Study on temporal and spatial evolution characteristics of water accumulation in coal mining subsidence area with high groundwater level: taking Anhui Province Mining Area as an example-taking Anhui Province Mining Area as an example
-
摘要:
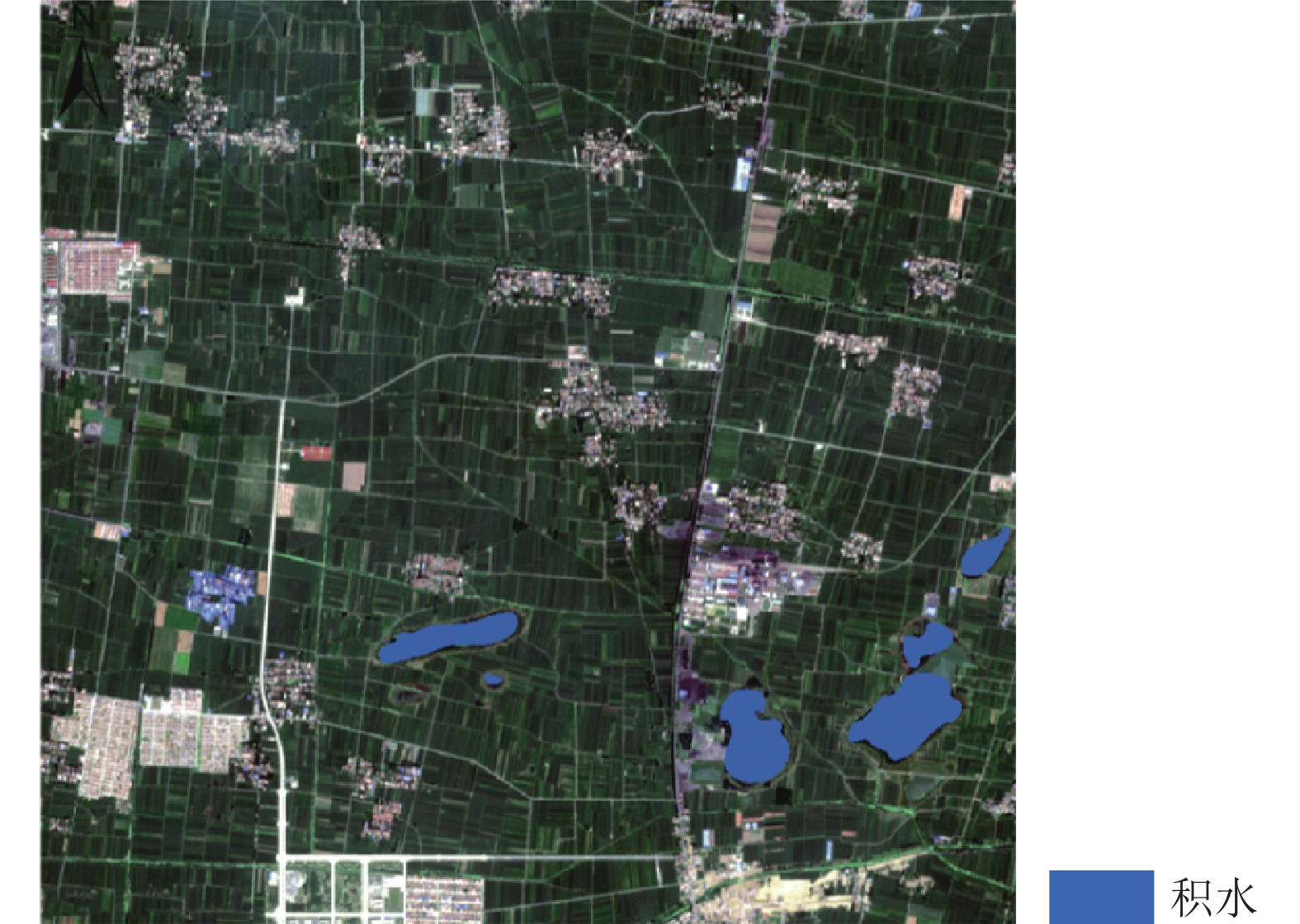
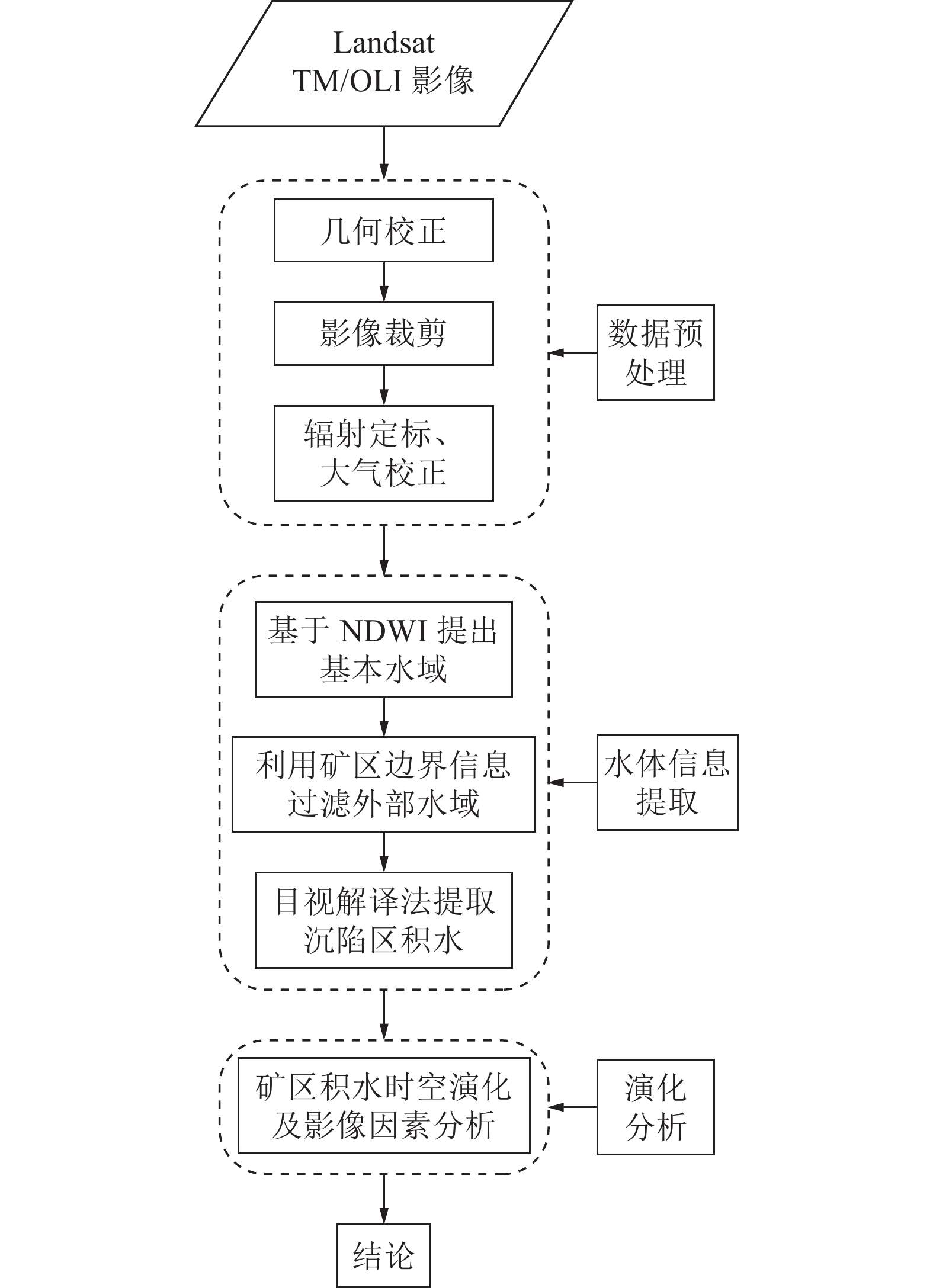
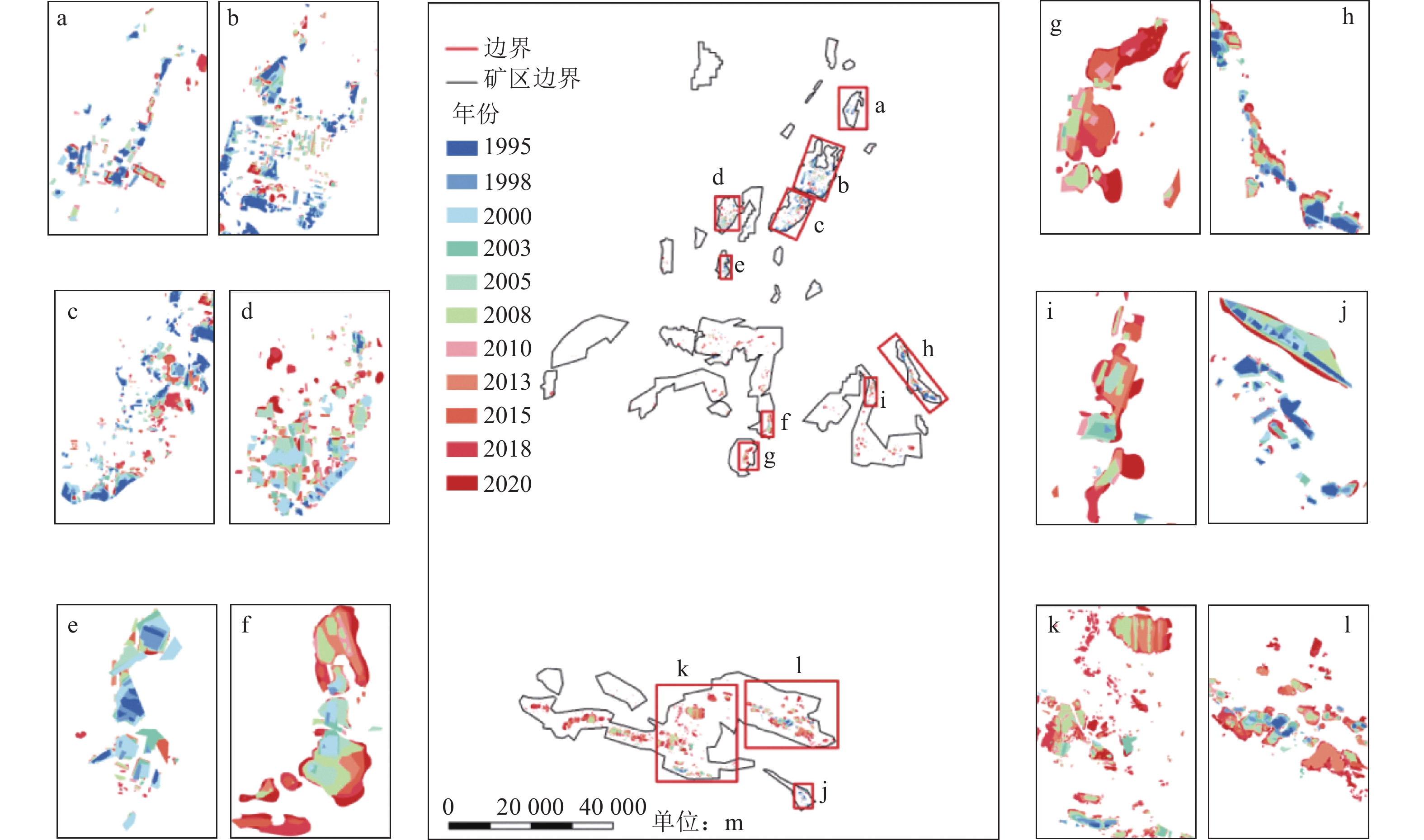
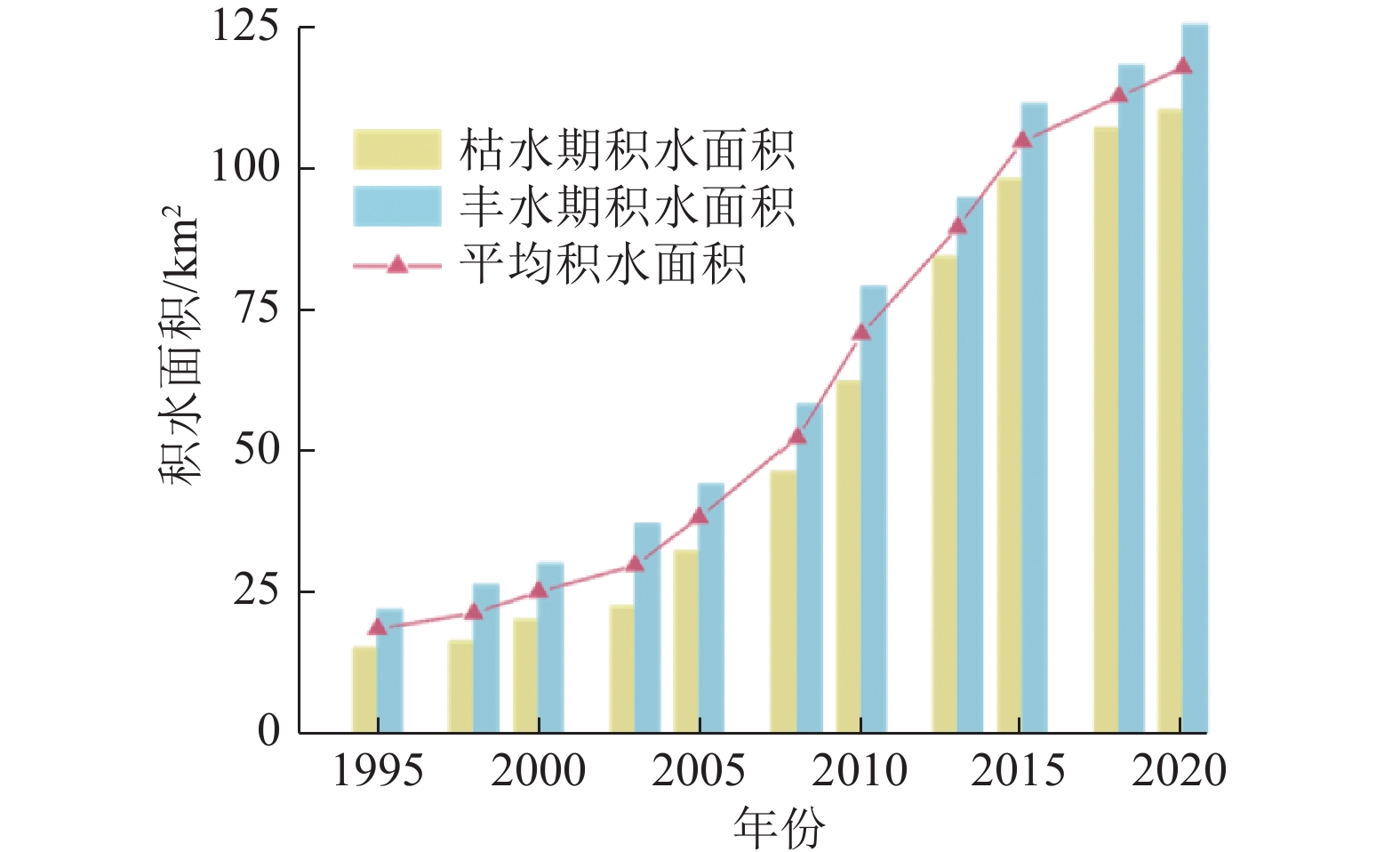
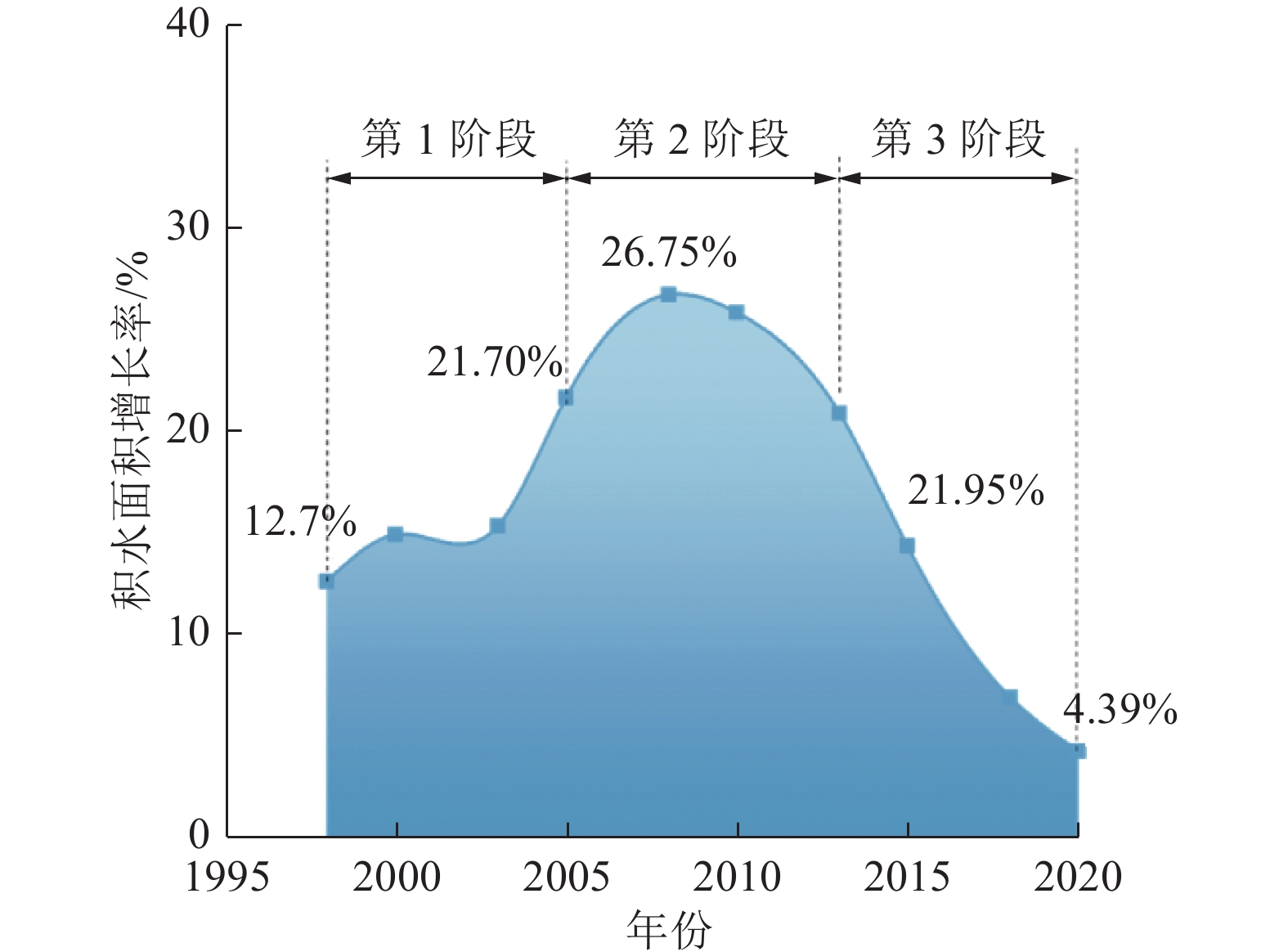
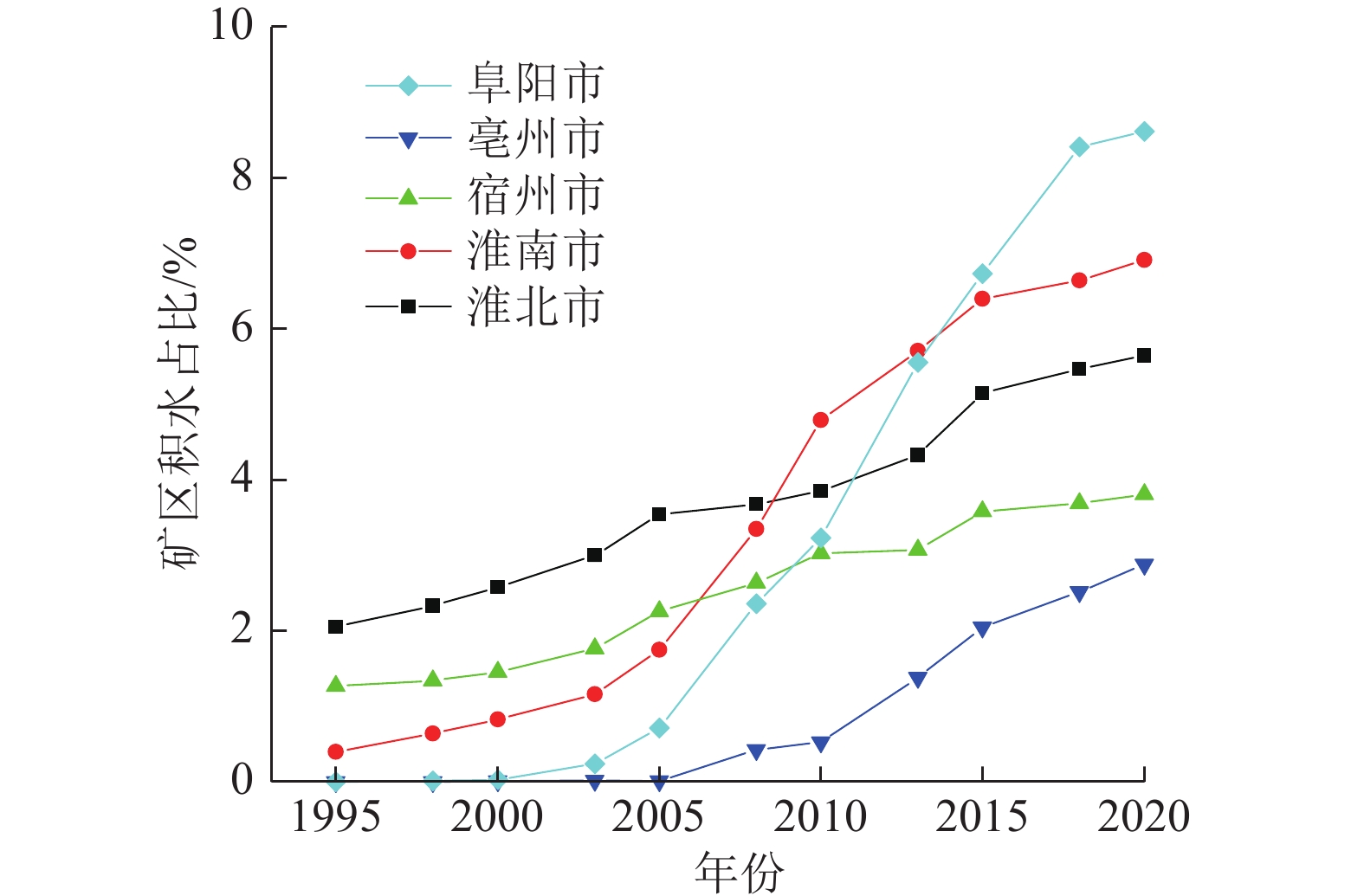
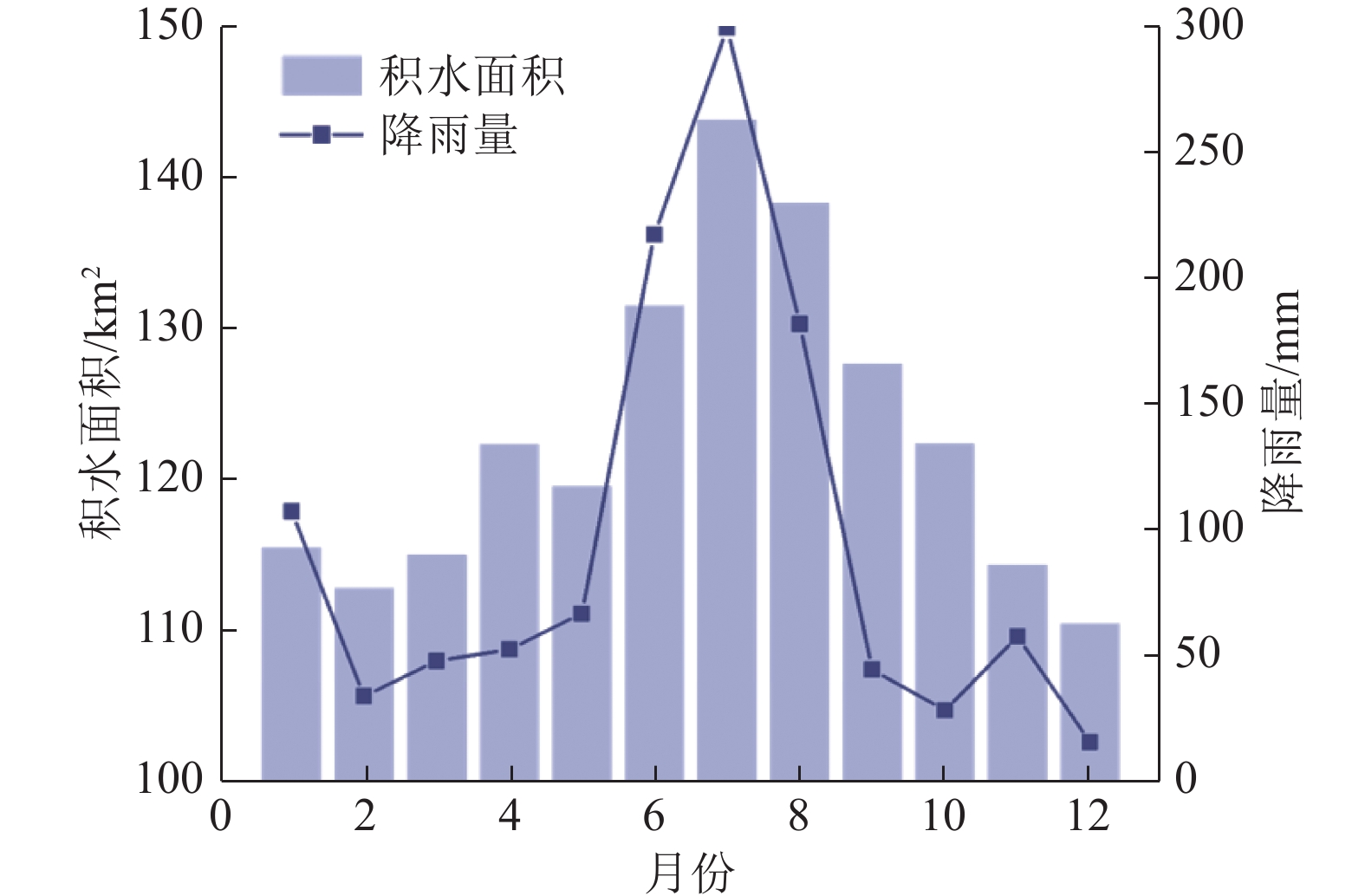
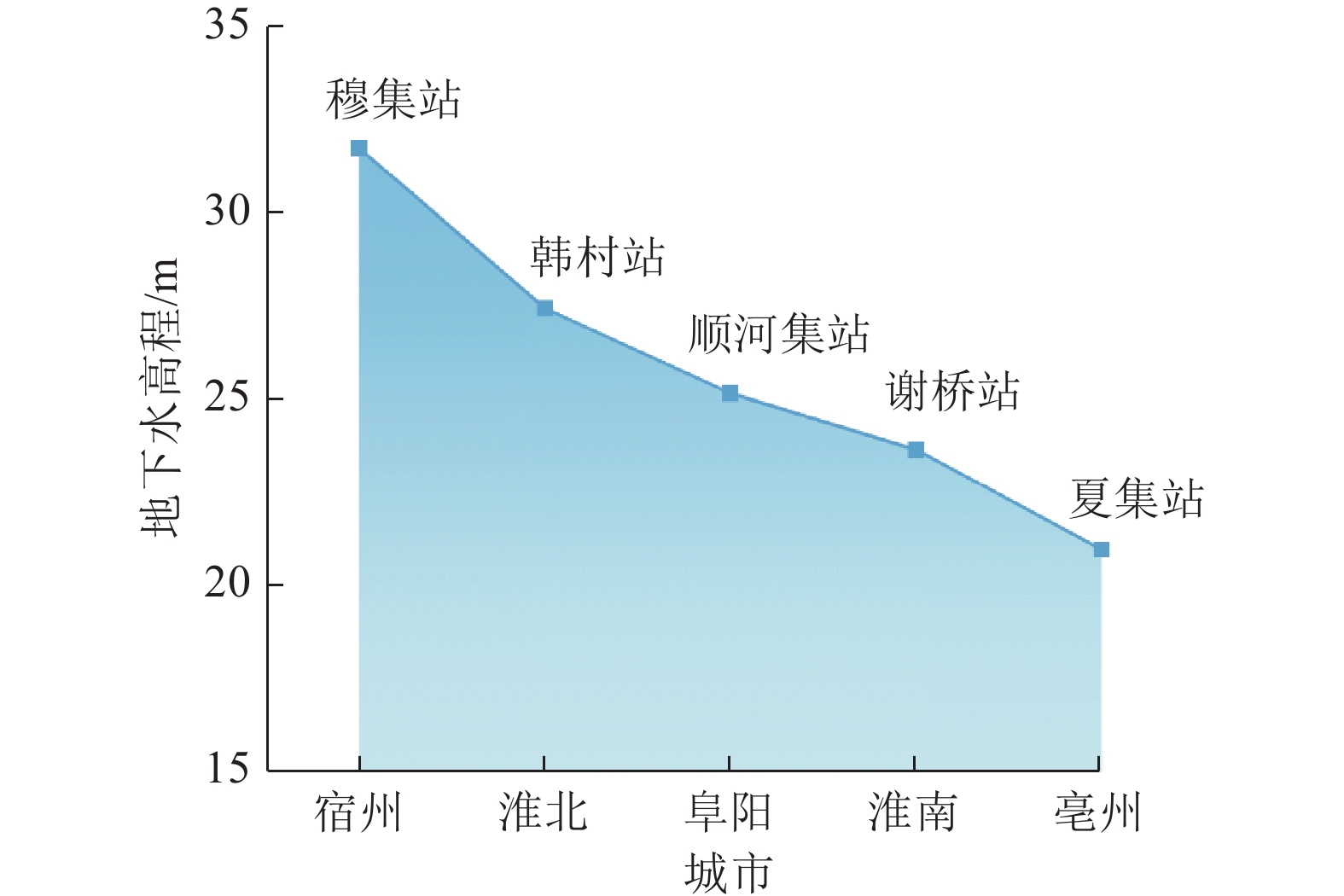
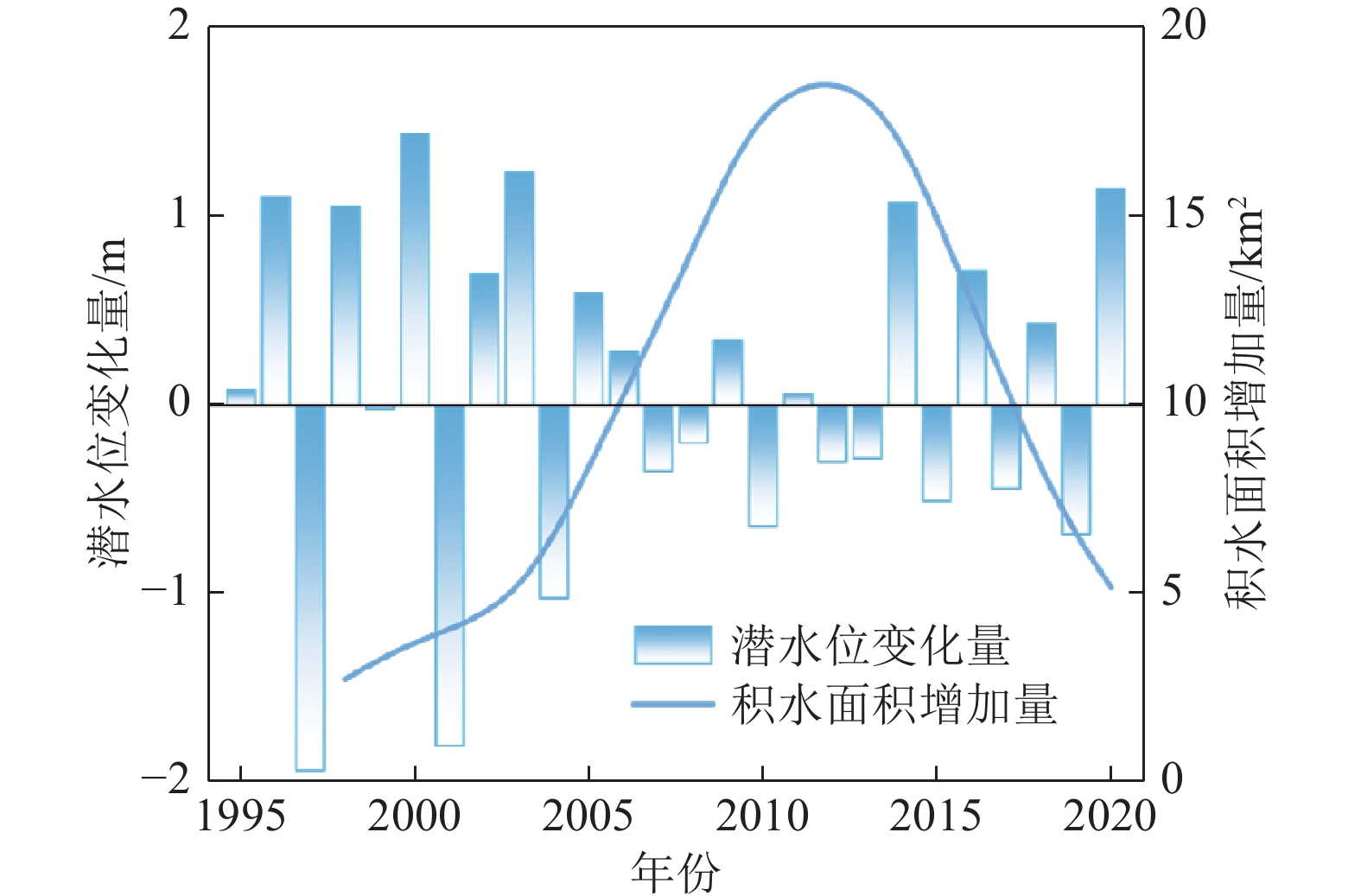
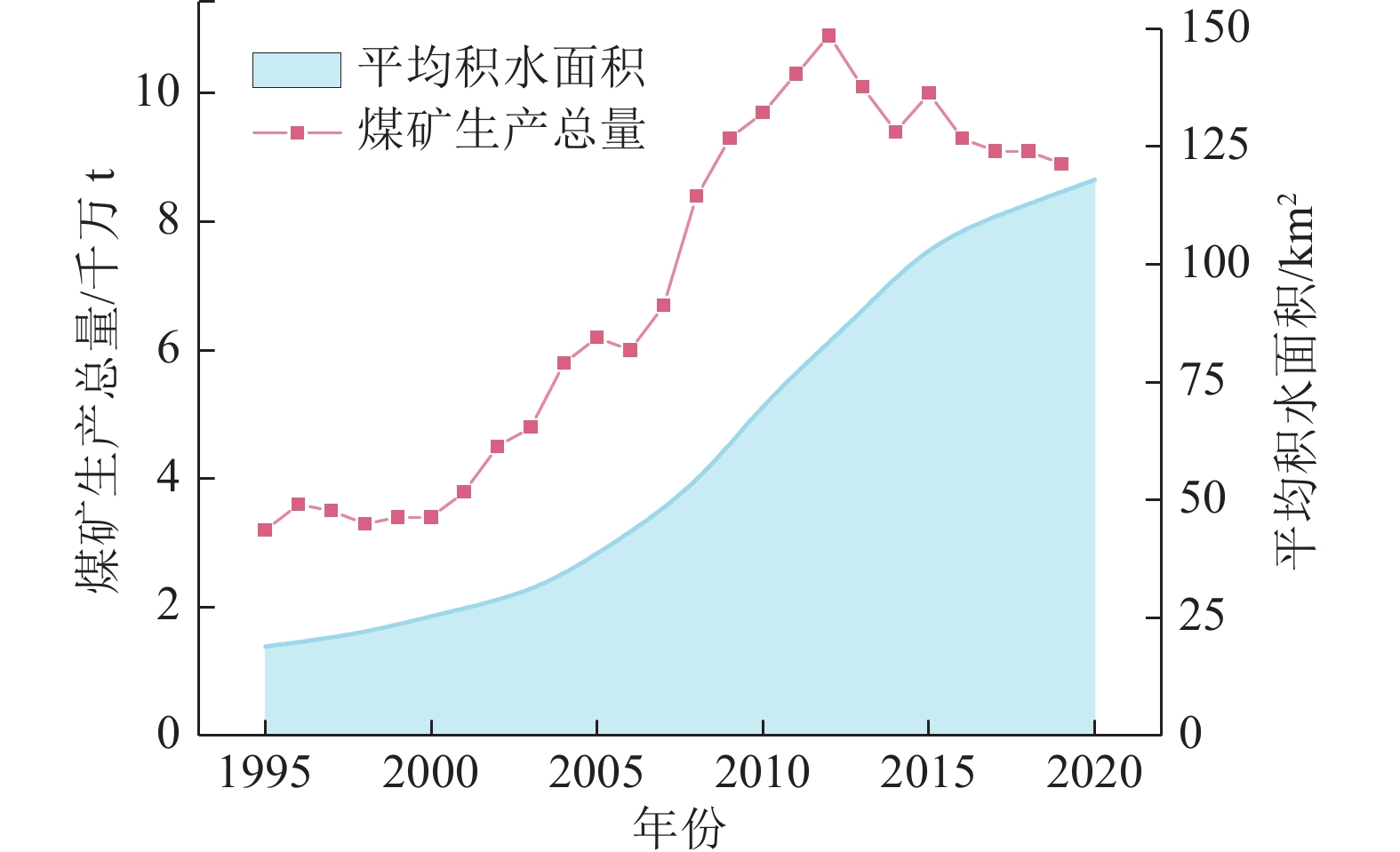
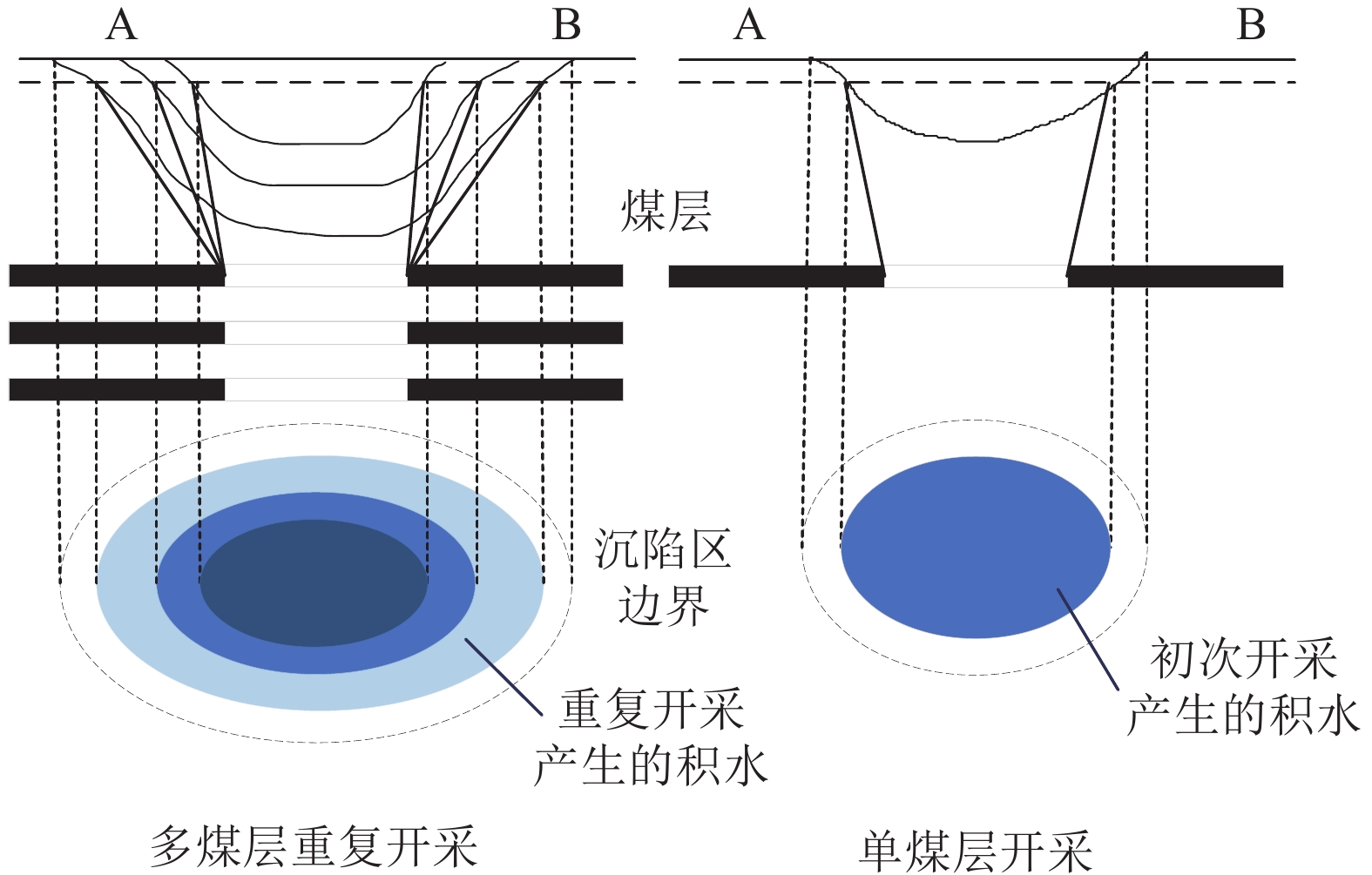
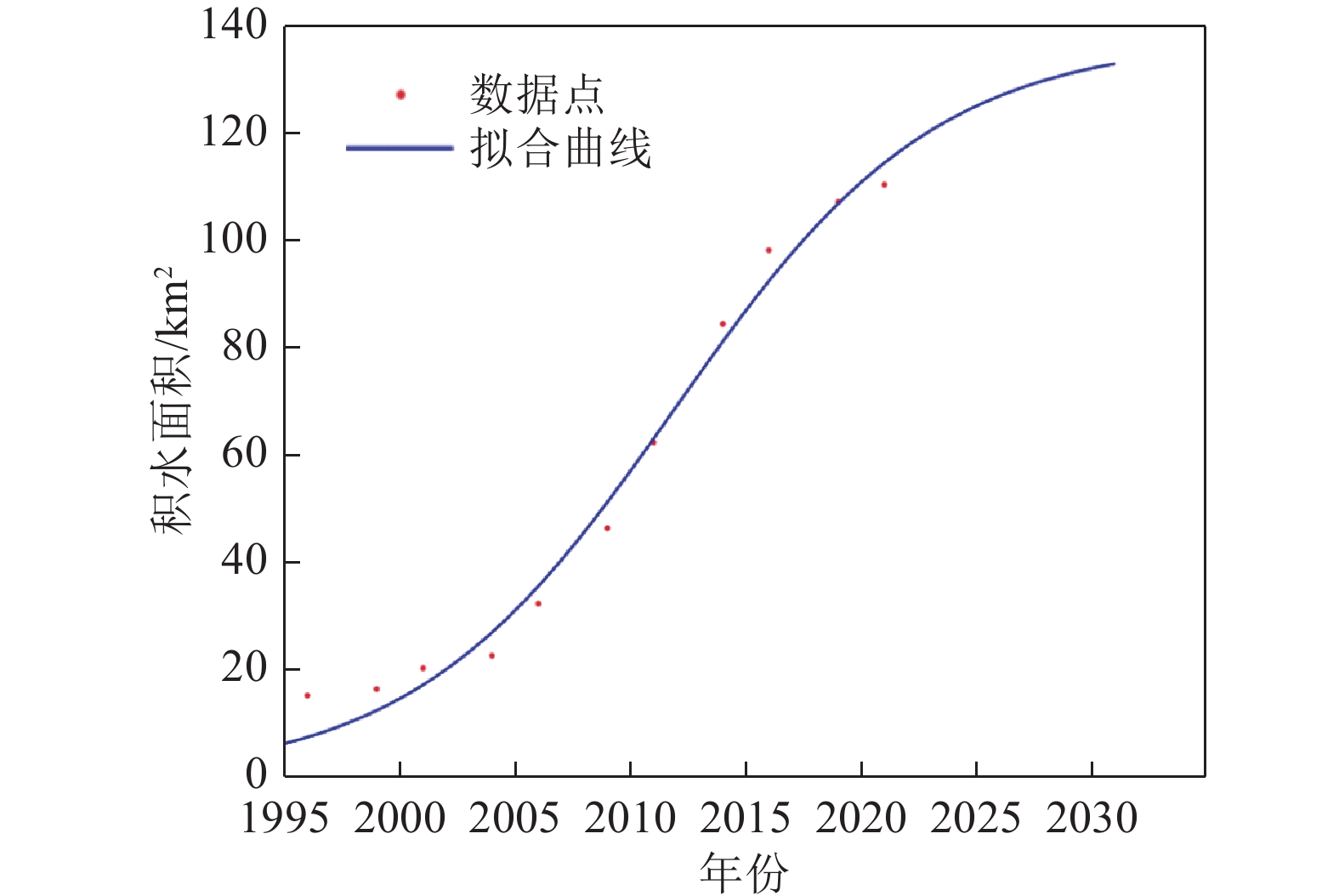
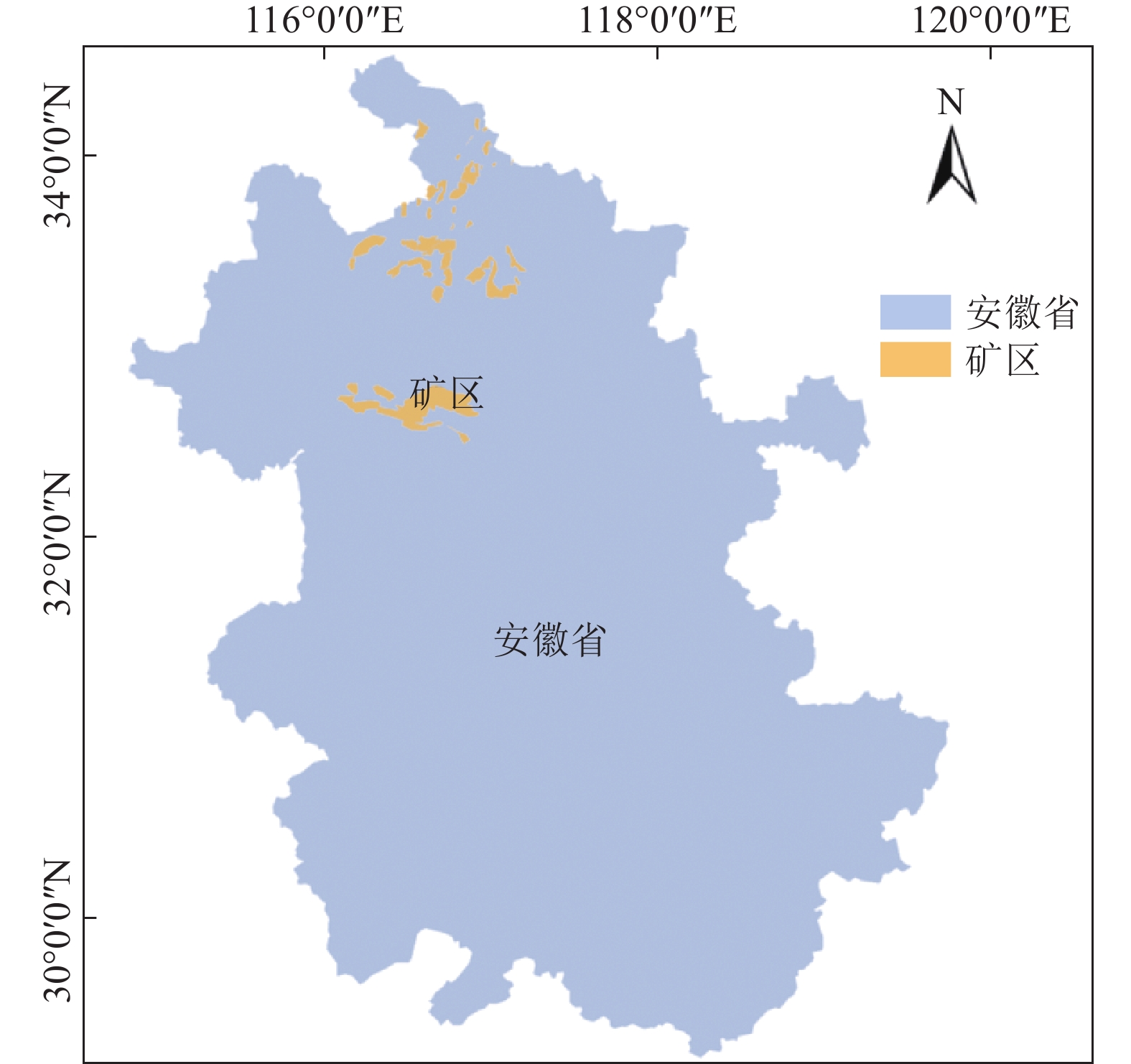
随着煤炭资源大面积、高强度开采,高潜水位矿区积水问题尤为突出,对周围生态环境产生了严重影响。为了给采煤沉陷积水区生态环境修复提供科学依据,开展了高潜水位采煤沉陷区积水的时空演化特征研究和影响因素分析。以整个安徽省矿区为研究区域,基于Landsat TM/OLI遥感数据,采用归一化水体指数法(NDWI)和目视解译法对1995—2020年(共计22期)和2020年12个月份(12期)沉陷区积水区域进行提取,获取了近25年安徽省采煤沉陷区积水空间信息,并结合水文和降雨资料分析和讨论了沉陷区积水时空演化的影响因素。结果表明:①近25年来,安徽省采煤沉陷区积水面积的增长呈“缓慢—快速—稳定”3阶段分布特征。研究期内平均积水面积增长了约6倍,从18.95 km2增长到118.09 km2,年均增长3.97 km2。②从时间尺度上沉陷区积水演化分为3阶段:第1阶段(1995—2005年),由于积水初步形成还未稳定,增长速度较为缓慢,年均增长率为4.65%;第2阶段(2005—2013年),基于安徽省煤炭开采量进入快速增长期,积水面积也增长迅速,年均增长率为6.64%;第3阶段(2013—2020年)增长率开始不断减小,积水面积逐渐趋于稳定,年均增长率为3.42%。空间尺度上,安徽省沉陷区积水主要集中在淮南市和淮北市,约占全部积水面积的70%。③安徽省采煤沉陷区积水演化长时间尺度的主要影响因素是煤炭开采量,短时间尺度的主要影响因素则是大气降雨。④利用Logistic回归曲线建立了安徽省采煤沉陷区积水面积预测模型,预测得到在未来一段时间安徽省采煤沉陷积水面积将仍处于低速增长阶段,到2030年,枯水期积水区面积约达到130 km2。获取了高精度的沉陷区积水信息,分析了其时空演化规律及影响因素,可以给高潜水位采煤沉陷区积水的治理以及沉陷区的生态修复提供科学依据。
Abstract:In recent years, with the large-scale and high-intensity mining of coal resources, the problem of water accumulation in mining areas with high groundwater levels has become particularly prominent, which has had a serious impact on the surrounding ecological environment. In order to provide scientific basis for the restoration of the ecological environment, the study on the temporal and spatial evolution characteristics and influencing factors of the coal mining subsidence area with high groundwater level were carried out. Taking the whole mining area of Anhui Province as the research subject, based on Landsat TM/OLI remote sensing data, the NDWI and visual interpretation method were used to conduct surveys on the water accumulation area in the subsidence area from 1995 to 2020 (22 periods ) and 12 months in 2020 (12 periods) and the spatial information of waterlogging in the coal mining subsidence area in Anhui Province in recent 25 years was obtained. Combined with hydrological and rainfall data, the factors affecting the spatio-temporal evolution of waterlogging in the subsidence area were analyzed and discussed. The results show that: ① In the past 25 years, the area of accumulated water in the coal mining subsidence area in Anhui Province has been growing in three stages: slow, fast and stable. During the study period, the average stagnant area increased by about 6 times, from 18.95 km2 to 118.09 km2, with an average annual increase of 3.97 km2. ② From the time scale, the evolution of accumulation area in the subsidence area can be divided into three stages: the first stage (1995—2005), due to the fact that most of the accumulation water has not yet stabilized initially, the growth rate is relatively slow, with an average annual growth rate of 4.65%; In the second stage (2005—2013), based on the rapid growth of coal mining, the area of accumulation water has also entered a period of rapid growth, with an average annual growth rate of 6.64%; In the third stage (2013—2020), the growth rate has begun to decrease, and the accumulation water has gradually stabilized, with an average annual growth rate of 3.42%. From the spatial scale, the accumulation water is mainly concentrated in Huainan and Huaibei cities, accounting for about 70% of the total accumulated water area. ③The long-term factor for the change of the water accumulation is coal mining volume, while the main influencing factor in short time scale is atmospheric rainfall. ④The logistic regression curve was used to establish a prediction model for the water accumulation area of coal mining subsidence in Anhui Province. It is predicted that the coal mining subsidence water area in Anhui Province will still be in a low-speed growth stage in the future. By 2030, the accumulation area in the dry season will reach about 130 km2. The high-precision water accumulation information in the subsidence area was obtained, and its temporal and spatial evolution laws and influencing factors were analyzed, which can provide a scientific basis for the treatment of water accumulation in the coal mining subsidence area with high groundwater level and the ecological restoration of the subsidence area.
-
-
表 1 安徽省矿区遥感影像信息
Table 1 Remote sensing image information of mining areas in Anhui Province
年份 传感器类型 时期 获取日期 分辨率/m 年份 传感器类型 时期 获取日期 分辨率/m 1995 Landsat-5 TM 枯水期
丰水期1995-02-02
1995-06-2130 2010 Landsat-5 TM 枯水期
丰水期2010-02-06
2010-09-1830 1998 Landsat-5 TM 枯水期
丰水期1998-12-15
1998-07-1530 2013 Landsat-8 OLI 枯水期
丰水期2013-02-15
2013-07-2430 2000 Landsat-5 TM 枯水期
丰水期2000-02-20
2000-06-1130 2015 Landsat-8 OLI 枯水期
丰水期2015-01-28
2015-07-3030 2003 Landsat-5 TM 枯水期
丰水期2003-12-20
2003-06-2030 2018 Landsat-8 OLI 枯水期
丰水期2018-02-21
2018-07-2230 2005 Landsat-5 TM 枯水期
丰水期2005-01-07
2005-06-1130 2020 Landsat-8 OLI 枯水期
丰水期2020-02-02
2020-08-2830 2008 Landsat-5 TM 枯水期
丰水期2008-02-10
2008-06-2430 表 2 部分煤矿积水情况
Table 2 Water accumulation in some coal mines
煤矿 年份 1995 1998 2000 2003 2005 2008 2010 2013 2015 2018 2020 谢桥煤矿 0 0.07 0.15 0.60 0.92 2.12 3.81 5.00 6.11 6.83 7.74 张集煤矿 0 0.20 0.32 0.56 1.16 3.36 4.60 7.33 6.87 9.17 15.50 潘一煤矿 0.83 1.82 1.77 3.06 3.14 3.15 4.00 7.90 5.22 10.52 9.07 潘三煤矿 0 0.63 0.44 1.07 1.59 1.87 2.10 3.50 4.10 5.01 7.07 临涣煤矿 0 0.61 0.39 0.22 0.22 0.35 0.64 0.92 1.33 1.69 1.46 百善煤矿 0.36 0.75 2.68 2.91 1.72 1.65 1.47 1.67 1.62 1.28 1.68 刘桥煤矿 0.18 0.31 1.61 0.80 1.91 2.08 2.17 1.95 2.50 2.04 3.69 杨庄煤矿 2.16 3.18 3.46 3.53 4.97 3.76 2.77 2.93 3.33 4.42 6.48 双龙煤矿 2.27 1.93 3.16 2.20 1.89 1.96 2.10 1.54 1.91 1.85 2.86 石台煤矿 0.96 1.09 1.68 1.60 2.29 2.06 1.93 1.67 2.01 2.19 2.95 -
[1] 胡炳南,郭文砚. 我国采煤沉陷区现状、综合治理模式及治理建议[J]. 煤矿开采,2018,23(2):1−4. doi: 10.13532/j.cnki.cn11-3677/td.2018.02.001 HU Bingnan,GUO Wenyan. The status quo of coal mining subsidence areas in my country, comprehensive treatment models and treatment suggestions[J]. Coal Mining Technology,2018,23(2):1−4. doi: 10.13532/j.cnki.cn11-3677/td.2018.02.001
[2] 李新举,周晶晶. 高潜水位煤矿区地表沉陷信息提取方法研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2020,48(4):105−112. doi: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2020.04.010 LI Xinju,ZHOU Jingjing. Study on the method of surface subsidence information extraction in coal mine area with high phreatic level[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2020,48(4):105−112. doi: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2020.04.010
[3] 刘欢欢,张有全,王 荣,等. 京津高铁北京段地面沉降监测及结果分析[J]. 地球物理报,2016,59(7):2424−2432. LIU Huanhuan,ZHANG Youquan,WANG Rong,et al. Monitoring and analysis of land subsidence along the Beijing–Tianjin high–speed railway (Beijing section)[J]. Acta Geophysica Sinica,2016,59(7):2424−2432.
[4] QU Feifei,ZHANG Qin,LU Zhong,et al. Land subsidence and ground fissures in Xi'an, China 2005–2012 revealed by multi-band InSAR time-series analysis[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment,2014,9(8):366−376.
[5] 孙 达,聂振邦,余兴江,等. 浅谈湖北省大冶市某露天矿山地质环境治理与恢复[J]. 资源环境与工程,2021,35(1):68−71. doi: 10.16536/j.cnki.issn.1671-1211.2021.01.013 SUN Da,NIE Zhenbang,YU Xingjiang,et al. On the treatment and restoration of the geological environment of an open-pit mine in Daye City, Hubei Province[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering,2021,35(1):68−71. doi: 10.16536/j.cnki.issn.1671-1211.2021.01.013
[6] 彭苏萍,王 磊,孟召平,等. 遥感技术在煤矿区积水塌陷动态监测中的应用:以淮南矿区为例[J]. 煤炭学报,2002(4):374−378. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2002.04.009 PENG Suping,WANG Lei,MENG Zhaoping,et al. The application of remote sensing technology in the dynamic monitoring of water accumulation in coal mine area: Taking Huainan Mining Area as an example[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2002(4):374−378. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2002.04.009
[7] 汪宝存,苗 放,晏明星,等. 基于遥感技术的开滦煤矿地面塌陷积水动态监测[J]. 国土资源遥感,2007(3):94−97,112. WANG Baocun,MIAO Fang,YAN Mingxing,et al. Dynamic monitoring of ground subsidence and water in Kailuan coal mine based on remote sensing technology[J]. Remote Sensing for Land and Resources,2007(3):94−97,112.
[8] 陈晓谢,张文涛,朱晓峻,等. 高潜水位采煤沉陷区积水范围动态演化规律[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2020,48(2):126−133. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.02.020 CHEN Xiaoxie,ZHANG Wentao,ZHU Xiaojun,et al. Dynamic evolution law of water accumulation area in coal mining subsidence area with high phreatic level[J]. Coal Geology and Exploration,2020,48(2):126−133. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.02.020
[9] 乔丛林,史明礼,苏 娅,等. 淮北平原地区水文特征[J]. 水文,2000(3):55−58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0852.2000.03.019 QIAO Conglin,SHI Mingli,SU Ya,et al. Hydrological characteristics of Huaibei Plain[J]. Hydrology,2000(3):55−58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0852.2000.03.019
[10] XU Zhanjun,ZHANG Yuan,YANG Jason,et al. Effect of underground coal mining on the regional soil organic carbon pool in farmland in a mining subsidence area[J]. Sustainability,2019,11(18):4961.
[11] 王发信,柏 菊. 淮北平原浅层地下水埋深区域分布特点[J]. 地下水,2014,36(5):51−53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2014.05.017 WANG Faxin,BAI Ju. The regional distribution characteristics of shallow groundwater depth in Huaibei Plain[J]. Groundwater,2014,36(5):51−53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2014.05.017
[12] 姜 岳, R. MISA, 李鹏宇, 等矿山开采沉陷理论发展历程综述[J]. 金属矿山,2019(10):1−7. JIANG Yue, R. MISA, LI Pengyu, et alOverview of the development history of mining subsidence theory[J]. Metal Mine,2019(10):1−7.
[13] HUANG Chang,CHEN Yun, ZHANG Shiqiang,et al. Detecting, extracting, and monitoring surface water from space using optical sensors: a review[J]. Reviews of Geophysics,2018,56(2):333−360. doi: 10.1029/2018RG000598
[14] 刘瑞杰. 基于多源遥感数据提取密云水库水体的方法效果探究[J]. 国土资源信息化,2020(3):50−57. LIU Ruijie. Exploration of the method effect of water body extraction in Miyun Reservoir based on multi-source remote sensing data[J]. Informatization of Land and Resources,2020(3):50−57.
[15] 许 冬,吴 侃. 济宁煤矿区地表塌陷积水时空演变[J]. 辽宁工程技术大学学报(自然科学版),2014,33(10):1307−1311. XU Dong,WU Kan. The temporal and spatial evolution of surface subsidence water in Jining coal mine area[J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University (Natural Science Edition),2014,33(10):1307−1311.
[16] 魏矿灵,王启春,郭广礼,等. 利用遥感数据监测矿区开采沉陷积水变化[J]. 煤矿安全,2014,45(1):13−16. WEI Kuangling,WANG Qichun,GUO Guangli,et al. Using remote sensing data to monitor changes in mining subsidence water in mining areas[J]. Safety in Coal Mines,2014,45(1):13−16.
[17] 万华伟,康 峻,高 帅,等. 呼伦湖水面动态变化遥感监测及气候因素驱动分析[J]. 中国环境科学,2016,36(3):894−898. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.03.035 WAN Huawei,KANG Jun,GAO Shuai,et al. Remote sensing monitoring of water surface dynamic changes in Hulun Lake and analysis of driving factors of climate factors[J]. China Environmental Science,2016,36(3):894−898. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.03.035
[18] 张 磊,秦小光,刘嘉麒,等. 淮南采煤沉陷区积水来源的氢氧稳定同位素证据[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2015,45(5):1502−1514. ZHANG Lei,QIN Xiaoguang,LIU Jiaqi,et al. Hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopic evidence of the source of accumulated water in Huainan coal mining subsidence area[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2015,45(5):1502−1514.
[19] 申 涛,朱占荣. 陕北矿区煤炭开采沉陷实测参数分析[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2019,47(12):207−213. SHEN Tao,ZHU Zhanrong. Analysis of measured parameters of coal mining subsidence in northern Shaanxi mining area[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2019,47(12):207−213.
[20] 陈登红,华心祝,李寒旭,等. 安徽省煤炭产业发展概况及未来发展趋向[J]. 安徽科技,2020(10):36−38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7855.2020.10.017 CHEN Denghong,HUA Xinzhu,LI Hanxu,et al. General situation and future development trend of coal industry in Anhui Province[J]. Anhui Science and Technology,2020(10):36−38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7855.2020.10.017
[21] 林承辰,郑刘根,魏祥平,等. 淮北中湖采煤沉陷区治理前后景观格局变化研究[J]. 环境监测管理与技术,2021,33(2):14−19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2009.2021.02.004 LIN Chengchen,ZHENG Liugen,WEI Xiangping,et al. Study on the change of landscape pattern before and after the treatment of Huaibei Zhonghu Coal Mining Subsidence Area[J]. Environmental Monitoring Management and Technology,2021,33(2):14−19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2009.2021.02.004
[22] 许正刚. 采煤沉陷区治理技术现状及发展趋势[J]. 区域治理,2019(44):69−71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-4595.2019.44.024 XU Zhenggang. The status quo and development trend of coal mining subsidence area treatment technology[J]. Regional Management,2019(44):69−71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-4595.2019.44.024




 下载:
下载: