锋,等. CO2-ECBM中气固作用对煤体应力和强度的影响分析[J]. 岩土力学,2007,28(4):823−826. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2007.04.037 BAI Bing,LI Xiaochun,LIU Yanfeng,et al. Preliminary theoretical study on impact on coal caused by interactions between CO2 and coal[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2007,28(4):823−826. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2007.04.037
[13] 岳立新,孙可明,张凤嘉,等. 超临界CO2作用下有效应力对煤体渗透性影响[J]. 辽宁工程技术大学学报(自然科学版),2013,32(9):1157−1160. YUE Lixin,SUN Keming,ZHANG Fengjia,et al. Effect of effective stress on coal sample permeability under supercritical carbon dioxide[J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University (Natural Science),2013,32(9):1157−1160.
[14] LIU S Q,MA J S,SANG S X,et al. The effects of supercritical CO2 on mesopore and macropore structure in bituminous and anthracite coal[J]. Fuel,2018,223:32−43. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.03.036
[15] LIU C J,WANG G X,SANG S X,et al. Fractal analysis in pore structure of coal under conditions of CO2 sequestration process[J]. Fuel,2015,139:125−132. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2014.08.035
[16] 肖畅,王开,张小强,等. 超临界CO2作用后无烟煤力学损伤演化特性及机理[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(6):2340−2351. XIAO Chang,WANG Kai,ZHANG Xiaoqiang,et al. Mechanical damage evolution characteristics and mechanism of anthracite treated with supercritical CO2[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2022,47(6):2340−2351.
[17] 刘佳佳,聂子硕,于宝种,等. 超临界二氧化碳对煤体增透的作用机理及影响因素分析[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2023,51(2):204−216. LIU Jiajia,NIE Zishuo,YU Baozhong,et al. Analysis of the mechanism and influencing factors of supercritical carbon dioxide on coal permeability enhancement[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2023,51(2):204−216.
[18] 王磊,陈礼鹏,刘怀谦,等. 不同初始瓦斯压力下煤体动力学特性及其劣化特征[J]. 岩土力学,2023,44(1):144−158. WANG Lei,CHEN Lipeng,LIU Huaiqian,et al. Dynamic behaviors and deterioration characteristics of coal under different initial gas pressures[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2023,44(1):144−158.
[19] WANG G,QIN X J,SHEN J N,et al. Quantitative analysis of microscopic structure and gas seepage characteristics of low-rank coal based on CT three-dimensional reconstruction of CT images and fractal theory[J]. Fuel,2019,256:115900. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2019.115900
[20] 王登科,张平,浦海,等. 温度冲击下煤体裂隙结构演化的显微CT实验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2018,37(10):2243−2252. WANG Dengke,ZHANG Ping,PU Hai,et al. Experimental research on cracking process of coal under temperature variation with industrial micro-CT[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2018,37(10):2243−2252.
[21] JIANG C B,YANG Y,WEI W H,et al. A new stress-damage-flow coupling model and the damage characterization of raw coal under loading and unloading conditions[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences,2021,138:104601. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2020.104601
[22] 张艳博,徐跃东,刘祥鑫,等. 基于CT的岩石三维裂隙定量表征及扩展演化细观研究[J]. 岩土力学,2021,42(10):2659−2671. ZHANG Yanbo,XU Yuedong,LIU Xiangxin,et al. Quantitative characterization and mesoscopic study of propagation and evolution of three-dimensional rock fractures based on CT[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2021,42(10):2659−2671.
[23] 王磊,刘怀谦,谢广祥,等. 含瓦斯煤孔裂隙结构精细表征及强度劣化机制[J]. 岩土力学,2021,42(12):3203−3216. WANG Lei,LIU Huaiqian,XIE Guangxiang,et al. Fine characterization of the pore and fracture structure and strength degradation mechanism of gas bearing coal[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2021,42(12):3203−3216.
[24] WENG L,WU Z J,LIU Q S,et al. Energy dissipation and dynamic fragmentation of dry and water-saturated siltstones under sub-zero temperatures[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics,2019,220:106659. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2019.106659
[25] 何立国. 超临界CO2作用下煤体宏观力学特性及细观结构研究[D]. 太原:太原理工大学,2022. HE Liguo. Study on macro mechanical properties and micro structure of coal under supercritical CO2[D]. Taiyuan:Taiyuan University of Technology,2022.
[26] 张小东,张瑜,张硕,等. 超临界CO2对高阶构造煤微观结构的影响机制[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2023,51(5):45−53. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.22.10.0778 ZHANG Xiaodong,ZHANG Yu,ZHANG Shuo,et al. Influencing mechanisms of SC-CO2 extraction on the microstructures of high-rank tectonic coals[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2023,51(5):45−53. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.22.10.0778
[27] ZHANG G L,RANJITH P G,LI Z S,et al. Application of synchrotron ATR-FTIR microspectroscopy for chemical characterization of bituminous coals treated with supercritical CO2[J]. Fuel,2021,296:120639. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2021.120639
[28] CHEN K,LIU X F,WANG L K,et al. Influence of sequestered supercritical CO2 treatment on the pore size distribution of coal across the rank range[J]. Fuel,2021,306:121708. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2021.121708
[29] 曾梦茹. 不同温度超临界CO2条件下煤微观结构特征及改造机理研究[D]. 重庆:重庆大学,2020. ZENG Mengru. Study on the coal microstructural characteristics and transformation mechanism treated by supercritical CO2 at different temperatures[D]. Chongqing:Chongqing University,2020.
[30] 张宇杰,郭红光,李治刚,等. 超临界CO2萃取提高褐煤生物甲烷产气模拟实验[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(10):3278−3285. ZHANG Yujie,GUO Hongguang,LI Zhigang,et al. Promoted microbial degradation of lignite by supercritical CO2 extraction to enhance coalbed methane production[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2021,46(10):3278−3285.
[31] 代旭光,王猛,冯光俊,等. 超临界CO2−水−页岩作用矿物溶蚀/沉淀特征及其对页岩吸附性的影响[J]. 煤炭学报,2023,48(7):2813−2826. DAI Xuguang,WANG Meng,FENG Guangjun,et al. Mineralogical erosion and precipitation characteristics and their effects on adsorption property of shale during scCO2-H2O-shale interaction[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2023,48(7):2813−2826.
[32] 孙可明,吴迪,粟爱国,等. 超临界CO2作用下煤体渗透性与孔隙压力–有效体积应力–温度耦合规律试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2013,32(S2):3760−3767. SUN Keming,WU Di,SU Aiguo,et al. Experimental study on the coupling law of coal permeability and pore pressure-effective volume stress-temperature under the action of supercritical CO2[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2013,32(S2):3760−3767.
[33] 王登科,张航,魏建平,等. 基于工业CT扫描的瓦斯压力影响下含瓦斯煤裂隙动态演化特征[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(11):3550−3564. WANG Dengke,ZHANG Hang,WEI Jianping,et al. Dynamic evolution characteristics of fractures in gas-bearing coal under the influence of gas pressure using industrial CT scanning technology[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2021,46(11):3550−3564.
[34] 卢平,沈兆武,朱贵旺,等. 含瓦斯煤的有效应力与力学变形破坏特性[J]. 中国科学技术大学学报,2001,31(6):686−693. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2778.2001.06.009 LU Ping,SHEN Zhaowu,ZHU Guiwang,et al. The effective stress and mechanical deformation and damage characteristics of gas-filled coal[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology of China,2001,31(6):686−693. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2778.2001.06.009
[35] 李祥春,郭勇义,吴世跃,等. 考虑吸附膨胀应力影响的煤层瓦斯流–固耦合渗流数学模型及数值模拟[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2007,26(S1):2743−2748. LI Xiangchun,GUO Yongyi,WU Shiyue,et al. Mathematical model and numerical simulation of fluid-solid coupled flow of coal-bed gas considering swelling stress of adsorption[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2007,26(S1):2743−2748.
[36] 吴世跃,赵文. 含吸附煤层气煤的有效应力分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2005,24(10):1674−1678. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.10.007 WU Shiyue,ZHAO Wen. Analysis of effective stress in adsorbed methane-coal system[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2005,24(10):1674−1678. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.10.007
[37] 王双明,申艳军,孙强,等. “双碳” 目标下煤炭开采扰动空间CO2地下封存途径与技术难题探索[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(1):45−60. WANG Shuangming,SHEN Yanjun,SUN Qiang,et al. Underground CO2 storage and technical problems in coal mining area under the “dual carbon” target[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2022,47(1):45−60.
[38] 张军建,常象春,吕大炜,等. 双碳目标下煤层发育区CO2地质封存研究与评价[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2023,51(S1):206−214. doi: 10.12438/cst.2022-0538 ZHANG Junjian,CHANG Xiangchun,LYU Dawei,et al. Carbon dioxide geological storage system in coal seam development area under the premise of double carbon target[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2023,51(S1):206−214. doi: 10.12438/cst.2022-0538
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 覃美满,寇向宇,鄢德波,董培林,魏星,张柏. 基于组合赋权-TOPSIS的地下矿山安全风险评价研究. 矿冶工程. 2025(01): 35-40 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王石,汤明昆,吴锐,刘耀华,刘龙,杨琨,马翔宇. 曹家滩煤矿超远距离管道输送堵塞风险评估. 安全与环境学报. 2025(04): 1275-1285 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王政,朱彬,康虔. 基于多维联系云的巷道围岩稳定性评价模型. 有色金属工程. 2024(03): 156-167 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 柯愈贤,曾杰,胡凯建,沈阳,虞松涛,马永超. 渗透水压作用下全尾砂胶结充填体的三轴力学特性及演变机制. 有色金属科学与工程. 2024(03): 422-431 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 周晏渔,豆龙,林卫星,王亚军. 基于IAHP-GRA和多维联系云的岩体质量评价和应用. 矿业研究与开发. 2024(08): 173-181 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 耿向帅. 云模型在高后果区管道风险评价的应用. 油气田地面工程. 2024(08): 39-45+51 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 孔翔生,王朝隆,刘毓,莫裕哲,龙世武,闫家赫,王运森,邱景平. 高浓度超细尾砂泵送充填智能调压控制系统. 有色金属工程. 2024(09): 130-137 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 艾纯明,苗泉,张馨,王凤山. 基于层次分析熵权组合法-云模型的充填管道堵塞风险评估. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版). 2024(05): 684-690+699 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载: