Review on resource utilization of coal gasification slag
-
摘要:
随着“双碳”目标的推进,社会对煤气化渣处理的关注与需求日渐紧迫。综合过往研究,介绍了煤气化渣的主要来源与排渣方式,并分别对比了粗渣与细渣在形貌、粒度组成、矿物物相、化学组成等方面的性质特点,为实现其“减量化、资源化、无害化”利用提供了理论依据。基于气流床煤气化粗渣、细渣显著的性质差异,探索了两者不同的资源化处理方式,并分析了当下利用途径存在的局限性。粗渣具有优秀的水化活性与火山灰活性,在矿井回填、路基填筑、水泥与混凝土骨料、陶粒材料以及墙体材料等中低值利用领域应用广泛,但存在重金属浸出风险、经济效益低等问题。细渣中残炭含量丰富,主要采用重选法与浮选法进行可燃体回收与灰渣分离。但其较高的细粒级含量降低了重选分选精度,复杂的炭−灰结合形态提高了浮选回收难度。同时细渣孔隙结构发达,比表面积高达258.29 m2/g,具有一定的吸附能力,在土壤改良、催化剂载体、化工原料、陶瓷材料、吸附材料等领域应用潜力巨大,但高值化处理工艺复杂,成本较高,工业应用难度较大。针对这些问题,需基于煤气化渣的物化性质,探索大规模消纳与高值化利用相结合的途径,实现对煤气化渣分类分级的资源化利用。此外,需结合现场生产实践,探索煤气化渣就地解决的处理方法以降低运输成本,以及在其产生工艺过程中进行物化性质的诱导改善处理。
Abstract:With the promotion of the “carbon peaking and carbon neutrality” goals, the social’s concern and demand for the treatment of coal gasification slag is becoming more and more urgent. Based on previous research, this paper introduces the main sources and discharge methods of coal gasification slag, and compares the properties and characteristics of coarse and fine slag in terms of morphology, particle size composition, mineral phase, chemical composition, etc, which providing a theoretical basis for the realization of its “reduction, resourcefulness and harmlessness” utilization. According to the obvious differences in properties between coarse slag and fine slag in entrained-flow gasification, this paper explores the different resource treatment methods both of them, and analyzes the limitations of the current utilization methods. Coarse slag has excellent hydration activity and volcanic ash activity, and is widely used in mine backfilling, roadbed filling, cement and concrete aggregate, ceramic materials, wall materials and other low-value utilization fields, but there are problems such as the risk of heavy metal leaching and low economic benefits. Fine slag contains rich carbon residue, and gravity separation and flotation are mainly used for combustible recovery and ash separation. However, the high fine-grained content reduces the precision of gravity separation, and the complex carbon-ash combination morphology increases the difficulty of flotation recovery. At the same time, the pore structure of fine slag is developed, with a specific surface area as high as 258.29 m2/g and certain adsorption capacity. Fine slag has great application potential in fields such as soil improvement, catalyst carrier, chemical raw materials, ceramic materials, adsorption materials, etc. But the complex high-value treatment process and high cost make industrial applications more difficult. In order to address these problems, it is necessary to explore the way of combing large-scale elimination with high-value utilization based on the physical and chemical properties of coal gasification slag, and realize the classified and graded resource utilization of coal gasification slag. It is necessary to explore the treatment method of on-site solution of coal gasification slag, combined with field production practice, which benefits to reduce the transportation cost. As well as the induction of physical and chemical properties to improve the treatment in the process of its generation.
-
0. 引 言
煤炭作为我国主体能源,2023年原煤产量达到47.1亿t;其消费途径不仅包括传统的火力发电等方式,还有煤制油、煤制烃烯、煤制乙二醇、煤制气等现代煤化工产业链。作为推动煤炭绿色转型、开展清洁高效利用的重要一环,现阶段我国主流煤气化工艺包括固定床技术、流化床技术、气流床技术[1]。气化过程中,一般将炉底排出的大粒径灰渣称为气化粗渣,而由合成气夹带进入净化系统后收集的小粒径灰渣称为气化细渣。我国每年向煤气化工艺投入大约6%的煤炭产量,通过煤气化转化的原料煤近2.5亿t[2],煤气化渣的年排放量超过
3300 万t[1]。但由于缺乏合适的资源化利用技术及处理设备完全消纳,只能通过堆存或填埋处理,成为一种难以处理的煤系固废。因此煤气化渣的归置处理不仅占用大量土地资源,且在酸雨的冲刷、地表水以及地下水的浸透下,Cr、Zn、Cu、Pb、Ni、As、Cd等重金属会浸出污染土壤、水资源[3],同时粒度较细的煤气化渣带来粉尘污染,严重威胁着我们的生态环境安全。随着“双碳”目标逐步落实,煤气化渣资源化利用的探索日渐紧迫,而基础在于其物化性质的研究。尽管原煤煤质、气化炉型及运行工况的不同导致灰渣的性质存在一定差异,但大多煤气化渣富含Al、Si等资源,主要以Al2O3、SiO2的形式存在[4],具有较高的再利用潜力与价值。鉴于气化粗渣和细渣显著的性质差异,两者分别发展出不同的利用路线。粗渣含碳量较少、粒度大,通常可以作为回填材料、路基材料或建筑材料使用[5];细渣含碳量较高,可达30%以上,且粒度更细,可用于制备介孔二氧化硅材料、高分子复合材料、沸石/活性炭及复合材料[6]。近年来,煤气化渣相关探索多在实验室条件下开展,虽然所得材料具备优良性能,但还缺少工业生产的实践检验,昂贵的添加剂以及复杂的制备工艺阻碍了应用规模化,也证明煤气化渣的资源化利用还有很长的一段路要走。
迄今为止,许多学者对煤气化渣的资源化利用进行了总结,但往往聚焦在粗渣或细渣单个固废,或仅针对于某一领域的研究。冯向港等[7]对煤气化渣的高值化研究进行了总结与展望,张瑞梅等[8]对气化细渣的综合利用及炭−灰分离进展进行了综述。而粗渣和细渣同时产生于煤气化工艺,因此全面进行两者性质、资源化发展的对比对煤化工企业有着重要意义。笔者系统概述了气化粗渣、细渣的物理化学特性,为其资源化利用提供了理论依据;此外,进一步分类总结了其在不同领域的应用研究,分析了当下利用途径存在的局限性问题,包括可燃体回收、回填材料、建筑材料、化工原料、陶瓷材料等领域。以期为相关领域工作人员提供参考。
1. 煤气化渣的物理化学特性
气化粗渣产生于气化炉排渣口,由于原煤性质、气化工艺以及气化炉运行温度、压力的差异,其主要有2种排渣方式。流化床与固定床气化炉在温度接近
1000 ℃下运行,例如,鲁奇(Lurgi)气化炉、U-GAS气化炉,刚好低于煤灰的熔融温度,因此多采用固态(干灰)排渣。液态排渣多见于气流床与部分固定床技术(如BGL气化炉),在1400 ~1500 ℃运行,使得炉渣具有足够的流动性,附着在气化炉内壁,在炉底急冷凝固成粒径较大的固体残渣排出。细渣则由未反应炭粒与细小灰渣组成,由于气流在料层中和气化炉空间流动,所以被合成气裹挟出炉,由不同的净化除尘工序收集。其中,气流床气化炉被认为是最通用的气化炉类型,包括干煤粉气化炉(西门子(GSP)气化炉、AP干煤粉(原Shell)气化炉、HT-LZ、SE-东方炉、宁煤气化炉等)及水煤浆气化炉(AP水煤浆(原GE、Texaco)气化炉、多喷嘴对置式气化炉等)。其入料煤种选择广泛,碳转化率较高,且产生不含焦油和苯酚的合成气,被广泛应用于煤化工原料制备、IGCC发电等行业[9],因此本文主要针对气流床煤气化渣进行阐述。
1.1 煤气化渣物理特性
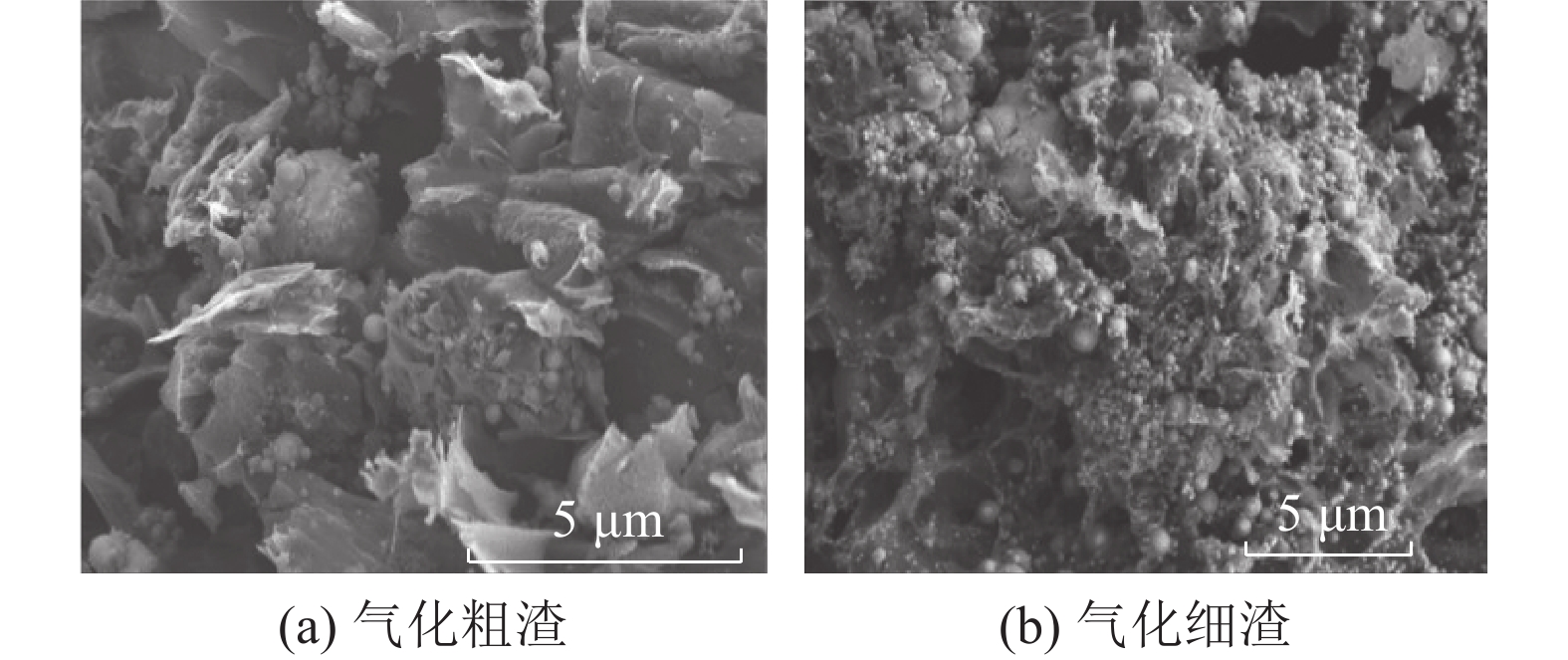
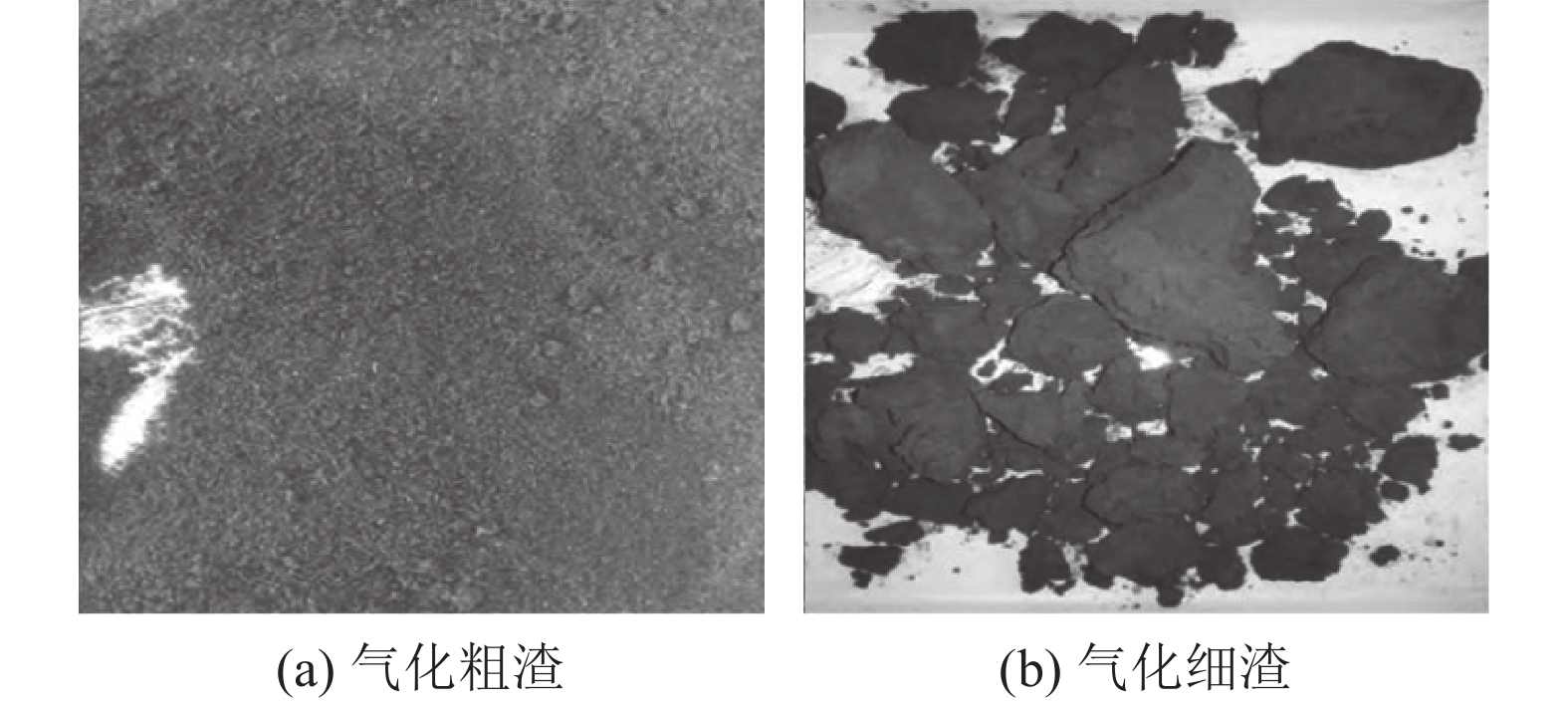
图1为宁煤干煤粉气化粗渣与细渣的表观形貌,粗渣在气化炉中滞留时间长,煤气转化率高,一般是灰褐色或黑色的块状颗粒物,残炭量低且密度较大,其密度大于2.8 g/cm3,且具有较高的机械强度。细渣由于气化反应不充分,残炭量较高,颜色比粗渣更黑且密度更低,一般是深灰色或灰黑色的细小粉末状颗粒,密度在2~2.5 g/cm3[11]。
GE水煤浆气化粗渣与细渣的微观形貌如图2所示[12];由图2a可见,粗渣颗粒多为片状,表面平整光滑,还有部分熔融态物质团聚而成的玻璃微珠,因此其比表面积较小,根据宋瑞领等[13]的研究,陕西水煤浆气化粗渣的比表面积为84.50 m2/g。如图2b所示,细渣颗粒粒度较小,表面氧化严重,具有丰富的多孔结构,研究表明其比表面积可达258.29 m2/g[14],还有较多致密的玻璃微珠分布在其中。
表1为国内一些不同原煤煤种、气化工艺及炉型生产的煤气化渣粒径分布试验数据[15],由表可知粗渣集中在+0.50 mm粒级,部分粗渣+0.50 mm产率高达84.26%[16];且随着粒径减小,各粒级含量递减。细渣粒度较小,中间粒度级分布较均匀,且在0.125~0.25 nm分布率较高,占比高达40.07%。
粒度级/mm +1.0 1.0~0.8 0.8~0.50 0.5~0.25 0.25~0.125 0.125~0.074 −0.074 粗渣质量分数/% 宁煤Texaco 69.06 10.67 5.23 2.58 2.46 2.46 2.46 宁煤GSP 9.45 17.37 23.44 19.6 20.77 5.33 4.04 陕西水煤浆 49.10 49.10 49.10 24.46 13.17 7.03 6.25 细渣质量分数/% 宁煤Texaco 18.75 18.75 18.75 23.87 28.85 4.47 14.06 宁煤GSP 13.59 13.59 13.59 11.97 40.07 24.87 9.50 陕西水煤浆 3.46 3.46 3.46 18.29 20.99 13.62 43.65 榆林气流床 1.03 1.03 1.03 14.27 32.36 9.25 43.09 残炭在煤气化渣中分布并不均匀。粗渣中残炭量随着粒径增大而递减[11];细渣中残炭量随粒径增大而递增。由于气化剂在煤炭的表面及孔隙中发生反应,其反应速率与扩散速率密切相关,而扩散速率受到孔隙扩散的影响。随着颗粒粒径增大,孔隙扩散阻力递增,导致扩散速率与反应速率随之递减[17]。因此,颗粒较大的细渣气化率较低,含碳量较高,颗粒较小的细渣则与之相反。
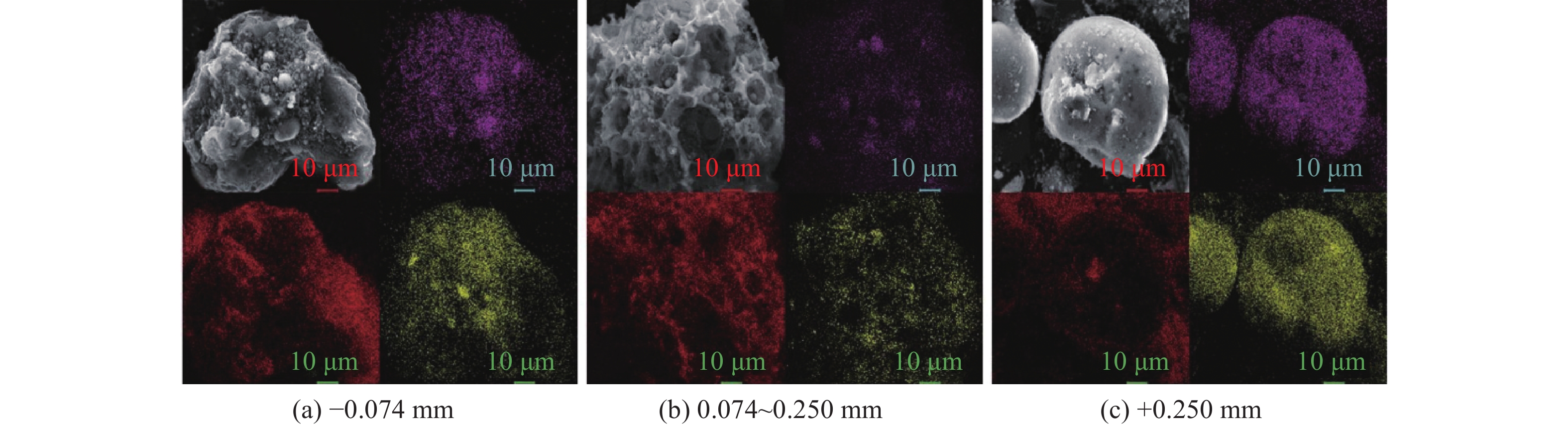
图3所示为不同粒级的宁东GSP干煤粉气化细渣中炭−灰结合的形态差异:−0.074 mm粒级中细灰以无定形态融合于致密碳基体上,0.074~0.250 mm粒级中球形灰填充于多孔碳的孔隙中,+0.250 mm粒级中少量碎屑炭附着在球形灰粒上,所以针对不同的炭−灰结合形态,可分粒级采取不同方法来实现炭−灰彻底解离。
而粗渣是气化炉内的熔融态炉渣沿着内壁到排渣口遇冷融合而成的大颗粒,其在气化炉中停留时间较长,因此气化率高且残炭少。总之,煤气化渣的残炭量与气化反应时间紧密相关,这为煤气化渣采用粒度分级实现炭−灰分离提供了理论支撑。
1.2 矿物组成
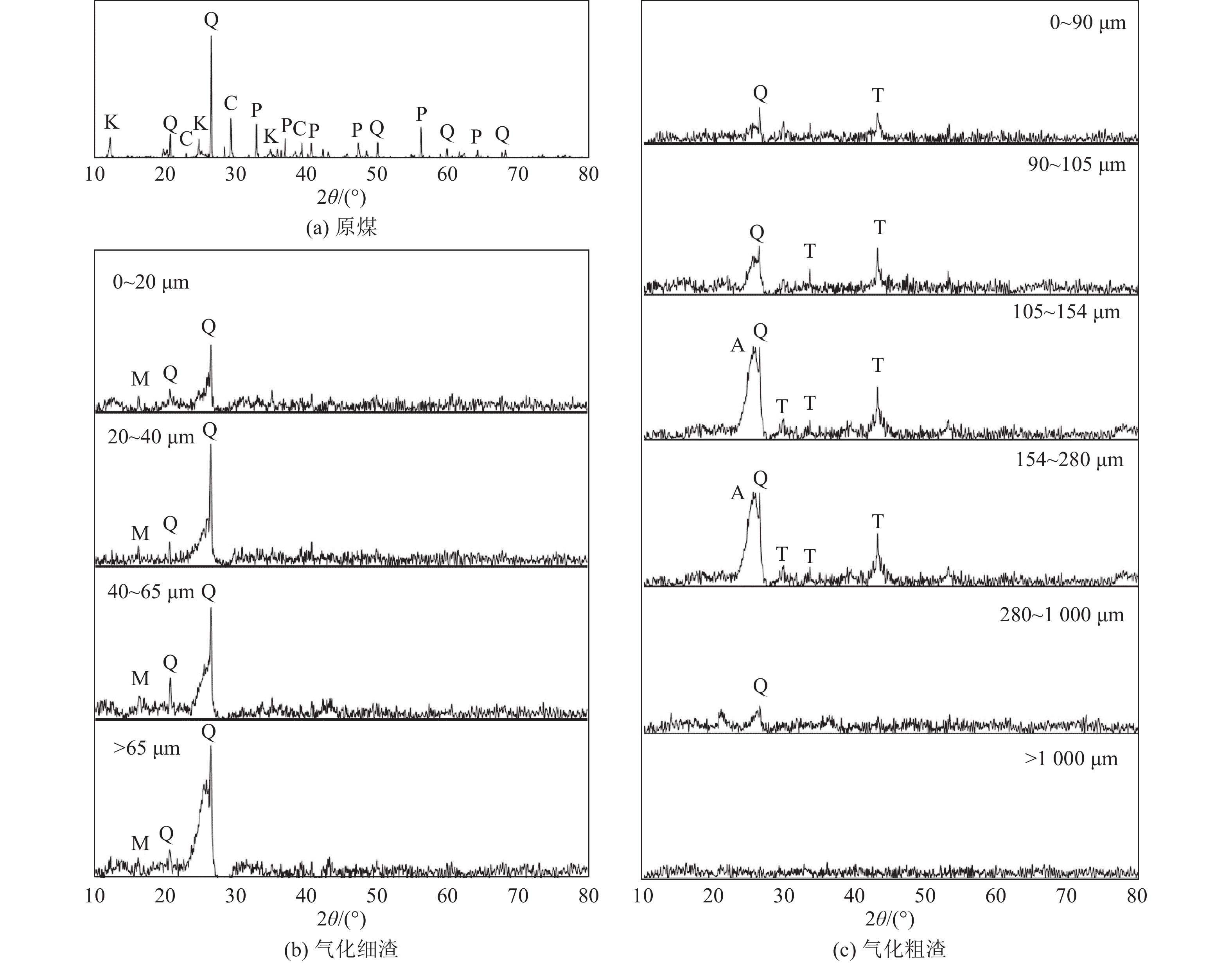
图4展示了原煤以及干煤粉气化渣的矿物组成分析结果[19]。在XRD分析图谱中,晶质矿物以尖锐衍射峰呈现,然而气化渣的XRD图谱仅能检测出少量衍射峰,这说明原煤的矿物质在气化过程中大多转变为熔融态并发生一系列物理化学反应,分解并生成以非晶态铝硅酸盐为主的气化渣。气化渣的矿物组成主要包括非晶态物质和结晶矿物质,其结晶矿物质含量较低,非晶态物质包括无定形残炭和铝硅盐玻璃相。由图4可得,原煤的矿物晶体主要包括石英、高岭石、黄铁矿等;粗渣中的矿物主要是石英、硫铁矿等,而细渣中的矿物主要是石英、方解石等。此外,气化渣中石英的衍射强度随着粒径的减小而降低[20]。
在气化过程中,原煤中大部分石英与高岭石等反应生成新的矿物质或非晶质;同时黄铁矿与H2反应生成硫铁矿,最终在高温状态下与O2反应生成赤铁矿。此外,原煤中方解石与莫来石受热分解生成方钙石,之后在
1200 ℃反应生成钙长石[21]。而细渣的莫来石是原煤中高岭石经过偏高岭石→Al−Si尖晶石→莫来石一系列连续转化在1000 ℃左右生成,且含量在1000 ~1400 ℃随温度升高而增加[22]。1.3 化学特性
表2为我国不同地区、不同气化炉型的气化粗渣和细渣的化学组成分析。尽管在原煤煤种、气化炉型及运行工况等方面存在差异,煤气化渣的化学组成均以SiO2、Al2O3、CaO、Fe2O3为主,还有MgO、TiO2、Na2O、K2O、B2O3、P2O5、SO3等成分,其中CaO含量较高可能是由于在气化过程中加入了助溶剂方解石[29]。由表2可得,酸性氧化物(SiO2、Al2O3等)通常占煤气化渣中无机成分的40%~50%,而碱性氧化物(如CaO、Fe2O3、MgO、Na2O和K2O)占比为20%~40%,并且粗渣中CaO、Fe2O3的含量高于细渣[30]。
表 2 我国不同地区和不同炉型气化粗渣和细渣主要化学组成Table 2. Main chemical composition of gasification coarse slag and fine slag in different regions and different furnace types in China样品 化学组成质量分数/% SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 CaO MgO K2O Na2O TiO2 SO3 陕西Texaco粗渣[23] 41.12 12.72 — 12.88 1.23 1.94 1.49 0.61 — 陕西Texaco细渣[23] 32.20 8.87 — 4.33 0.69 1.23 0.54 0.52 — 陕西多喷嘴对置式水煤浆气化粗渣[13] 41.44 13.91 17.37 17.37 2.26 1.46 1.40 0.65 1.38 陕西多喷嘴对置式水煤浆气化细渣[13] 35.93 15.48 18.13 17.19 2.11 1.39 2.31 0.88 3.25 安庆粉煤Shell气化粗渣[24] 46.90 20.38 7.66 8.57 1.02 2.03 1.65 1.01 2.12 安庆粉煤Shell气化细渣[24] 37.50 21.63 15.73 17.70 1.18 0.55 0.53 1.29 3.27 鄂尔多斯水煤浆气化粗渣[25] 55.30 19.14 9.79 8.65 1.14 2.44 1.45 1.16 0.66 鄂尔多斯水煤浆气化细渣[25] 54.40 21.93 8.36 6.70 1.09 2.70 1.86 1.28 1.23 Texaco气化粗渣[26] 42.90 13.27 5.20 13.44 1.28 2.02 1.55 0.64 — Texaco气化细渣[26] 37.02 10.20 2.86 4.98 0.79 1.41 0.62 0.60 — 宁煤粗渣[10] 48.82 19.33 10.34 10.64 2.90 2.42 1.31 1.03 2.39 宁煤细渣[10] 51.95 18.33 8.89 9.09 4.10 3.10 1.61 1.11 0.77 神木化工粗渣[27] 41.12 12.72 — 12.88 1.23 1.94 1.49 — — 神木化工细渣[27] 32.20 8.87 — 4.33 0.69 1.23 0.54 — — 神华集团粗渣[28] 50.59 18.44 12.06 8.77 3.27 2.13 1.20 1.18 — 神华集团细渣[28] 41.78 37.40 7.54 6.85 0.76 1.34 0.65 2.19 — 综上,煤气化渣特殊的矿物物相以及丰富的Si、Al、C等资源为其资源化利用奠定了基础。
2. 煤气化渣中可燃体回收及再利用研究现状
2.1 气化粗渣中可燃体回收及再利用研究现状
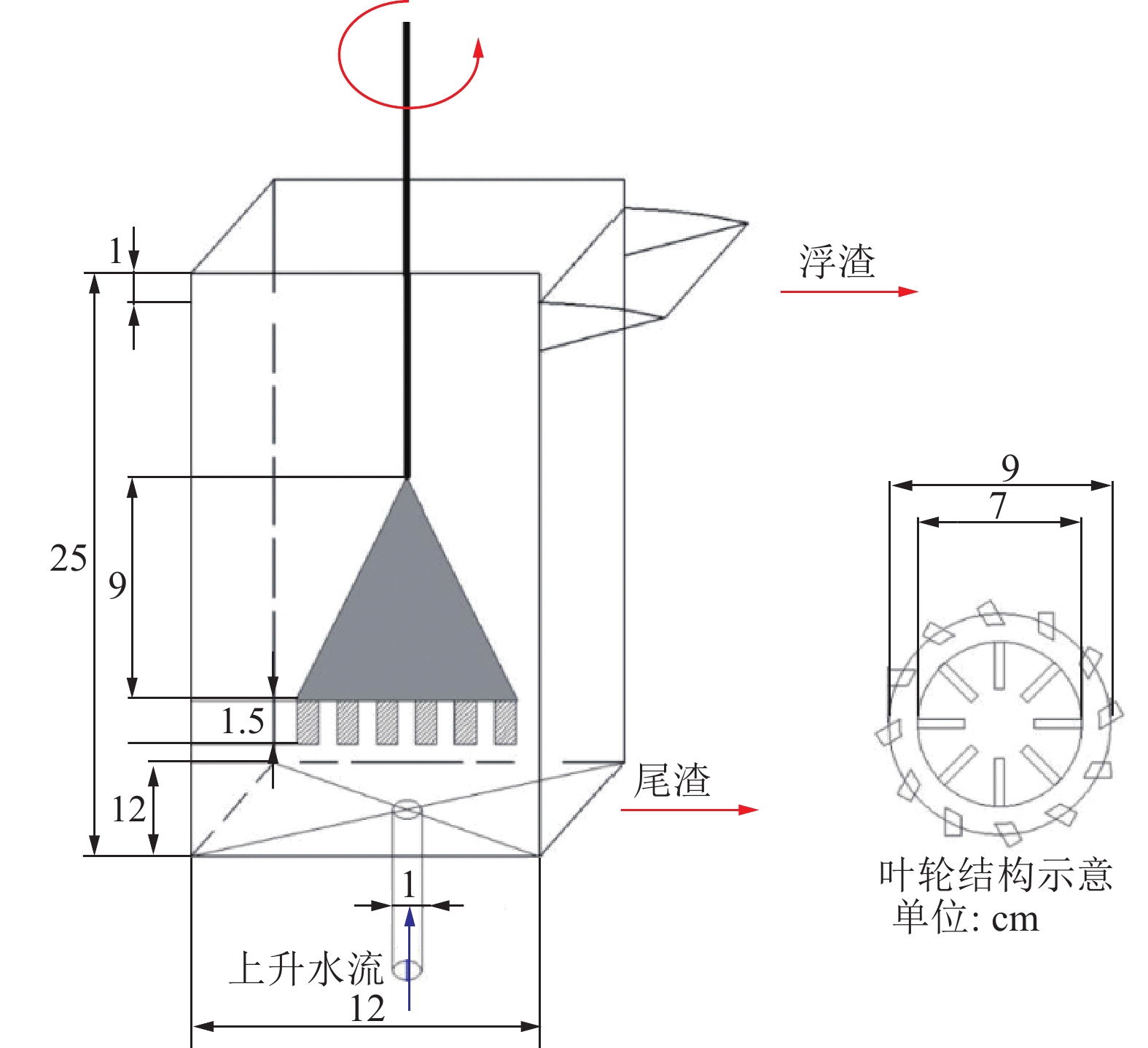
鉴于可燃体在粗渣及细渣中的分布存在差异,对煤气化渣进行分类利用十分重要。粗渣中残炭量随着粒径增大而递减,可以通过物理解离及筛分将未燃炭富集到细粒级[31],并进一步采用风选法或浮选法实现碳的提纯。章新喜等[32]通过粒度分级−脉动液固流化床分选机−浮选工艺将粗渣的灰分由65%降至27%。高增林等[33]采用图5所示水流分级装置,通过先湿法筛分再水流分级的组合途径,显著提高了榆林水煤浆气化粗渣的可燃体回收率与精矿烧失量,其中0.5~0.18 mm粒级的精矿烧失量可达70.05%,尾矿灰分均高于92%。
此外,史磊等[34]还提出一种利用循环流化床处理煤气化渣的新途径,即将粗渣研磨至80 μm送至溶解池进行溶解,沉淀物在煤场与原煤混合拌匀用作燃料;溶解池浆液与氨水混合,由雾化喷枪均匀地喷入水平烟道内再燃烧利用。但由于粗渣残炭量较低,目前其可燃体回收难以产生经济效益。
2.2 气化细渣中可燃体回收及再利用研究现状
2.2.1 细渣掺烧利用
高残炭使细渣的燃烧特性与劣质烟煤相当,其着火温度在601.6 ℃左右[19]。因此与原煤按比例在循环流化床或煤粉炉内掺烧利用,既可以降低化工厂运输成本,又能充分利用细渣的热值,是实现细渣规模化消纳最主要、最直接的利用方式。同时,经过掺烧利用,二次炉渣的残炭量进一步降低,可用作建材原料,实现煤气化渣的高附加值利用。
细渣与原煤共燃具有协同效应,其可燃性、综合燃烧特性随着掺混煤的比例增大而提高[35]。掺烧后的综合发热量既满足设计燃料要求,又不会对锅炉效率及安全稳定运行产生影响[36]。但由于掺烧比例较小,产生的经济效益有待深入研究。
2.2.2 细渣炭−灰分离技术
炭−灰分离技术可以进一步提高细渣的残炭量与热值,是实现其完全消纳与资源化再利用的重要支撑。目前主要采用重选法和浮选法等物理分选法,一方面富集可燃体并回收,另一方面得到高灰废渣进行资源化利用;同时一部分学者侧重于对细渣脱炭处理获得高灰废渣,因此采用的燃烧法、电选法导致了细渣中碳资源的浪费。
1)重选法。
气化细渣中未燃炭组分(−2.0 g/cm3)与高灰组分(+2.4 g/cm3)存在明显的密度差异,因此可采用重选法对其进行炭−灰分离[15]。李慧泽等[37]验证了采用水介质旋流器对宁夏+0.074 mm细渣进行炭−灰分离的可行性。任振玚等[38]进一步采用复锥结构水介旋流器分选国能集团GSP干煤粉气化细渣,得到产率为8.37%、灰分为12.69%的富碳产品,可燃体回收率高达97.09%。此外,还有学者采用摇床、跳汰机、螺旋溜槽、螺旋分级机等进行了细渣的炭−灰分离[39],但重选对细粒级气化渣分选效果较差,因此探索其他超细气化渣的深度分选方法是目前研究重点。
2)浮选法。
细渣中的残炭经过高温气化后表面仍有部分疏水官能团,而其他Si、Al等元素主要赋存于亲水性矿物,因此可采用浮选法对其进行炭−灰分离[15],且相比于重选法,浮选法更适合细粒级分选。目前对细渣浮选的探索主要集中在浮选药剂、设备与工艺等,常规浮选设备主要有浮选机与浮选柱;药剂分为捕收剂与起泡剂,一般选用柴油、煤油等作为捕收剂,起泡剂包括仲辛醇、2号油和甲基异丁基甲醇(MIBC)等。但细渣复杂的表面性质使得煤油、柴油等非极性烃类油较难吸附在其表面,大大削弱了药剂的捕收作用。
表3、表4展示了目前对于浮选药剂及工艺的部分探索。通过向非极性烃类油添加极性基团制备复配捕收剂,可以有效加强细渣的浮选效果,从而提高精矿产率与可燃体回收率。研究表明,油酸−煤油复配药剂中的长链烃可以通过范德华力吸附在未燃炭的非极性区,且其上的—COOH基团通过氢键吸附在未燃炭的—COOH和—OH的极性位上,两者协同作用增强了未燃炭表面的疏水性[41]。在相同药剂用量下,程延化等[40]分别采用煤油以及月桂酸与煤油复配药剂为捕收剂对榆林气化细渣进行浮选,可燃体回收率由67.50%提高至94.91%。
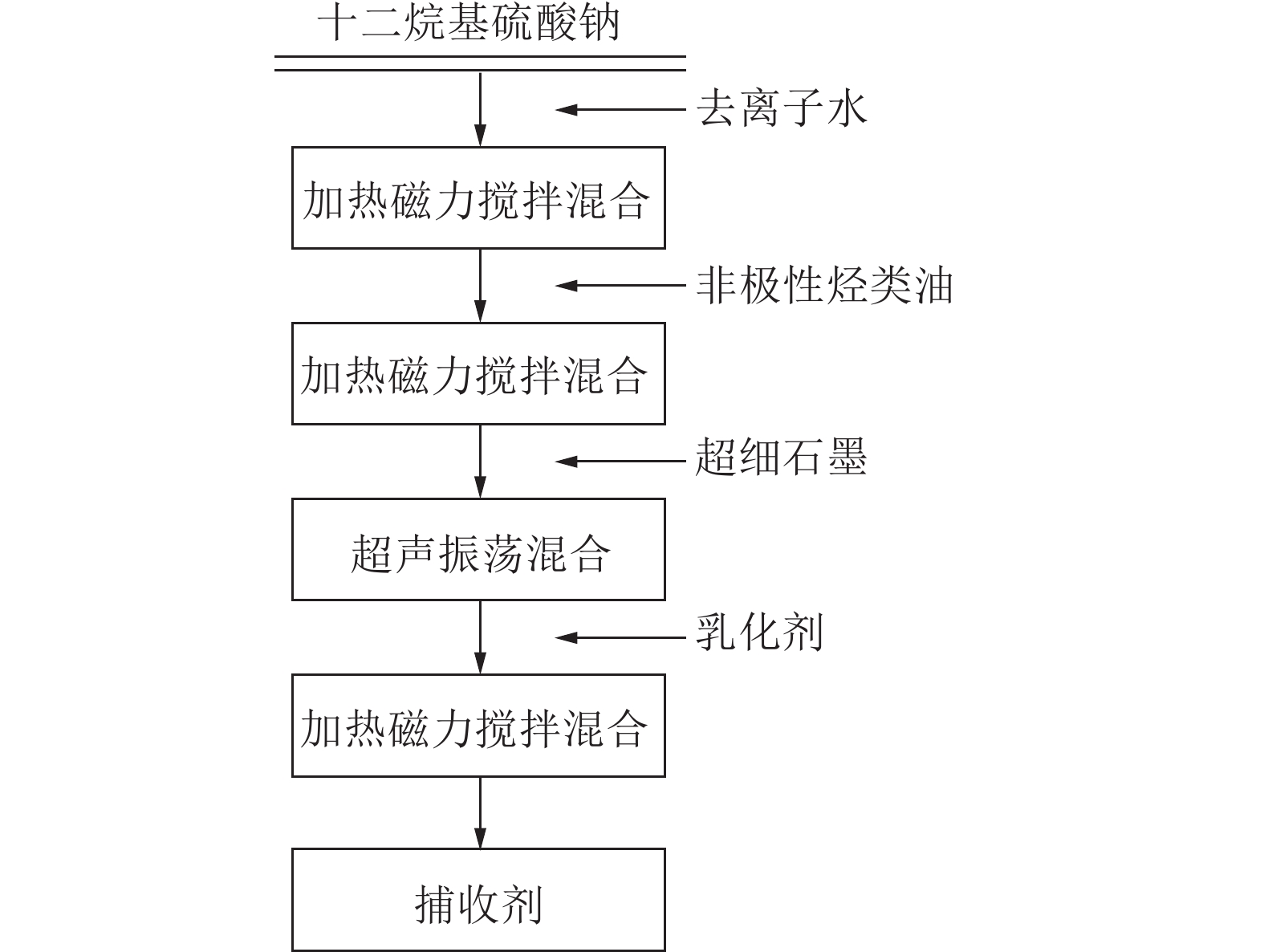
如图6所示,张海军等[41]分别采用柴油、煤油与十二烷基硫酸钠、超细石墨颗粒复配为捕收剂,结果表明,柴油复配效果优于煤油,相对于单独使用柴油,可燃体回收率由67.36%提高至88.26%。且添加疏水颗粒对于提高捕收剂的捕收效果具有积极作用。
此外,由表4可知,采用多段浮选及反浮选工艺可有效提高细渣的分选效果。在浮选设备方面,有研究表明采用机械搅拌式浮选机、旋流−微泡浮选柱分别对+0.04 mm粒级与−0.04 mm细渣进行浮选更有助于提高精细化分选效果[46]。
同时,由于细渣发达且不规则的孔隙结构,部分细灰嵌布在未燃炭的孔道内,对浮选产生较强的阻碍作用,因此可对矿浆采取磨矿预处理、微波预处理、超声波预处理或分散剂预处理等方法[47]。磨矿预处理可以促进细渣中的残炭与脉石矿物深度解离,且有助于提高细渣表面的疏水性[48],但同时由于相对比表面积增大,导致药剂的消耗量居高不下。超声波预处理可以消除细渣表面含氧官能团,显著弱化高灰微珠的夹带现象,并提高了浮选选择性[49−50]。
此外,调节浮选体系中的无机盐阳离子(Na+、Mg2+、Al3+)对细渣的浮选存在积极效果。随着无机盐阳离子价态的增加,浮选体系的表面张力降低,因此气泡的衰减受到抑制,同时颗粒表面的Zeta电位降低,改善了残炭固体颗粒的可浮性[51]。
总之,炭−灰分离是实现煤气化渣资源化利用的关键前提。目前,重选精度较低,对细粒级分选效果较差;浮选对细粒级分选精度高,但其特殊的表面性质和形貌结构导致常规浮选药剂消耗大、处理成本高等问题。因此对高效分离设备、新型浮选药剂、浮选工艺的探索和其他分选方法的研究至关重要,有利于综合各种分选方法的优点,实现高效低耗的分选路线。
3. 煤气化渣的资源化利用现状
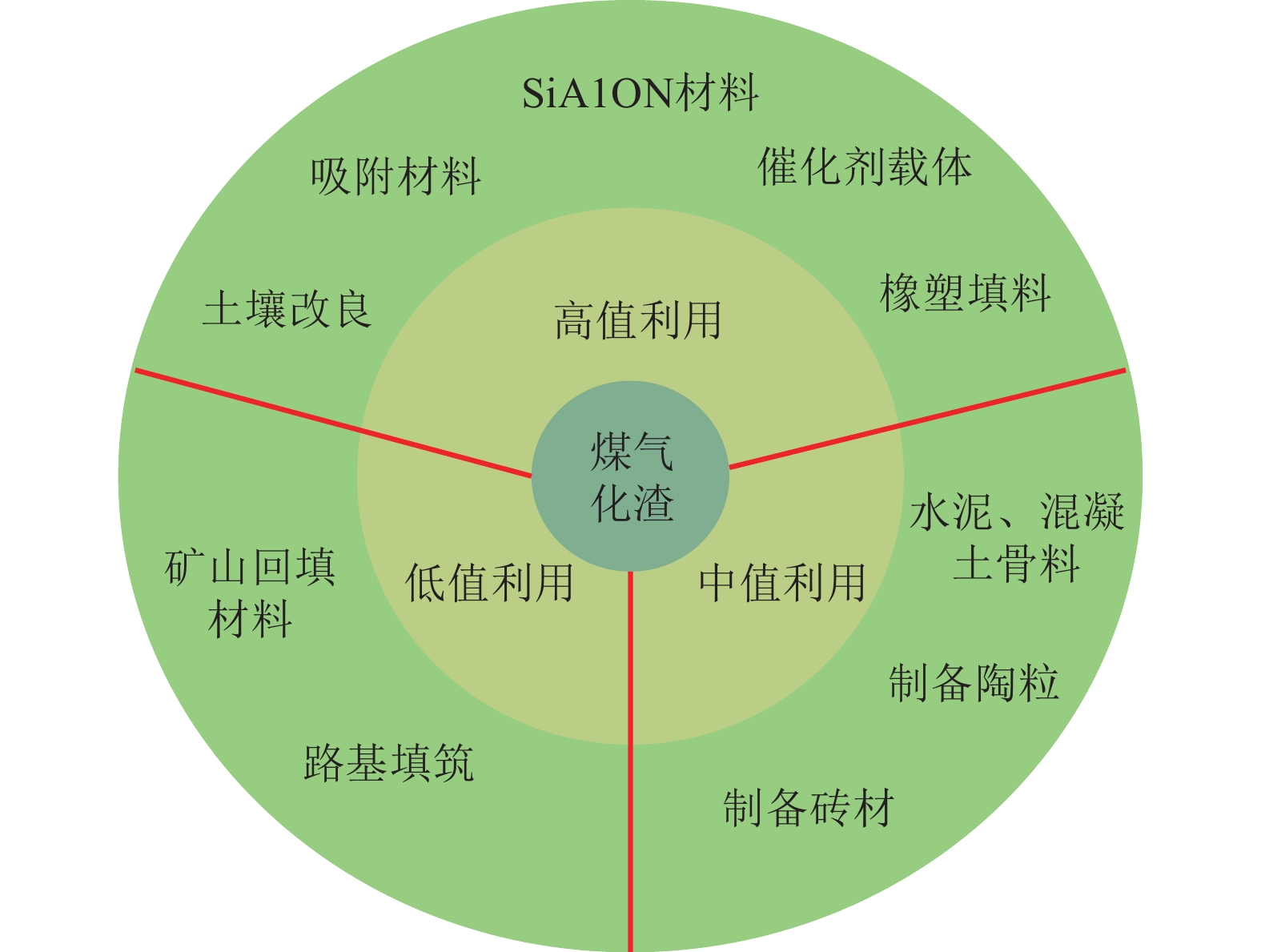
煤气化渣中除丰富的碳、硅、铝等资源,独特的多孔结构以及较好的水化活性和火山灰活性也为其资源化利用提供了巨大潜力。如图7所示,目前国内外许多研究聚焦于如何充分利用煤气化渣的自然禀赋,实现煤气化渣的清洁绿色、高性价比利用:①低值利用:矿山回填材料与路基填筑等;②中值利用:制备陶粒、砖材或用于水泥、混凝土的骨料等;③高值利用:土壤改良、吸附材料、催化剂载体、橡塑填料以及SiAlON材料等。
3.1 低值利用
由于粗渣残炭量低,具有一定的级配,其作为矿井回填材料、路基材料具有较好的发展前景。
3.1.1 矿井回填
矿井填充是消耗大量固体废物的重要途径,既可以减少水泥用量,降低煤矿充填成本,又有助于实现煤气化渣的充分利用。当采用粗渣作矿山充填原料时,需要采用激发剂对粗渣改性,从而提高粗渣充填体强度[52];或者以粗渣作为辅助胶凝材料,与煤矸石、硅酸盐水泥、激活剂等配制出一种满足矿山充填要求的新型充填材料[53]。
3.1.2 路基填筑
在路基材料中掺入粗渣有助于提高混合料的密实度和强度,改善路面的抗裂性与耐久性[54]。经筛分、磁选后可得到粒径较大、结构密实、稳定性高的粗渣颗粒,与骨料、砂浆等材料混合后可满足材料强度要求;同时粗渣残炭量较低,在一定程度上抑制了硅酸盐等矿物的聚合[55];此外,粗渣颗粒外形呈球状,表面光滑,不具有水硬性,与路石材料相比粒径更小,在拌合过程中可以填充孔隙从而增大密实度,起到缓冲作用,并降低和延缓材料裂纹的产生与发展[56],进而增强混合料的强度和密实性。研究表明,掺入内蒙古GE水煤浆气化粗渣制备的改性砂浆1 d抗压强度可提高74%,28 d抗压强度提高33.3% [57]。且由于细渣含碳量较多,粗渣比细渣更适合应用于半刚性基层材料中[12],但细渣分选后得到的富灰产品同样可充分应用于路基材料。
3.2 中值利用
3.2.1 水泥、混凝土骨料
根据GB/T 1596—2005《用于水泥和混凝土中的粉煤灰》标准规定,制备水泥和混凝土的粉煤灰烧失量不得高于15%。气化渣中的残炭遇水后会在材料表面形成一层憎水膜,阻碍水分进一步渗透,影响活性氧化物与水泥水化产物Ca(OH)2的反应,进而导致材料活性降低[30]。因此需根据残炭在高残炭气化渣中的分布特点,预先炭−灰分离后进行建材化利用。
基于煤气化渣的集料作用、水化活性以及火山灰特性,粗渣可以替代50%~70%的黏土配料制成水泥[58],有助于成核作用,增加水泥浆体中水化产物数量,进一步降低初凝时间和终凝时间[59],从而提高水泥浆体的抗压强度。
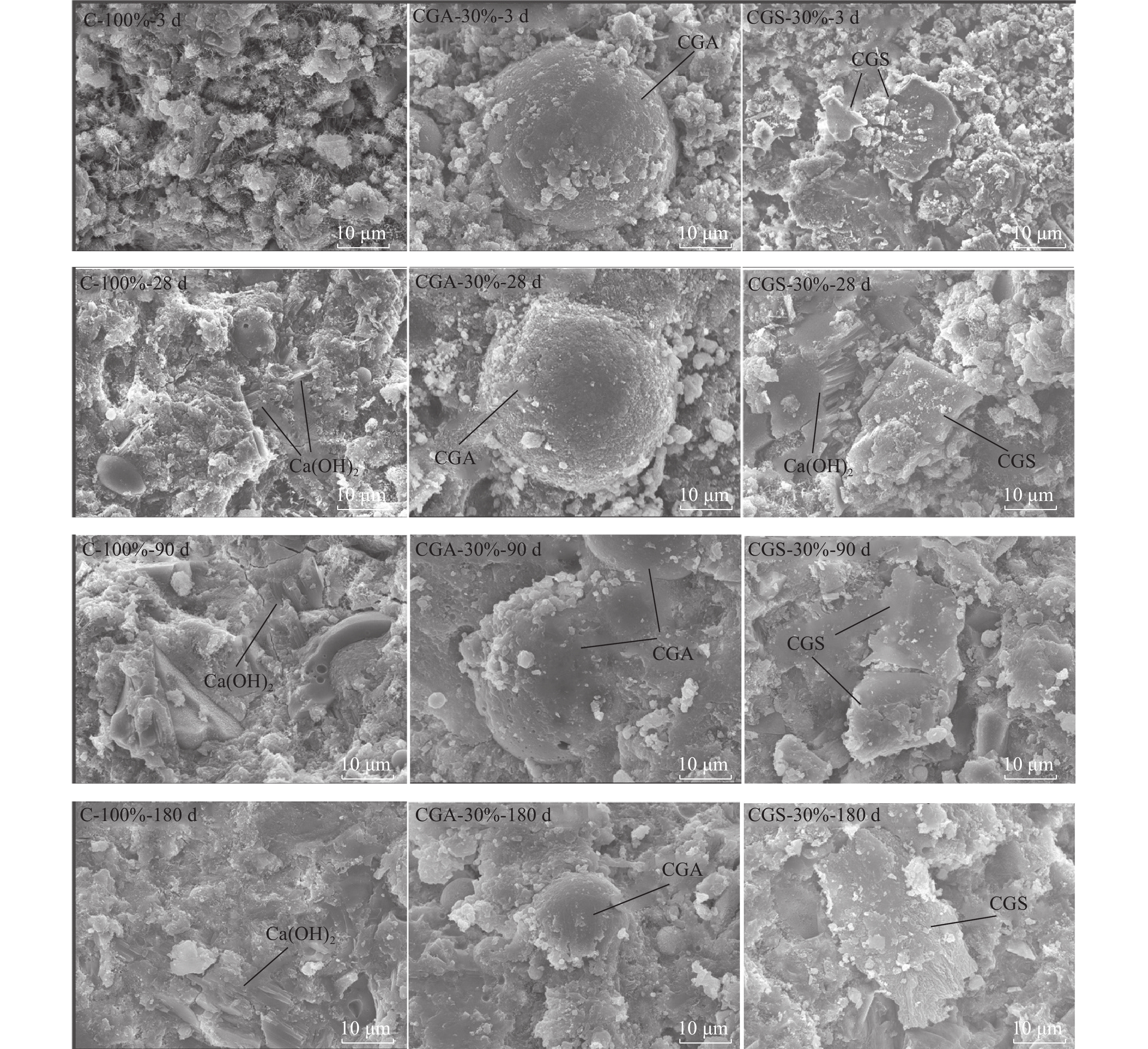
此外,采用预脱炭处理后的煤气化渣作制备水泥基材料更具可行性。经过600 ℃煅烧脱炭后的粗渣和细渣的强度活性指数分别为100.9%和82.7%,两者均可作活性剂添加到水泥基材料。如图8所示(图8中,C为水泥;CGA为粗渣;CGS为细渣。例,C-100-3d为100%的水泥水化100 d后的微观结构),在水化28 d后,内蒙古Texaco气化粗渣表面与大量水化产物相连,边缘开始被腐蚀,细渣的表面也因腐蚀产生凹坑。在水合后期,脱炭粗渣和细渣的原始形态受到严重破坏,且水泥水化产物中的Ca(OH)2含量大大降低,两种脱炭气化渣协同使用可能对水泥基材料的流动性和强度有更好的作用。
普通混凝土以水泥为胶凝材料,以砂、石为骨料,加水拌制成水泥混凝土。在使用粗渣作为掺合料时,通过研磨可以达到机械活化的效果,激发大量非晶态物质的活性,促进水化过程中硅酸钙凝胶的生成,有助于提高混凝土的抗压强度,同时减小混凝土干缩率[5]。此外,粗渣研磨改性后作为混凝土原料部分替代品还改善了混凝土抗裂性能、凝结时间等特性[61]。
3.2.2 制备陶粒
陶粒是一种陶质颗粒,表面光滑坚硬,内部具有蜂窝状结构;同时具备优良的耐火性与抗震性,以及保温隔热、耐风化等性能,在建材领域具有广阔的应用前景。目前陶粒的制备原料主要为页岩和黏土等,少有以固体废物为原料。
陶粒制备原料包括制陶成分、助融成分和发泡成分,制陶成分主要为SiO2和Al2O3;助融成分主要包括K2O、Na2O、MgO、FeO和CaO;发泡成分主要是有机物类、碳酸盐类、氧化铁类等物质[62]。煤气化渣中丰富的碳、硅、铝等资源使其满足制备陶粒的基本要求,目前已有研究通过免烧工艺将粗渣、石英砂、水泥按照一定比例制备出粗渣陶粒[63],其筒压强度达到8.71 MPa,吸水率随着粗渣用量增加而提高[64]。
3.2.3 墙体材料
煤气化渣含有丰富的SiO2、Al2O3、Fe2O3,其水化后形成的硅铝型玻璃体可以与CaO反应生成水化硅(铝)酸钙胶状玻璃体,并且残炭在烧结过程中起到内燃作用,既降低能源消耗,在燃烧后又会形成大量微小孔隙,降低坯体密度和导热率。因此被广泛作为原料用于制砖与新型墙体材料。
CHEN等[65]将集成气化联合循环(IGCC)系统细渣与黏土按质量比1∶4制得吸水性能符合美国材料实验协会等级规范的标准砖块。表5为国内外采用煤气化渣制备砖材的研究进展,以气化渣为原料可制出具备优秀的吸水率与抗压强度的免烧砖、黏土砖、蒸压砖、烧结砖等建筑材料,符合绿色环保的可持续发展理念。
表 5 不同煤气化渣制砖的性能对比Table 5. Performance comparison of different bricks prepared by coal gasification slag此外,冯银平等[26]将Texaco气化粗渣和细渣按气化炉排出比例混合磨细,与黏土混合采用挤出成型法制备出体积密度为1.00 g/cm3、导热系数为0.19 W/(m·K)、耐压强度为5.3 MPa的轻质隔热墙体材料。云正等[27]将神木化工粗渣和细渣按比例混合并破磨至−0.088 mm作为造孔剂,添加至铁尾矿、黏土中制备出密度低于1.45 g/cm3、导热系数低于0.23 W/(m·K)、抗压强度高于30 MPa的新型墙体材料,实现了铁尾矿烧结墙体材料体积密度的降低和保温隔热性能的提高。
综上,采用煤气化渣制备墙体材料工艺简单、经济低耗,同时产品具有良好的轻质高强、保温隔热性能,是清洁利用气化渣的重要途径。然而,气化渣的多孔性以及残炭量会改变墙体材料的特性(密度、吸水率、线性干缩率等),因此在应用前需要对气化渣的物理化学性质进行研究。
3.3 高值利用
3.3.1 土壤改良
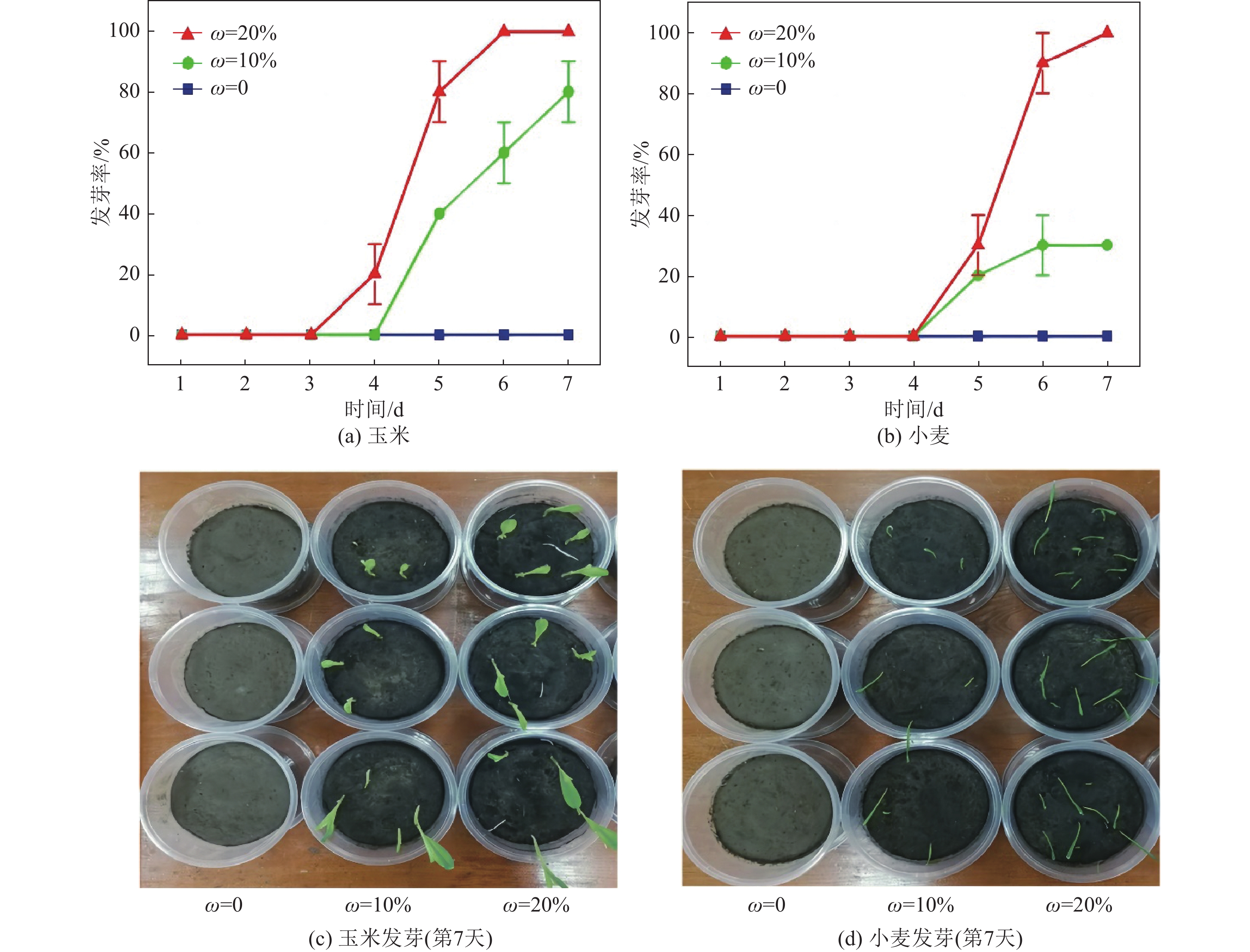
细渣含有丰富的N、P、K和作物所需微量元素,既可以增加土壤中的有机质含量,还可减轻使用化肥所造成的土壤板结情况,有助于提高农作物产量和品质[71]。同时,对内蒙古气化细渣酸、碱、盐、研磨、煅烧等处理后,发现细渣的可浸出Si含量高于其他硅源样品,为细渣制备硅肥提供了可行性支撑[72]。此外细渣pH值通常为碱性,适合酸性土壤的改良,如图9[73]所示,在未经处理的土壤中,发芽率为0的主要原因是土壤的持水能力较差,种子吸收了太多的水分,从而失去了活性。施用细渣(施用的细渣质量分数用ω表示)可以有效降低土壤容重,增加阳离子交换和持水量等理化性质,进一步提高土壤保水性能,促进玉米和小麦的发芽率。
细渣丰富的多孔结构有利于保持水分、空气和养分,提高土壤的透气性,同时细渣与生物炭类似的物理性质可以促进有机物分解,是良好的腐殖酸储存和释放介质[74],可以起到供肥和及保肥作用,因此在农业上作为有机肥辅料具有天然优势。采用细渣作辅料添加至猪粪、秸秆等有机堆肥,有助于加速堆肥体系的启动,延长堆肥的高温期,并降低pH,促进有机物及有毒物质的分解,从而提高堆肥效率[75];同时减少温室气体的排放、NH3和挥发性脂肪酸的积累,提高腐熟度和C/N比,缩短堆肥的成熟期,进一步提高肥料的质量和价值[76]。
此外,粗渣可通过配置种植砂的方式应用在土壤改良领域,李强等[77]分别对榆林气化粗渣、细渣进行物理与化学改性,按9∶2.2∶1的比例将风沙土、粗渣、细渣配制成气化渣复配土。相比单独使用沙土,采用复配土种植的苜蓿株高、地上生物量和根系生物量分别增加49.5%、24.7%和59.5%。
目前煤气化渣在土壤改良的应用方向主要为制备土壤调节剂、硅肥原料、种植砂等,为盐碱地改良、沙漠化防治取得较好的探索效果[78]。然而有研究指出粗渣中Cd、Hg、As、Zn、Ti、V、Sb的非残渣态含量约占90%,细渣中可浸出重金属含量均在90%以上;在土壤中添加粗渣、细渣培养大豆苗叶时,大豆苗叶中Pb、Hg、Ni、Cr含量均超过国家标准限值要求,且细渣中重金属更易被细菌吸附,以致添加细渣培养的细菌菌体重金属含量都显著高于添加粗渣的菌体[79]。煤气化渣中较高的有毒重金属含量存在一定环境风险,因此探索其制备土壤改良剂时需评判重金属浸出风险及解决方法。
3.3.2 吸附材料
目前,采用煤气化渣作为吸附剂处理染料废水、选煤废水等工业废水的探索已初见成效,包括直接处理、精炭处理以及改性处理,其中改性处理效果最显著,既提高了比表面积,还可促进水中胶体或絮凝物的形成,从而增强吸附性能。
研究表明粗渣对气化废水中COD的去除率可达41.9%,对酚类物质的去除率可达71.2%[80]。将粗渣中的残余炭分离后,通过酸碱浸渍方法进行改性,浸出硅、铝和铁等氧化物,可以增大其比表面积,提高吸附能力;并且碱改性效果优于酸改性,其对气化废水中苯酚的吸附量可达7.236 mg/g[81]。
采用细渣直接处理低浓度含汞废水时,其对汞的吸附效果在1.96~2.27 mg/g,且吸附在细渣上的汞浸出非常缓慢[82]。当采用干煤粉气化细渣处理造纸污水时,有效降低了废水Zeta电位,有利于减缓膜污染并提高污染物去除率[83]。在处理洗煤废水时,细渣的吸附率最大可达到99.33%,效果优于聚丙烯酰胺、聚合氯化铝等常用水处理助剂[84]。
此外,还可利用细渣中的未燃炭或通过改性、活化等方法制备性能优异的吸附剂。细渣中的残炭经过气化炉高温作用后,表面性质发生改变,可以获得类似活性炭的吸附能力。胡俊阳等[85]对榆林气化细渣浮选分离得到比表面积为29.50 m2/g的精炭,对模拟染色废水中甲基橙的去除率达到97.90%。
如表6所示,目前国内外采用细渣制备吸附材料的类型大致分为活性炭、沸石、复合材料等,获得了更大的比表面积与吸附能力,其中采用细渣浮选精炭可制得比表面积高达
1226.08 m2/g的活性炭。此外,以细渣为原料制备吸附剂时,通过负载铈可以增强吸附能力,其对刚果红的去除率达到了95.87%[86]。表 6 不同煤气化渣制备吸附材料的性能对比Table 6. Performance comparison of different adsorbing materials prepared by coal gasification slag制备原料 吸附材料 制备方法 比表面积/
(m2∙g−1)吸附量 细渣浮选精炭 活性炭 KOH活化法[87] 1226.80 亚甲蓝、碘吸附量分别为278、 1292 mg/g包头细渣未燃炭 活性炭 KOH活化法[88] 2481.00 Pb2+吸附量141 mg/g 内蒙古水煤浆气化细渣 活性炭 炭化、活化法[89] 104.30 碘吸附量582.19 mg/g 宁东细渣 高结晶度单相A型沸石 固相碱熔变法[90] 61.09 — 内蒙古GE水煤浆气化细渣 X型沸石复合材料 水蒸气高温活化→盐酸溶解→置于
NaOH中加入导向剂[91]294.98 甲基蓝、Cr3+吸附量分别为93.88 mg/g、
0.766 mmol/g宁东GSP干煤粉气化细渣 P型沸石/碳复合材料 碱性条件原位转换法[92] 189.30 结晶紫吸附量625.0 mg/g 山西细渣 铁改性碳/沸石复合材料 酸碱浸溶合成法→硫酸铁改性[93] 348.30 NH4+、PO43−吸附量分别为7.44、6.94 mg/g 上海细渣 碳硅复合材料 硫酸铵改性[94] 474.00 Pb2+吸附量124 mg/g 陕西细渣 改性壳聚糖/煤气化渣复合材料 微波处理→酸浸出→壳聚糖改性[95] 343.06 甲基橙、Cr(VI)吸附量分别为
125.23、8.70 mg/g宁夏GSP干煤粉气化细渣 煤气化基氨氮吸附剂 水热合成法[96] 311.00 氨氮吸附量3.50 mg/g 宁夏细渣 CO2吸附剂 胺基团改性法[97] 541.00 CO2吸附量132.50 mg/g 同时,细渣酸浸处理后的浸出液亦可制备净水剂。胡文豪等[98]以鄂尔多斯气化细渣酸浸液为原料制备出Al2O3含量为10%~11%,盐基度为44%~50%的聚合氯化铝净水剂。刘硕[99]通过在宁夏细渣酸浸液中加入适量聚乙烯酰胺作为聚合剂,调节pH使Fe(OH)3、Al(OH)3不断聚合,从而制成聚合氯化铝/铁净水剂。
综上,鉴于细渣具有优良的比表面积和吸附容量,其制备吸附剂前驱体有着巨大的发展潜力。且以细渣制备吸附材料具有较强的可再生性,但制备工艺复杂、成本较高,实际工业应用价值有待评定。
3.3.3 陶瓷材料
传统陶瓷材料采用黏土、偏高岭土为制备原料,其化学成分主要为SiO2、Al2O3、CaO、Fe2O3等氧化物,相似的化学组成为煤气化渣制备陶瓷材料提供了可行性。表7为国内外煤气化渣制备陶瓷材料的研究进展,粗渣可直接制备陶瓷材料,掺入发泡剂或黏结剂后在高温下烧制,可制得抗压强度与孔隙率优良的陶瓷材料。
如图10所示,王守飞等[101]以安庆Shell干煤粉气化细渣与碳化硅为原料,在
1200 ℃下烧制出体积密度为0.77 g/cm3,抗压强度为3.4 MPa的泡沫陶瓷材料。此外,部分学者采用细渣合成了SiAlON材料,为煤气化渣在陶瓷领域的高效利用开辟了途径。TANG等[102]对陕西Texaco气化细渣碳热还原氮化后,采用两步净化法制得高浓度Ca-α-SiAlON复相粉体,转化率高达45%,并以其为原料烧结制备出Ca-α-Sialon-SiC复相陶瓷。YIN等[103]将Texaco气化细渣和炭黑混合物在1400 ℃下热合成Ca-α-Sialon-SiC粉末,进一步制得维氏硬度18.6 GPa的Ca-α-Sialon-SiC复相陶瓷。当下利用煤气化渣中的多种物质制备陶瓷材料已初见成效,性能指标达到了国家标准,且实现了煤气化渣的高值利用。但制备流程复杂、成本较高、生产周期较长等问题限制了其工业化应用。
3.3.4 其他高附加值材料制备
煤气化渣制备催化剂载体、橡塑填料等工业材料具有广阔的应用前景。细渣表面活化点位较多,热稳定性良好,对其进行表面修饰及改性后可作为催化剂载体或其他金属氧化物的载体。HAN等[104]对细渣浸渍处理得到负载钒的催化剂,研究表明浸渍1%钒时,细渣基催化剂具有最佳的脱硝活性,NO转化率可从60%提高到100%。此外,采用化学沉积法可将掺锑氧化锡(Sb-SnO2)负载在细渣的多孔微珠上,制成细渣多孔微珠复合导电粉[105],其体积电阻率达到2.60×103 Ω·cm。
细渣作为橡塑填料可以改善橡胶树脂的物化性质。细渣煅烧处理后得到细渣玻璃珠,可替代CaCO3作为填料融入聚丙烯(PP)中制备PP/CGFSGB材料,有助于提高材料的抗拉强度、热稳定性和结晶性能,并减少挥发性有机物[106],为制备除臭剂提供了可行性。此外,细渣可用于制备低密度聚乙烯/细渣复合材料、细渣硅铝质玻璃微珠、聚丙烯/细渣玻璃微珠、丁苯橡胶/细渣复合材料,并进一步替代5.5 μm重钙粉作为填料应用于聚乙烯、ABS树脂、聚丙烯、丁苯橡胶,有助于提高橡胶树脂的力学性能[107]。
综上,细渣作为催化剂载体、橡胶树脂填料等具有较高的应用潜力,但其制备工艺复杂,导致成本居高不下,因此大多处于实验室研究阶段,实现规模化利用仍需进一步探索。
4. 结语与展望
随着煤气化技术的逐步推广与发展,气流床煤气化渣堆存量日益增多,其产量巨大、孔隙结构发达以及富含SiO2、Al2O3、Fe2O3资源等优点构成了资源化利用的基础。目前,煤气化渣资源化工艺尚不完善,相关探索多处于实验室阶段,导致其资源化利用占比极低。
1)由于气化粗渣与细渣物化性质不同,尤其是残炭量的显著差异,分类分级利用才能充分发挥煤气化渣的最大价值。
2)气化粗渣残炭量较少,在矿井回填、路基填筑、水泥与混凝土骨料、墙体材料等中低值利用领域应用广泛,因此高效应对重金属浸出风险并提高材料性能是其发展重点。
3)目前气化细渣可燃体回收存在重选精度低、浮选药剂用量大、处理成本高等问题,因此进行高效分离设备、新型浮选药剂、浮选工艺的探索和其他分选方法的研究至关重要,有利于综合各种分选方法的优点,实现高效低耗的分选路线。
4)此外,细渣的多孔特性提高了其在制备吸附材料、橡塑填料、催化剂载体等方面的应用潜力,但相关研究仍处于实验室阶段,工艺复杂且成本较高。探索大规模消纳与高值化利用相结合的途径,实现煤气化渣的“减量化、资源化、无害化”处理,仍是研究者要坚持的发展方向。
-
粒度级/mm +1.0 1.0~0.8 0.8~0.50 0.5~0.25 0.25~0.125 0.125~0.074 −0.074 粗渣质量分数/% 宁煤Texaco 69.06 10.67 5.23 2.58 2.46 2.46 2.46 宁煤GSP 9.45 17.37 23.44 19.6 20.77 5.33 4.04 陕西水煤浆 49.10 49.10 49.10 24.46 13.17 7.03 6.25 细渣质量分数/% 宁煤Texaco 18.75 18.75 18.75 23.87 28.85 4.47 14.06 宁煤GSP 13.59 13.59 13.59 11.97 40.07 24.87 9.50 陕西水煤浆 3.46 3.46 3.46 18.29 20.99 13.62 43.65 榆林气流床 1.03 1.03 1.03 14.27 32.36 9.25 43.09 表 2 我国不同地区和不同炉型气化粗渣和细渣主要化学组成
Table 2 Main chemical composition of gasification coarse slag and fine slag in different regions and different furnace types in China
样品 化学组成质量分数/% SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 CaO MgO K2O Na2O TiO2 SO3 陕西Texaco粗渣[23] 41.12 12.72 — 12.88 1.23 1.94 1.49 0.61 — 陕西Texaco细渣[23] 32.20 8.87 — 4.33 0.69 1.23 0.54 0.52 — 陕西多喷嘴对置式水煤浆气化粗渣[13] 41.44 13.91 17.37 17.37 2.26 1.46 1.40 0.65 1.38 陕西多喷嘴对置式水煤浆气化细渣[13] 35.93 15.48 18.13 17.19 2.11 1.39 2.31 0.88 3.25 安庆粉煤Shell气化粗渣[24] 46.90 20.38 7.66 8.57 1.02 2.03 1.65 1.01 2.12 安庆粉煤Shell气化细渣[24] 37.50 21.63 15.73 17.70 1.18 0.55 0.53 1.29 3.27 鄂尔多斯水煤浆气化粗渣[25] 55.30 19.14 9.79 8.65 1.14 2.44 1.45 1.16 0.66 鄂尔多斯水煤浆气化细渣[25] 54.40 21.93 8.36 6.70 1.09 2.70 1.86 1.28 1.23 Texaco气化粗渣[26] 42.90 13.27 5.20 13.44 1.28 2.02 1.55 0.64 — Texaco气化细渣[26] 37.02 10.20 2.86 4.98 0.79 1.41 0.62 0.60 — 宁煤粗渣[10] 48.82 19.33 10.34 10.64 2.90 2.42 1.31 1.03 2.39 宁煤细渣[10] 51.95 18.33 8.89 9.09 4.10 3.10 1.61 1.11 0.77 神木化工粗渣[27] 41.12 12.72 — 12.88 1.23 1.94 1.49 — — 神木化工细渣[27] 32.20 8.87 — 4.33 0.69 1.23 0.54 — — 神华集团粗渣[28] 50.59 18.44 12.06 8.77 3.27 2.13 1.20 1.18 — 神华集团细渣[28] 41.78 37.40 7.54 6.85 0.76 1.34 0.65 2.19 — 表 3 不同气化细渣复配捕收剂
Table 3 Different compound collectors for gasification fine slag
表 4 不同气化细渣浮选工艺
Table 4 Different flotation process for gasification fine slag
表 5 不同煤气化渣制砖的性能对比
Table 5 Performance comparison of different bricks prepared by coal gasification slag
表 6 不同煤气化渣制备吸附材料的性能对比
Table 6 Performance comparison of different adsorbing materials prepared by coal gasification slag
制备原料 吸附材料 制备方法 比表面积/
(m2∙g−1)吸附量 细渣浮选精炭 活性炭 KOH活化法[87] 1226.80 亚甲蓝、碘吸附量分别为278、 1292 mg/g包头细渣未燃炭 活性炭 KOH活化法[88] 2481.00 Pb2+吸附量141 mg/g 内蒙古水煤浆气化细渣 活性炭 炭化、活化法[89] 104.30 碘吸附量582.19 mg/g 宁东细渣 高结晶度单相A型沸石 固相碱熔变法[90] 61.09 — 内蒙古GE水煤浆气化细渣 X型沸石复合材料 水蒸气高温活化→盐酸溶解→置于
NaOH中加入导向剂[91]294.98 甲基蓝、Cr3+吸附量分别为93.88 mg/g、
0.766 mmol/g宁东GSP干煤粉气化细渣 P型沸石/碳复合材料 碱性条件原位转换法[92] 189.30 结晶紫吸附量625.0 mg/g 山西细渣 铁改性碳/沸石复合材料 酸碱浸溶合成法→硫酸铁改性[93] 348.30 NH4+、PO43−吸附量分别为7.44、6.94 mg/g 上海细渣 碳硅复合材料 硫酸铵改性[94] 474.00 Pb2+吸附量124 mg/g 陕西细渣 改性壳聚糖/煤气化渣复合材料 微波处理→酸浸出→壳聚糖改性[95] 343.06 甲基橙、Cr(VI)吸附量分别为
125.23、8.70 mg/g宁夏GSP干煤粉气化细渣 煤气化基氨氮吸附剂 水热合成法[96] 311.00 氨氮吸附量3.50 mg/g 宁夏细渣 CO2吸附剂 胺基团改性法[97] 541.00 CO2吸附量132.50 mg/g -
[1] 朱菊芬,李健,闫龙,等. 煤气化渣资源化利用研究进展及应用展望[J]. 洁净煤技术,2021,27(6):11−21. ZHU Jufen,LI Jian,YAN Long,et al. Research progress and application prospect of coal gasification slag resource utilization[J]. Clean Coal Technology,2021,27(6):11−21.
[2] 王辅臣. 煤气化技术在中国:回顾与展望[J]. 洁净煤技术,2021,27(1):1−33. WANG Fuchen. Coal gasification technologies in China:review and prospect[J]. Clean Coal Technology,2021,27(1):1−33.
[3] 袁蝴蝶. 煤气化炉渣本征特征及应用基础研究[D]. 西安:西安建筑科技大学,2020:1-14. YUAN Hudie. Intrinsic characteristics of coal gasification slag and its fundamental research for applications[D]. Xi’an:Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology,2020:1-14.
[4] 宁永安,段一航,高宁博,等. 煤气化渣组分回收与利用技术研究进展[J]. 洁净煤技术,2020,26(S1):14−19. NING Yongan,DUAN Yihang,GAO Ningbo,et al. Progress of component recycling and utilization technology of coal gasification slag[J]. Clean Coal Technology,2020,26(S1):14−19.
[5] 刘开平,赵红艳,李祖仲,等. 煤气化渣对水泥混凝土性能的影响[J]. 建筑科学与工程学报,2017,34(5):190−195. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2049.2017.05.021 LIU Kaiping,ZHAO Hongyan,LI Zuzhong,et al. Influence of coal gasification slag on cement concrete performance[J]. Journal of Architecture and Civil Engineering,2017,34(5):190−195. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2049.2017.05.021
[6] YUAN N,ZHAO A,HU Z,et al. Preparation and application of porous materials from coal gasification slag for wastewater treatment:a review[J]. Chemosphere,2022,287:132227. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132227
[7] 冯向港,葛奋飞,张印民,等. 煤气化渣高值化利用的研究进展及应用展望[J]. 洁净煤技术,2023,29(11):122−132. FENG Xianggang,GE Fengfei,ZHANG Yinmin,et al. Research progress and application prospect of high-value utilization of coal gasification slag [J]. Clean Coal Technology,2023,29(11):122−132.
[8] 张瑞梅,刘定桦,何浩,等. 煤气化细渣综合利用与碳灰分离技术现状[J]. 煤炭工程,2023,55(5):175−182. ZHANG Ruimei,LIU Dinghua,HE Hao. Study on residue features and decarbonization of Texaco entrained flow gasifier[J]. Coal Engineering,2023,55(5):175−182.
[9] 王亚丰. 煤气化产物的矿物学和环境地球化学研究[D]. 北京:中国矿业大学(北京),2021:31−40. WANG Yafeng. Study on mineralogy and environmental geochemistry of coal gasification products[D]. Beijing:China University of Mining and Technology-Beijing,2021:31−40.
[10] 李俏,董阳,JINDER JOW,等. 煤气化渣的基本性能及其应用途径分析[J]. 新型建筑材料,2023,50(3):33−36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-702X.2023.03.008 LI Qiao,DONG Yang,JINDER JOW,et al. Fundamental characteristics and application of coal gasification slags[J]. New Building Materials,2023,50(3):33−36 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-702X.2023.03.008
[11] 高旭霞,郭晓镭,龚欣. 气流床煤气化渣的特征[J]. 华东理工大学学报(自然科学版),2009,35(5):677−683. GAO Xuxia,GUO Xiaolei,GONG Xin. Characterization of slag from entrained-flow coal gasification[J]. Journal of East China University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition),2009,35(5):677−683.
[12] 雷彤. 掺煤气化粗渣水泥稳定基层材料组成及路用性能研究[D]. 西安:长安大学,2017:17-18. LEI Tong. Study on composition and pavement performance of cement stabilized base material for coal gasification coarse slag[D]. Xi’an:Chang’an University,2017:17-18.
[13] 宋瑞领,李静,付亮亮,等. 多喷嘴对置式水煤浆气化炉炉渣特性研究[J]. 洁净煤技术,2018,24(5):43−49. SONG Ruiling,LI Jing,FU Liangliang,et al. Characteristics of slags generated from multi-nozzle opposed coal-water slurry gasifier[J]. Clean Coal Technology,2018,24(5):43−49.
[14] 袁傲,杨靖,张庆,等. 煤气化细渣资源化利用途径及发展趋势[J]. 应用化工,2022,51(3):891−896. YUAN Ao,YANG Jing,ZHANG Qing,et al. Ways and development trends of resource utilization of coal gasification fine slag[J]. Applied Chemical Industry,2022,51(3):891−896.
[15] 范宁,张逸群,樊盼盼,等. 煤气化渣特性分析及资源化利用研究进展[J]. 洁净煤技术,2022,28(8):145−154. FAN Ning,ZHANG Yiqun,FAN Panpan,et al. Research progress on characteristic analysis and resource utilization of coal gasification slag[J]. Clean Coal Technology,2022,28(8):145−154.
[16] 吴阳. 煤气化灰渣的分选加工利用研究[D]. 西安:西安科技大学,2017:50−62. WU Yang. Study on the separation and utilization of gasified residues[D]. Xi’an:Xi’an University of Science and Technology,2017:50−62.
[17] HUO W,ZHOU Z,WANG F,et al. Experimental study of pore diffusion effect on char gasification with CO2 and steam[J]. Fuel,2014,131:59−65. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2014.04.058
[18] 石旭,初茉,董建飞,等. 气流床气化细渣中碳−灰的结合形态及其解离特性[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2023,52(3):576−584. SHI Xu,CHU Mo,DONG Jianfei,et al. Combined morphology and dissociation characteristics of carbon-ash in fine slag of entrained flow gasification[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology,2023,52(3):576−584.
[19] PAN C,LIANG Q,GUO X,et al. Characteristics of different sized slag particles from entrained-flow coal gasification[J]. Energy & Fuels,2016,30(2):1487−1495.
[20] GUO Y,MA C,ZHANG Y,et al. Comparative study on the structure characteristics,combustion reactivity,and potential environmental impacts of coal gasification fine slag with different particle size fractions[J]. Fuel,2022,311:122493. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2021.122493
[21] VAN DYK J C,MELZER S,SOBIECKI A. Mineral matter transformation during Sasol-Lurgi fixed bed dry bottom gasification-utilization of HT-XRD and Fact Sage modelling[J]. Minerals Engineering,2006,19(10):1126−1135. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2006.03.008
[22] 须藤俊男. 黏土矿物学[M]. 北京:地质出版社,1981. [23] 尹洪峰,汤云,任耘,等. Texaco气化炉炉渣基本特性与应用研究[J]. 煤炭转化,2009,32(4):30−33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4248.2009.04.008 YIN Hongfeng,TANG Yun,REN Yun,et al. Study on the characteristic and application of gasification slag from Texaco gasifier[J]. Coal Conversion,2009,32(4):30−33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4248.2009.04.008
[24] 王守飞. 粉煤气化灰渣制备泡沫陶瓷保温建筑材料[D]. 淮南:安徽理工大学,2019:17−53. WANG Shoufei. Foamed ceramic insulation building materials were prepared from gasification ash and slag[D]. Huainan:Anhui University of Science and Technology,2019:17−53.
[25] 张婷,于露,李宇,等. 水煤浆气化炉渣的特性分析及应用探讨[J]. 当代化工研究,2020(19):88−90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8114.2020.19.039 ZHANG Ting,YU Lu,LI Yu,et al. Characteristic analysis and application discussion of coal water slurry gasifier slag[J]. Modern Chemical Research,2020(19):88−90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8114.2020.19.039
[26] 冯银平,尹洪峰,袁蝴蝶,等. 利用气化炉渣制备轻质隔热墙体材料的研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报,2014,33(3):497−501. FENG Yinping,YIN Hongfeng,YUAN Hudie,et al. Study on the preparation of lightweight heat - insulation wall materials using gasification slag[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2014,33(3):497−501.
[27] 云正,于鹏超,尹洪峰. 气化炉渣对铁尾矿烧结墙体材料性能的影响[J]. 金属矿山,2010(11):183−186. YUN Zheng,YU Pengchao,YIN Hongfeng. Effect of gasification slag on the properties of sintered wall materials with iron ore tailings[J]. Metal Mine,2010(11):183−186.
[28] 吴海骏. 固体废弃物为原料制备无机多孔材料(膜)及其性能研究[D]. 合肥:合肥工业大学,2015:38−50. WU Haijun. The preparation and characterization of inorganic porous material (membrane) from solid waste [D]. Hefei:Hefei University of Technology,2015:38−50.
[29] 汤云,袁蝴蝶,尹洪峰,等. 几种典型煤气化炉渣的碳热还原氮化过程[J]. 煤炭学报,2016,41(12):3136−3141. TANG Yun,YUAN Hudie,YIN Hongfeng,et al. Carbothermal reduction nitridation process of several typical coal gasification slag[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2016,41(12):3136−3141.
[30] LI Z,ZHANG Y,ZHAO H,et al. Structure characteristics and composition of hydration products of coal gasification slag mixed cement and lime[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2019,213:265−274. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.03.163
[31] 景娟,李兆锋. 航天炉粉煤加压技术气化粗渣的研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报,2018,37(8):2601−2605. JING Juan,LI Zhaofeng. Study on the coarse slag from Hangtian pulverized coal pressure gasification technology (HT-L)[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2018,37(8):2601−2605.
[32] 章新喜,章明玥,段超红. 气化炉灰渣中碳的回收方法[P]. 中国:CN101870896B,2015−04−01. [33] 高增林,张乾,高晨明等. 水煤浆煤气化粗渣水流分级提炭分质[J]. 化工进展, 2024, 43(3): 1576-1583. GAO Zenglin, ZHANG Qian, GAO Chenming, et al. Extraction and separation of carbon from coal water slurry gasification coarse slag by waterflow classifier[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2024, 43(3): 1576-1583.
[34] 史磊,邱国华,李楠,等. 循环流化床锅炉处理煤气化炉渣的综合利用模式探索[J]. 中国资源综合利用,2021,39(6):77−79,82. SHI Lei,QIU Guohua,LI Nan,et al. Exploration on the comprehensive utilization mode of coal gasification slag treated by circulating fluidized bed boiler[J]. China Resources Comprehensive Utilization,2021,39(6):77−79,82.
[35] DAI G,ZHENG S,WANG X,et al. Combustibility analysis of high-carbon fine slags from an entrained flow gasifier[J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2020,271:111009. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111009
[36] 晁岳建,王洪记. 循环流化床锅炉掺烧气化渣和煤泥的可行性研究[J]. 化肥工业,2015,42(3):48−50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7779.2015.03.015 CHAO Yuejian,WANG Hongji. Feasibility study of circulating fluidized bed boiler blending burning gasification slag and coal slime[J]. Fertilizer Industry,2015,42(3):48−50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7779.2015.03.015
[37] 李慧泽,董连平,鲍卫仁,等. 基于视密度的煤气化渣水介质旋流炭−灰分离[J]. 化工进展,2021,40(3):1344−1353. LI Huize,DONG Lianping,BAO Weiren,et al. Carbon-ash separation of coal gasification slag in swirling water based on apparent density[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2021,40(3):1344−1353.
[38] 任振玚,井云环,樊盼盼,等. 气化渣水介重选及其分离炭制备脱硫脱硝活性焦试验研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(4):1164−1172. REN Zhenyang,JING Yunhuan,FAN Panpan,et al. Experimental study on the water-medium gravity separation of gasification slag and the preparation of desulfurization and denitrification activated coke using separated carbon[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2021,46(4):1164−1172.
[39] 杨进进,樊盼盼,樊晓婷,等. 煤气化细渣碳灰分离技术研究进展[J]. 洁净煤技术,2023,29(7):51−64. YANG Jinjin,FAN Panpan,FAN Xiaoting,et al. Research progress of carbon ash separation technology on coal gasification fine slag[J]. Clean Coal Technology,2023,29(7):51−64.
[40] 程延化. 月桂酸对煤气化细渣浮选的促进作用研究[J]. 现代矿业,2022,38(7):162−167. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2022.07.040 CHENG Yanhua. Study on the promotion effect of lauric acid on flotation of coal gasification fine slag[J]. Modern Mining,2022,38(7):162−167. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2022.07.040
[41] 张海军,王海楠,李文峰,等. 一种气化渣浮选捕收剂及其制备方法[P]. 中国:CN113351376B,2023−03−31. [42] SHI D,ZHANG J,HOU X,et al. Adsorption mechanism of a new combined collector (PS-1) on unburned carbon in gasification slag[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2021(8):151856.
[43] 王晓波,符剑刚,赵迪,等. 煤气化细渣载体浮选提质研究[J]. 煤炭工程,2021,53(1):155−159. WANG Xiaobo,FU Jiangang,ZHAO Di,et al. Flotation and quality improvement of gasified fine slag carrier[J]. Coal Engineering,2021,53(1):155−159.
[44] 于伟,王学斌,白永辉,等. 煤气化细渣浮选脱碳试验研究[J]. 洁净煤技术,2021,27(3):81−87. YU Wei,WANG Xuebin,BAI Yonghui,et al. Experimental study on decarbonization of coal gasification fine slag by flotation[J]. Clean Coal Technology,2021,27(3):81−87.
[45] GUO F,ZHAO X,GUO Y,et al. Fractal analysis and pore structure of gasification fine slag and its flotation residual carbon[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2020,585:124148.
[46] 张晓峰,王玉飞,范晓勇,等. 煤气化细渣浮选脱碳分析[J]. 能源化工,2016,37(5):54−57. ZHANG Xiaofeng,WANG Yufei,FAN Xiaoyong,et al. Analysis on decarbonization of coal gasification fine slag flotation[J]. Energy and Chemical Industry,2016,37(5):54−57.
[47] 史达,张建波,杨晨年,等. 煤气化灰渣脱碳技术研究进展[J]. 洁净煤技术,2020,26(6):1−10. SHI Da,ZHANG Jianbo,YANG Chennian,et al. Research progress of the decarburization technology of coal gasification ash slag[J]. Clean Coal Technology,2020,26(6):1−10.
[48] 黄海珊. 机械活化强化气化细渣炭灰分离机制及精炭吸附性能研究[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2022:34−64. HUANG Haishan. Research on enhancing mechanism of mechanical activation on the carbon-ash separation of gasification fine slag and adsorption properties of fine carbon[D]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology,2022:34−64.
[49] WANG W,LIU D,TU Y,et al. Enrichment of residual carbon in entrained-flow gasification coal fine slag by ultrasonic flotation[J]. Fuel,2020,278:118195. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.118195
[50] 赵世永,吴阳,李博. Texaco气化炉灰渣理化特性与脱碳研究[J]. 煤炭工程,2016,48(9):29−32. ZHAO Shiyong,WU Yang,LI Bo. Study on residue features and decarbonization of Texaco entrained flow gasifier[J]. Coal Engineering,2016,48(9):29−32.
[51] ZHANG R,GUO F,XIA Y,et al. Recovering unburned carbon from gasification fly ash using saline water[J]. Waste Management,2019,98:29−36. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2019.08.014
[52] 刘娟红,许鹏玉,周昱程,等. 改性煤气化渣用于矿山充填的试验研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报,2020,39(8):2528−2535. LIU Juanhong,XU Pengyu,ZHOU Yucheng,et al. Experimental study on modified coal gasification slag Used for Mine Filling[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2020,39(8):2528−2535.
[53] 屈慧升,索永录,刘浪,等. 改性煤气化渣基矿用充填材料制备与性能[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(5):1958−1973. QU Huisheng,SUO Yonglu,LIU Lang,et al. Preparation and properties of modified coal gasification slag-based filling materials for mines[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2022,47(5):1958−1973.
[54] 徐阳,徐再刚,谢红飞,等. 煤气化渣高水充填材料的制备及其性能研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2020,51(9):41−46. XU Yang,XU Zaigang,XIE Hongfei,et al. Preparation and properties of high water filling material from coal gasification slag[J]. Safety in Coal Mines,2020,51(9):41−46,51.
[55] 武立波,宋牧原,谢鑫,等. 中国煤气化渣建筑材料资源化利用现状综述[J]. 科学技术与工程,2021,21(16):6565−6574. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.16.004 WU Libo,SONG Muyuan,XIE Xin,et al. A review on resource utilization of coal gasification slag as building materials in China[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2021,21(16):6565−6574. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.16.004
[56] 郭照恒,杨文,祝小靓,等. 不同比表面积煤气化渣掺合料活性及力学性能研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报,2020,39(11):3567−3573,3588. GUO Zhaoheng,YANG Wen,ZHU Xiaoliang,et al. Activity and mechanical properties of coal gasification slag admixture with different specific surface area[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2020,39(11):3567−3573.
[57] 李冠杰,郝广成,雒锋. 煤气化渣对环氧树脂砂浆道路修补材料性能的影响[J]. 粉煤灰综合利用,2019(3):13−17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8249.2019.03.004 LI Guanjie,HAO Guangcheng,LUO Feng. Effect of coal gasification ash on the properties of road repair materials of epoxy resin mortar[J]. Fly Ash Comprehensive Utilization,2019(3):13−17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8249.2019.03.004
[58] 申改燕,李金洲,王敬. 关于煤化工气化炉渣资源化利用技术的探讨[J]. 能源与节能,2020(7):58−59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0802.2020.07.024 SHEN Gaiyan,LI Jinzhou,WANG Jing. Discussion on Resource Utilization Technology of Coal Chemical Gasification Slag[J]. Energy and Energy Conservation,2020(7):58−59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0802.2020.07.024
[59] 傅博,马梦凡,申旺,等. 气化渣对硅酸盐水泥强度和微观结构的影响研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报,2020,39(8):2523−2527. FU Bo,MA Mengfan,SHEN Wang,et al. Influence of coal gasification slag on strength and microstructure of Portland cement[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2020,39(8):2523−2527.
[60] LUO F,JIANG Y,WEI C. Potential of decarbonized coal gasification residues as the mineral admixture of cement-based material[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2021,269:121259. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.121259
[61] 刘艳丽,李强,陈占飞,等. 煤气化渣特性分析及综合利用研究进展[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(11):251-257. LIU Yanli,LI Qiang,CHEN Zhanfei,et al. Research progress characteristics analysis and comprehensive utilization of coal gasification slag[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2022,50(11):251-257.
[62] 谢紫珺. 底泥陶粒制备及生态毯水处理效果研究[D]. 宜昌:三峡大学,2022:26−45. XIE Zijun. Research on preparation of sediment ceramsite and water treatment effect of ecological blanket[D]. Yichang:China Three Gorges University,2022:26−45.
[63] 张凯,刘舒豪,张日新,等. 免烧法煤气化粗渣制备陶粒工艺及其性能研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2018,46(10):222−227. ZHANG Kai,LIU Shuhao,ZHANG Rixin,et al. Research on preparation of non-sintered ceramsite from gasification cinder and its performance[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2018,46(10):222−227.
[64] ZHAO S,YAO L,HE H,et al. Preparation and environmental toxicity of non-sintered ceramsite using coal gasification coarse slag[J]. Archives of Environmental Protection,2019,45(2):84−90.
[65] CHEN L,CHOU M M,CHOU S J,et al. Producing fired bricks using coal slag from a gasification plant in Indian[C]//World of Coal Ash (WOCA) Conference,Lexington,2009.
[66] 何桂玉,包宗义. 采用煤气化废渣制造的免烧砖及其制造方法[P]. 中国:CN111662054A,2020−09−15. [67] ACOSTA A,IGLESIAS I,AINETO M,et al. Utilisation of IGCC slag and clay steriles in soft mud bricks (by pressing) for use in building bricks manufacturing[J]. Waste Management,2002,22(8):887−891. doi: 10.1016/S0956-053X(02)00075-2
[68] 章丽萍,温晓东,马圣存,等. 煤间接液化残渣制备免烧砖研究[J]. 煤炭工程,2015,44(2):354−358. ZHANG Liping,WEN Xiaodong,MA Shengcun,et al. Research on making non - burnt brick from indirect coal liquefaction residues[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology,2015,44(2):354−358.
[69] 张成,裴超. 煤气化渣生产蒸压砖的技术研究[J]. 砖瓦世界,2019(10):49−52. ZHANG Cheng,PEI Chao. Technological research on production of autoclaved bricks from coal gasification slag[J]. Brick & Tile World,2019(10):49−52.
[70] 牛国峰. 煤气化渣制备烧结墙体材料工艺及烧结机理研究[D]. 包头:内蒙古科技大学,2021:19−47. NIU Guofeng. Study on the process and burning mechanism of coal gasification slag for preparing sintered wall materials[D]. Baotou:Inner Mongolia University of Science and Technology,2021:19−47.
[71] 魏召召. 一种掺有煤气化渣的有机肥及其制备方法[P]. 中国:CN105777427A,2016−07−20. [72] ZHU D,XUE B,JIANG Y,et al. Using chemical experiments and plant uptake to prove the feasibility and stability of coal gasification fine slag as silicon fertilizer[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2019,26(6):5925−5933. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-4013-8
[73] ZHU D,MIAO S,XUE B,et al. Effect of coal gasification fine slag on the physicochemical properties of soil[J]. Water,Air,& Soil Pollution,2019,230(7):1−11.
[74] ZHU D,ZUO J,JIANG Y,et al. Carbon-silica mesoporous composite in situ prepared from coal gasification fine slag by acid leaching method and its application in nitrate removing[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2020,707:136102. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136102
[75] 路春亚. 煤气化渣对农业废弃物堆肥过程中抗生素抗性基因的影响[D]. 咸阳:西北农林科技大学,2019:18−32. LU Chunya. Effects of coal gasification slag on antibiotic resistance genes during agricultural waste composting[D]. Xianyang:Northwest A&F University,2019:18−32.
[76] LIU T,AWASTHI M K,AWASTHI S K,et al. Influence of fine coal gasification slag on greenhouse gases emission and volatile fatty acids during pig manure composting[J]. Bioresource Technology,2020,316:123915. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123915
[77] 李强,孙利鹏,亢福仁,等. 煤气化渣−沙土复配对毛乌素沙地苜蓿生长及重金属迁移的影响[C]// 中国环境科学学会2019年科学技术年会, 西安,2019. LI Qiang,SUN Lipeng,KANG Furen,et al. Effects of coal gasification slag and sand compound soil on alfalfa growth and heavy metal migration in mu us sandy land[C]// 2019 CSES Annual Conference on Environmental Science and Technolog,Xi’an,2019.
[78] 刘娜,李强,孙利鹏,等. 增施养分对复配气化渣−沙土的激发效应研究[J]. 榆林学院学报,2021,31(2):28−31. LIU Na,LI Qiang,SUN Lipeng,et al. Study on the Excitation effect of adding nutrient on gasified slag-sand soil[J]. Journal of Yulin University,2021,31(2):28−31.
[79] 相微微,李夏隆,严加坤,等. 榆林煤气化渣重金属生物有效性评价[J]. 农业环境科学学报,2021,40(5):1097−1105. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-1326 XIANG Weiwei,LI Xialong,YAN Jiakun,et al. Bioavailability evaluation of heavy metals in Yulin coal gasification slag[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2021,40(5):1097−1105. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-1326
[80] 普煜,马永成,陈樑,等. 鲁奇炉渣在废水净化中的应用研究[J]. 工业水处理,2007,27(5):59−62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-829X.2007.05.018 PU Yu,MA Yongcheng,CHEN Liang,et al. Application of Lurgi slag to wastewater purification[J]. Industrial Water Treatment,2007,27(5):59−62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-829X.2007.05.018
[81] 刘转年,全海山,舒瑞,等. 煤气发生炉炉渣改性和吸附性能[J]. 环境工程学报,2013,7(3):1139−1144. LIU Zhuannian,QUAN Haishan,SHU Rui,et al. Modification and adsorption property of gas furnace slag[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering,2013,7(3):1139−1144.
[82] DUAN L,HU X,SUN D,et al. Rapid removal of low concentrations of mercury from wastewater using coal gasification slag[J]. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering,2020,37(7):1166−1173. doi: 10.1007/s11814-020-0546-x
[83] 凌琪,李尚尚,伍昌年,等. 投加气化渣对DMBR处理造纸废水污泥性能及膜污染的影响[J]. 阜阳师范学院学报(自然科学版),2018,35(2):15−20. LING Qi,LI Shangshang,WU Changnian,et al. Effect of dosing gasification slag on sludge performance and membrane fouling of papermaking wastewater from DMBR treatment[J]. Journal of Fuyang Normal University (Natural Science),2018,35(2):15−20.
[84] 董茹,陈碧. 气化炉渣吸附剂的制备及其处理洗煤废水效果的研究[J]. 当代化工,2019,48(6):1149−1153. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0460.2019.06.009 DONG Ru,CHEN Bi. Preparation of waste slag based adsorbent and its application effect in coal washing wastewater treatment[J]. Contemporary Chemical Industry,2019,48(6):1149−1153. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0460.2019.06.009
[85] 胡俊阳,黄阳,王维清,等. 煤气化炉渣浮选精炭在染色废水中的应用[J]. 环境工程,2018,36(3):59−63. HU Junyang,HUANG Yang,WANG Weiqing,et al. Applied of concentrate carbon from coal gasification slag by flotation on dyeing wastewater[J]. Environmental Engineering,2018,36(3):59−63.
[86] DENG X. Study on adsorption performance of ce-loaded coal gasification slag to congo red[J]. Academic Journal of Engineering and Technology Science,2019,2(5).
[87] 刘冬雪,胡俊阳,冯启明,等. 煤气化炉渣浮选及其精炭制备活性炭的研究[J]. 煤炭转化,2018,41(5):73−80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4248.2018.05.012 LIU Dongxue,HU Junyang,FENG Qiming,et al. Study on flotation of coal gasification slag and preparation of activated carbon from carbon concentrate[J]. Coal Conversion,2018,41(5):73−80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4248.2018.05.012
[88] XU Y,CHAI X. Characterization of coal gasification slag-based activated carbon and its potential application in lead removal[J]. Environmental Technology,2018,39(3):382−391. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2017.1301569
[89] 朱仁帅,吕飞勇,汤茜,等. 利用水煤浆气化炉飞灰合成吸附材料的研究[J]. 粉煤灰综合利用,2017(3):12−15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8249.2017.03.003 ZHU Renshuai,LYU Feiyong,TANG Qian,et al. Study on synthesis of adsorbent from fly ash of coal-water slurry gasifier[J]. Fly Ash Comprehensive Utilization,2017(3):12−15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8249.2017.03.003
[90] JI W,FENG N,ZHAO P,et al. Synthesis of single-phase zeolite a by coal gasification fine slag from Ningdong and its application as a high-efficiency adsorbent for Cu2+ and Pb2+ in simulated waste water[J]. ChemEngineering,2020,4(4):65. doi: 10.3390/chemengineering4040065
[91] 姚阳阳. 煤气化粗渣制备活性炭/沸石复合吸附材料及其性能研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学,2018:33−41. YAO Yangyang. Preparation and performance of activated carbon/zeolite composite adsorptive materials from coal gasification coarse slag[D]. Changchun:Jilin University,2018:33−41.
[92] WU Y,XUE K,MA Q,et al. Removal of hazardous crystal violet dye by low-cost P-type zeolite/carbon composite obtained from in situ conversion of coal gasification fine slag[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials,2021,312:110742. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2020.110742
[93] MA X,LI Y,XU D,et al. Simultaneous adsorption of ammonia and phosphate using ferric sulfate modified carbon/zeolite composite from coal gasification slag[J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2022,305:114404. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.114404
[94] 顾彧彦,乔秀臣. 煤气化细渣制备碳硅复合材料吸附去除水中Pb2+[J]. 化工环保,2019,39(1):87−93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1878.2019.01.017 GU Yuyan,QIAO Xiuchen. Adsorption of Pb2+ from water by carbon-silica composite prepared from coal gasification fine slag[J]. Environmental Protection of Chemical Industry,2019,39(1):87−93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1878.2019.01.017
[95] 何玟玟. 改性壳聚糖/煤气化渣复合材料的制备及其吸附性能研究[D]. 西安:西安科技大学,2021:16−40. HE Wenwen. Preparation of modified chitosan/coal gasification slag composite materials and study on adsorption performance [D]. Xi’an:Xi’an University of Science and Technology,2021:16−40.
[96] 马超,王兵,樊盼盼,等. 煤气化渣基氨氮吸附剂的制备及吸附性能研究[J]. 洁净煤技术,2021,27(3):109−115. MA Chao,WANG Bing,FAN Panpan,et al. Research on preparation and adsorption properties of ammonia nitrogen sorbent based on coal gasification slag[J]. Clean Coal Technology,2021,27(3):109−115.
[97] ZHANG J,ZUO J,AI W,et al. Preparation of mesoporous coal-gasification fine slag adsorbent via amine modification and applications in CO2 capture[J]. Applied Surface Science,2021,537:147938. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.147938
[98] 胡文豪,张建波,李少鹏,等. 煤气化渣制备聚合氯化铝工艺研究[J]. 洁净煤技术,2019,25(1):154−159. HU Wenhao,ZHANG Jianbo,LI Shaopeng,et al. Study on the preparation of polyaluminium chloride from coal gasification residue[J]. Clean Coal Technology,2019,25(1):154−159.
[99] 刘硕. 煤气化细渣制备介孔材料及净水剂研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学,2019:65−68. LIU Shuo. Study on Preparation of Mesoporous Materials and Water Purifying Agent from Coal Gasification Fine Slag[D]. Changchun:Jilin University,2019:65−68.
[100] 赵永彬,吴海骏,张学斌,等. 煤气化残渣基多孔陶瓷的制备研究[J]. 洁净煤技术,2016,22(5):7−11. ZHAO Yongbin,WU Haijun,ZHANG Xuebin,et al. Fabrication of porous ceramic from coal gasification residual[J]. Clean Coal Technology,2016,22(5):7−11.
[101] 王守飞,李寒旭,何军. 正交试验法筛选煤气化灰渣制备泡沫陶瓷工艺条件[J]. 山东化工,2019,48(7):32−34. WANG Shoufei,LI Hanxu,HE Jun. The Technological conditions of preparing foamed ceramics from coal gasification ash and slag were screened by orthogonal test[J]. Shandong Chemical Industry,2019,48(7):32−34.
[102] TANG Y,YIN H,YUAN H,et al. Phase and morphological transformation stages during carbothermal reduction nitridation process:from coal gasification slag wastes to Ca-α-SiAlON powders[J]. Advanced Powder Technology,2016,27(5):2232−2237. doi: 10.1016/j.apt.2016.08.008
[103] YIN H F, TANG Y. Preparation of Ca-α-Sialon-SiC multiphase ceramics from gasification slag[C]//Materials Science Forum. Trans Tech Publications Ltd, 2011, 695: 328-331.
[104] HAN F,GAO Y,HUO Q,et al. Characteristics of vanadium-based coal gasification slag and the NH3-selective catalytic reduction of NO[J]. Catalysts,2018,8(8):327. doi: 10.3390/catal8080327
[105] ZHANG J,ZUO J,JIANG Y,et al. Synthesis and characterization of composite conductive powders prepared by Sb-SnO2-coated coal gasification fine slag porous microbeads[J]. Powder Technology,2021,385:409−417. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2021.03.003
[106] AI W,LIU S,ZHANG J,et al. Mechanical and nonisothermal crystallization properties of coal gasification fine slag glass bead-filled polypropylene composites[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2019,136(30):47803. doi: 10.1002/app.47803
[107] AI W,XUE B,WEI C,et al. Mechanical and thermal properties of coal gasification fine slag reinforced low density polyethylene composites[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2018,135(17):46203. doi: 10.1002/app.46203
-
期刊类型引用(9)
1. 丁天昱,王龙江,鱼涛,陈刚. 煤气化渣的改性及其在水泥增强中的应用研究. 化工技术与开发. 2025(Z1): 66-69 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李飞,王福宁,金涛,朱建华,刘向辉. 大宗煤基固废利用研究现状与展望. 山东化工. 2025(01): 75-78 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 阿拉腾沙嘎,段乐乐. 煤气化渣资源化利用的研究进展. 化工技术与开发. 2025(03): 44-47 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 廖昌建,王晶,金平,刘志禹,徐婉怡,王坤. 煤气化渣理化特性及其所含重金属迁移规律综述. 煤炭科学技术. 2025(02): 426-443 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 周柏屹,王浩南,夏良志. 气化渣破碎与预干燥过程数值仿真及实验研究. 现代化工. 2024(S2): 359-365 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 杨帆. 煤气化过程中副产物气化渣的综合利用技术研究. 化工管理. 2024(31): 90-93 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 周季龙,王亚茹,魏怡菲,孙建平,孙伟,岳彤. 气化渣酸浸液去除铁铬及聚合氯化铝制备. 中国有色金属学报. 2024(12): 4111-4125 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 程臻赟,王占银,傅博,雷华,苏梦,丁楠,陈美庆. 煤气化渣黏土复合地基填料力学特性研究. 江西建材. 2024(10): 217-220 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 傅博,程臻赟,雷华. 助磨剂对气化渣球磨特性的影响. 化学反应工程与工艺. 2024(06): 516-520+539 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)



 下载:
下载: