Application of drainage technology for L-shaped coalbed methane horizontal well in Southern Qinshui Basin
-
摘要:
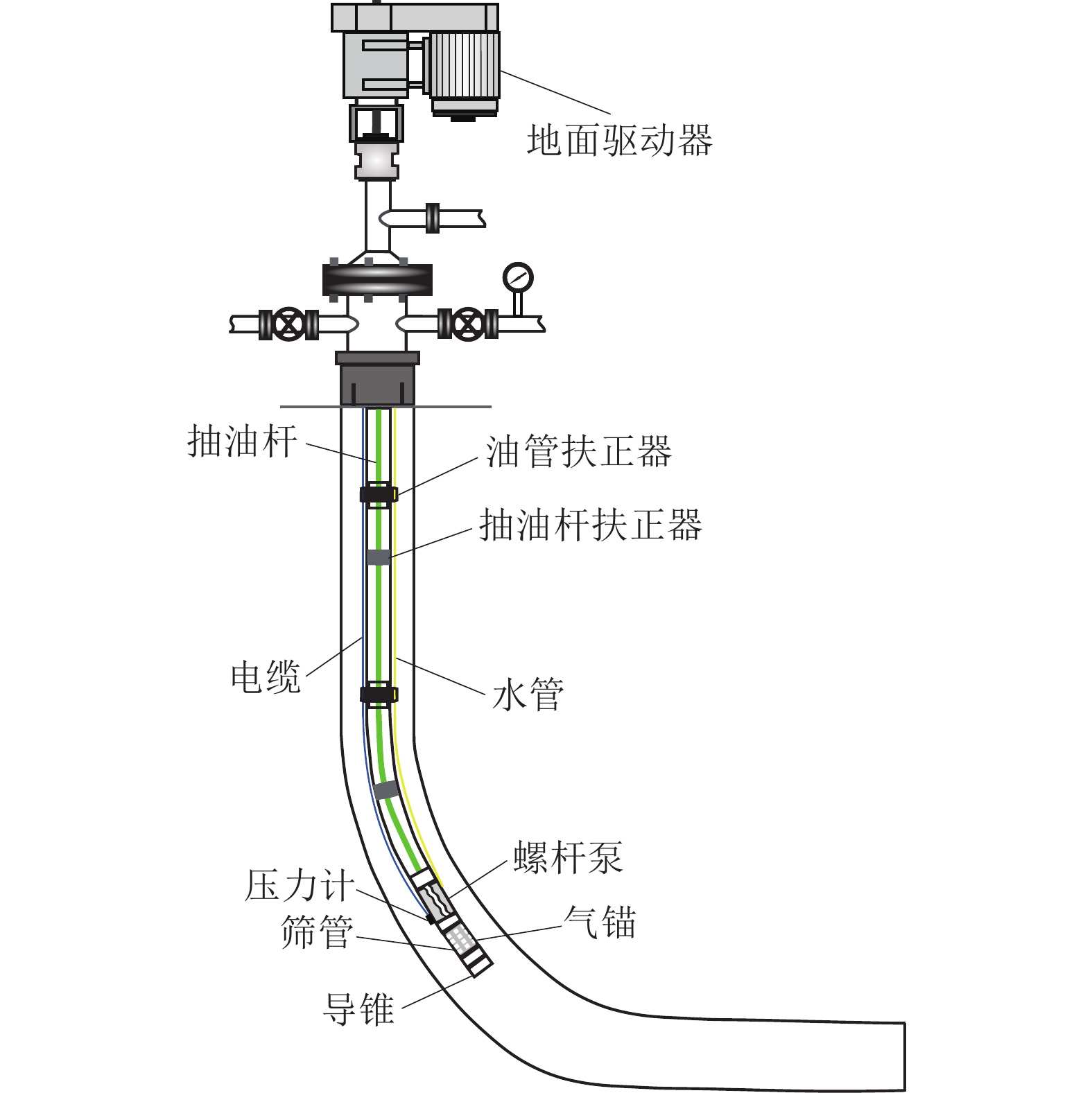
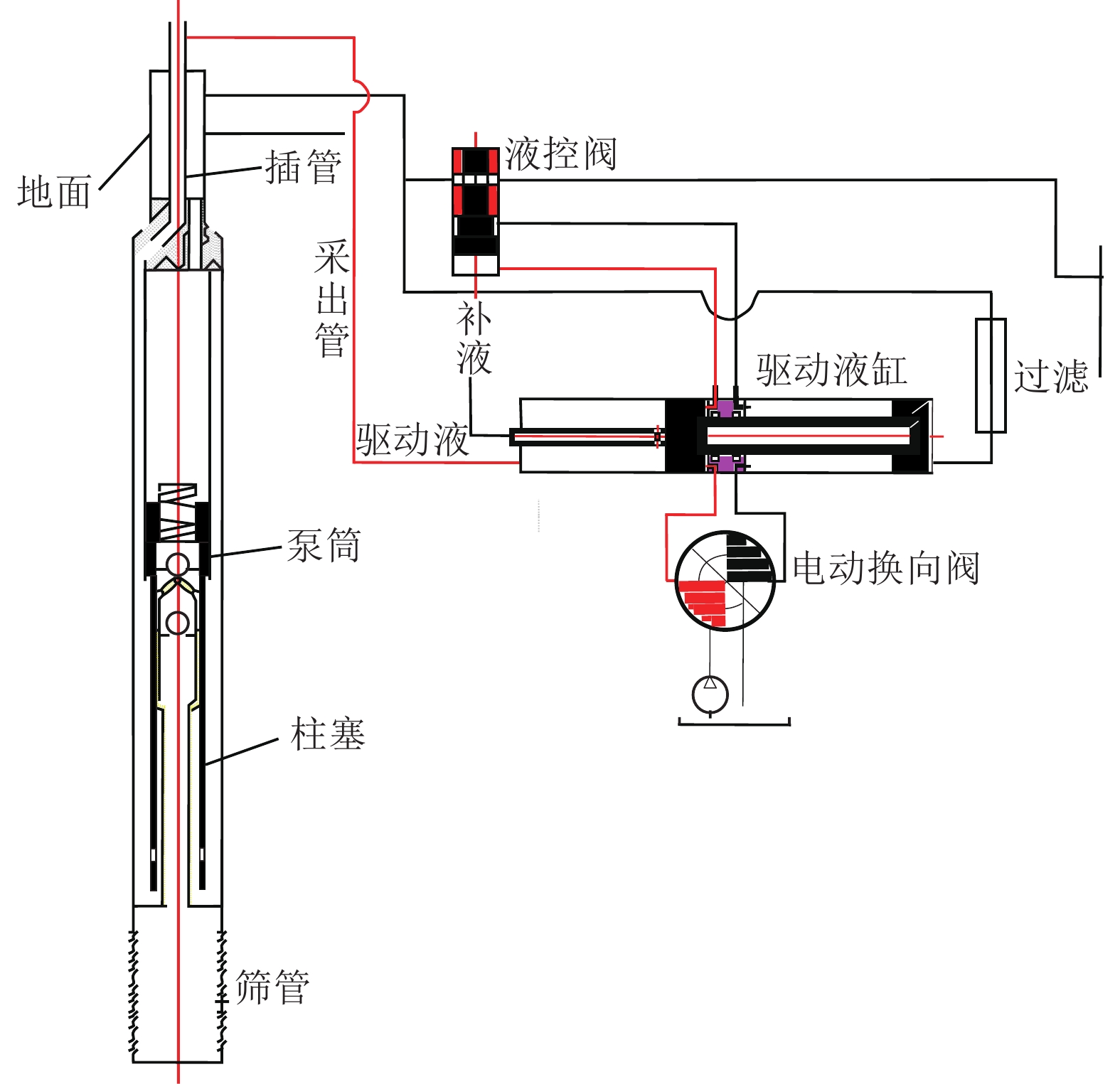
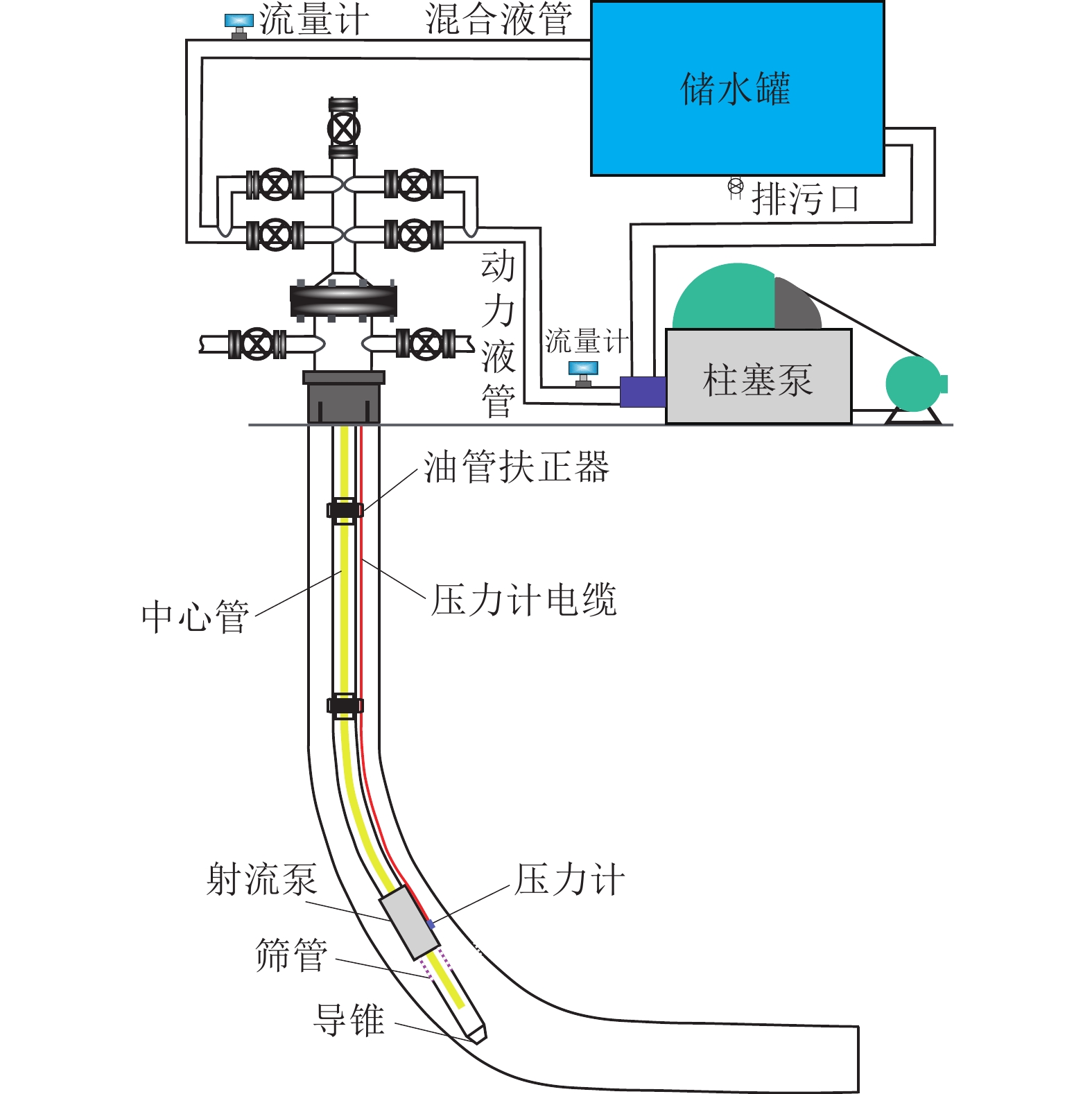
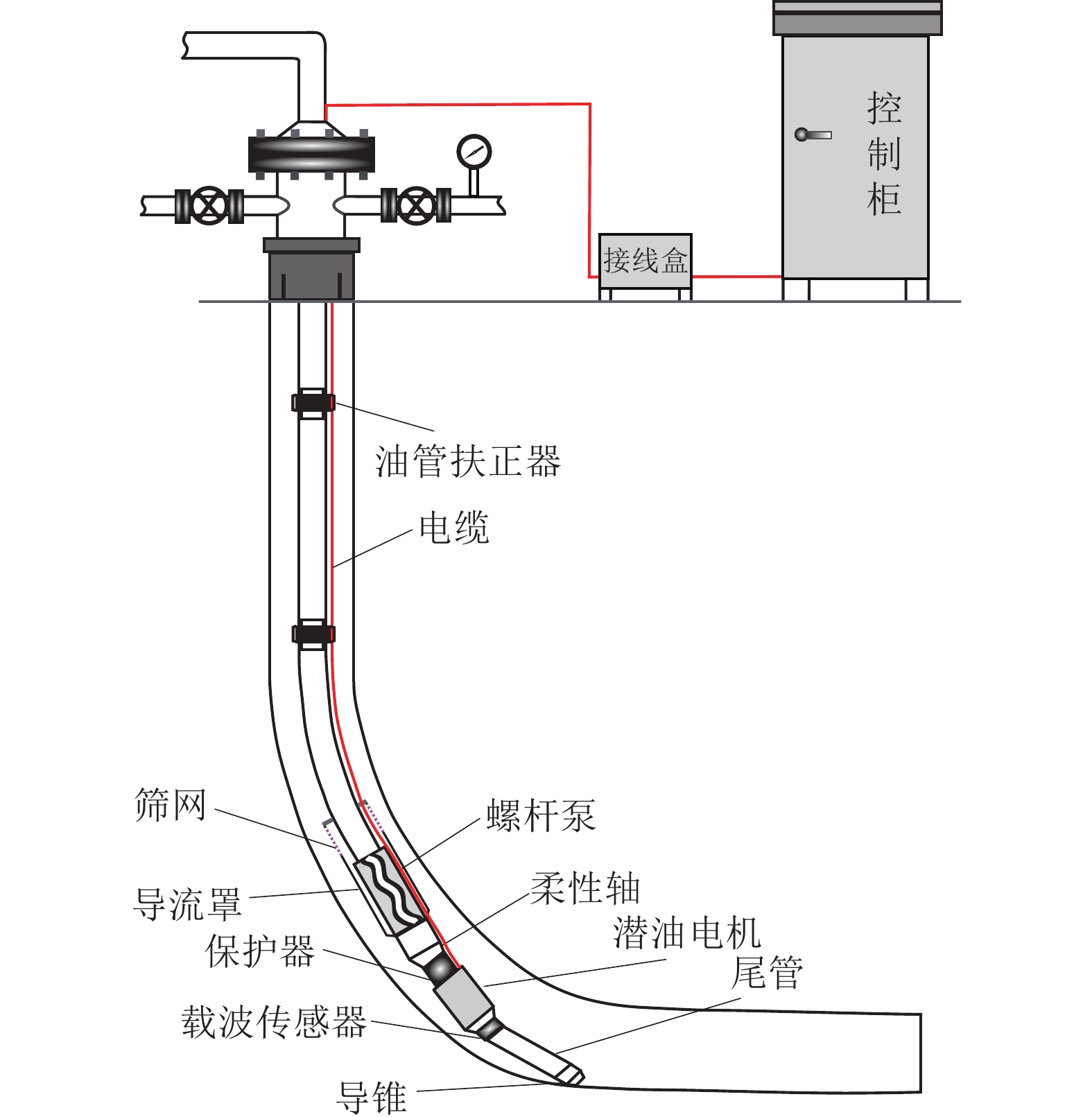
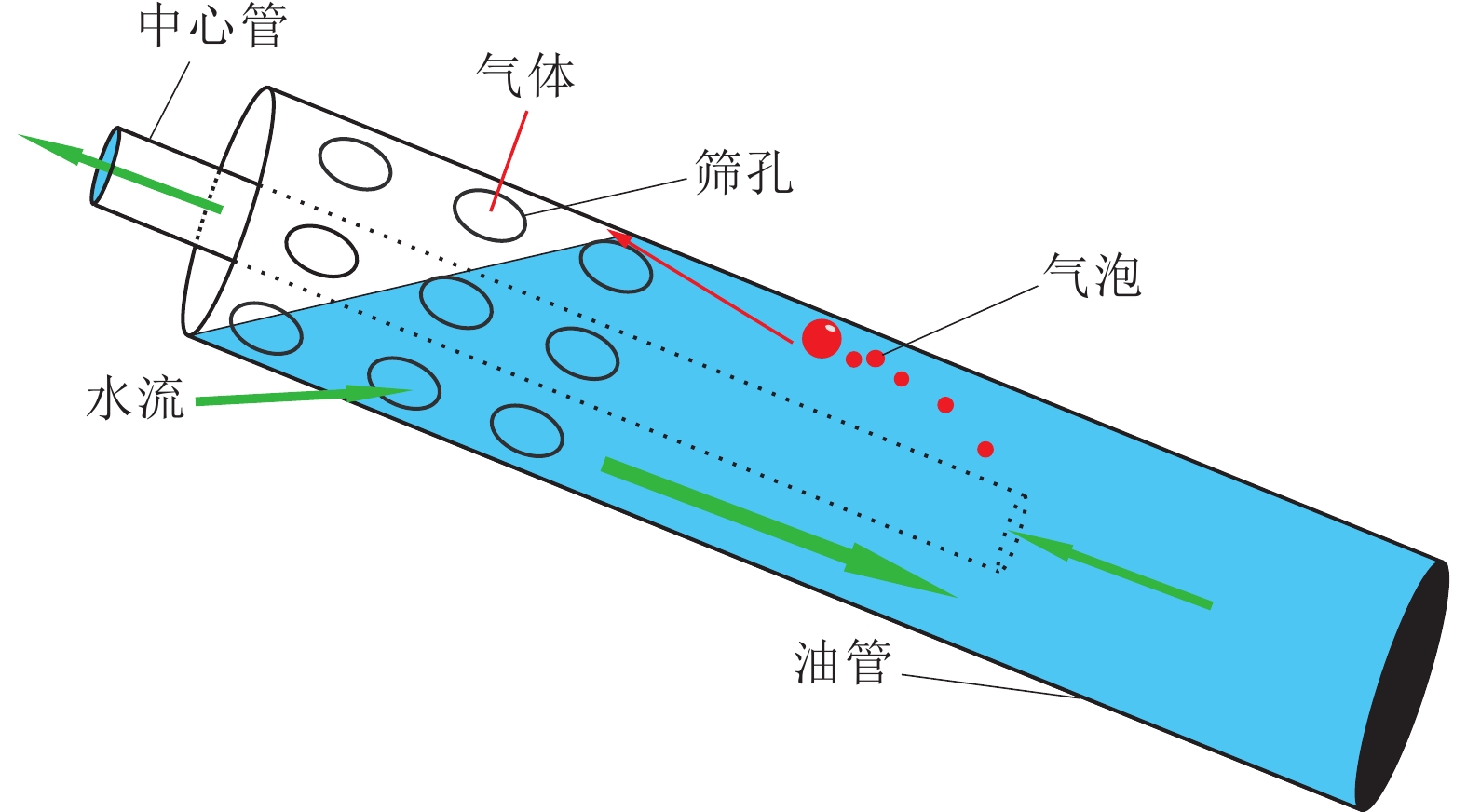
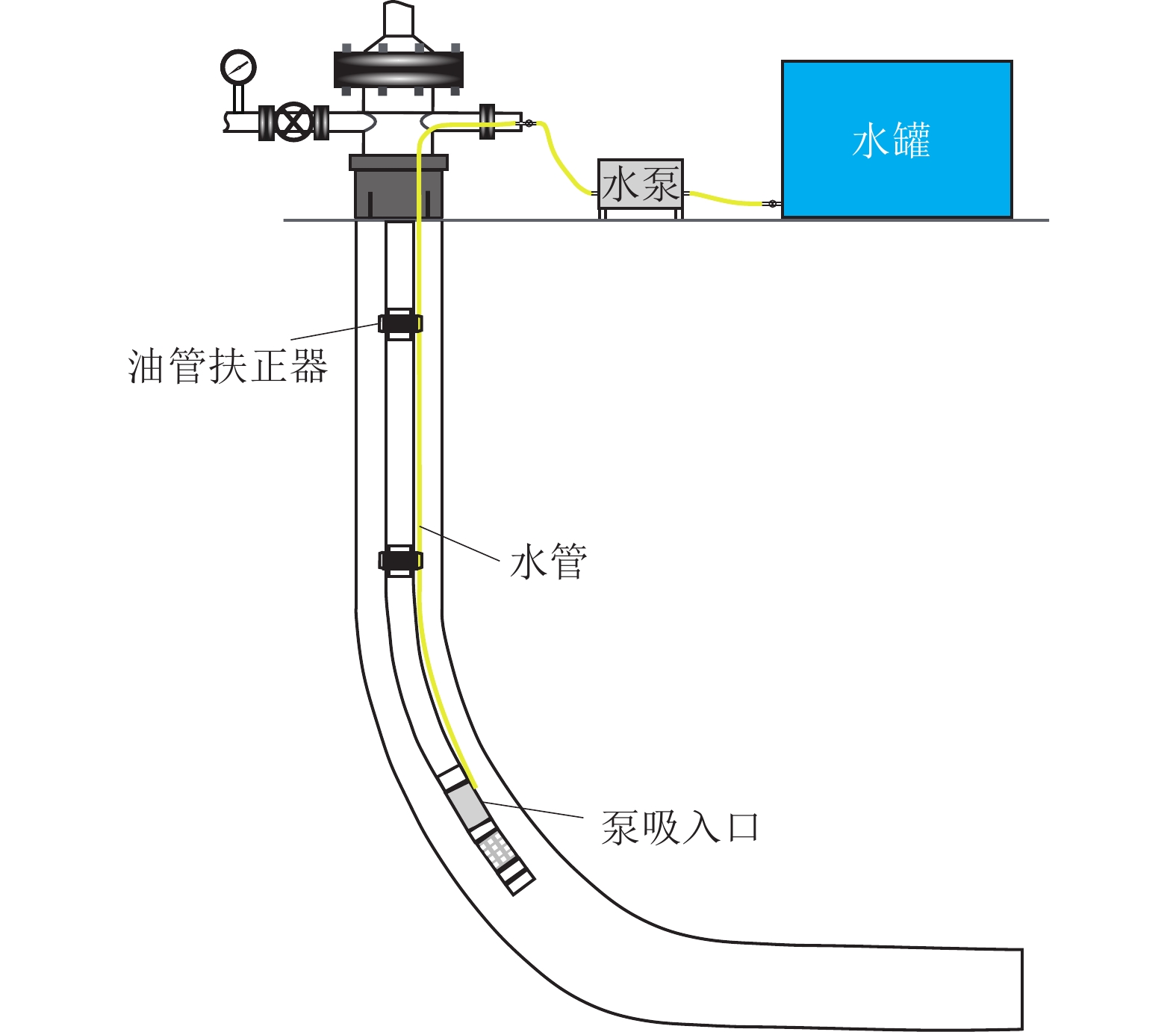
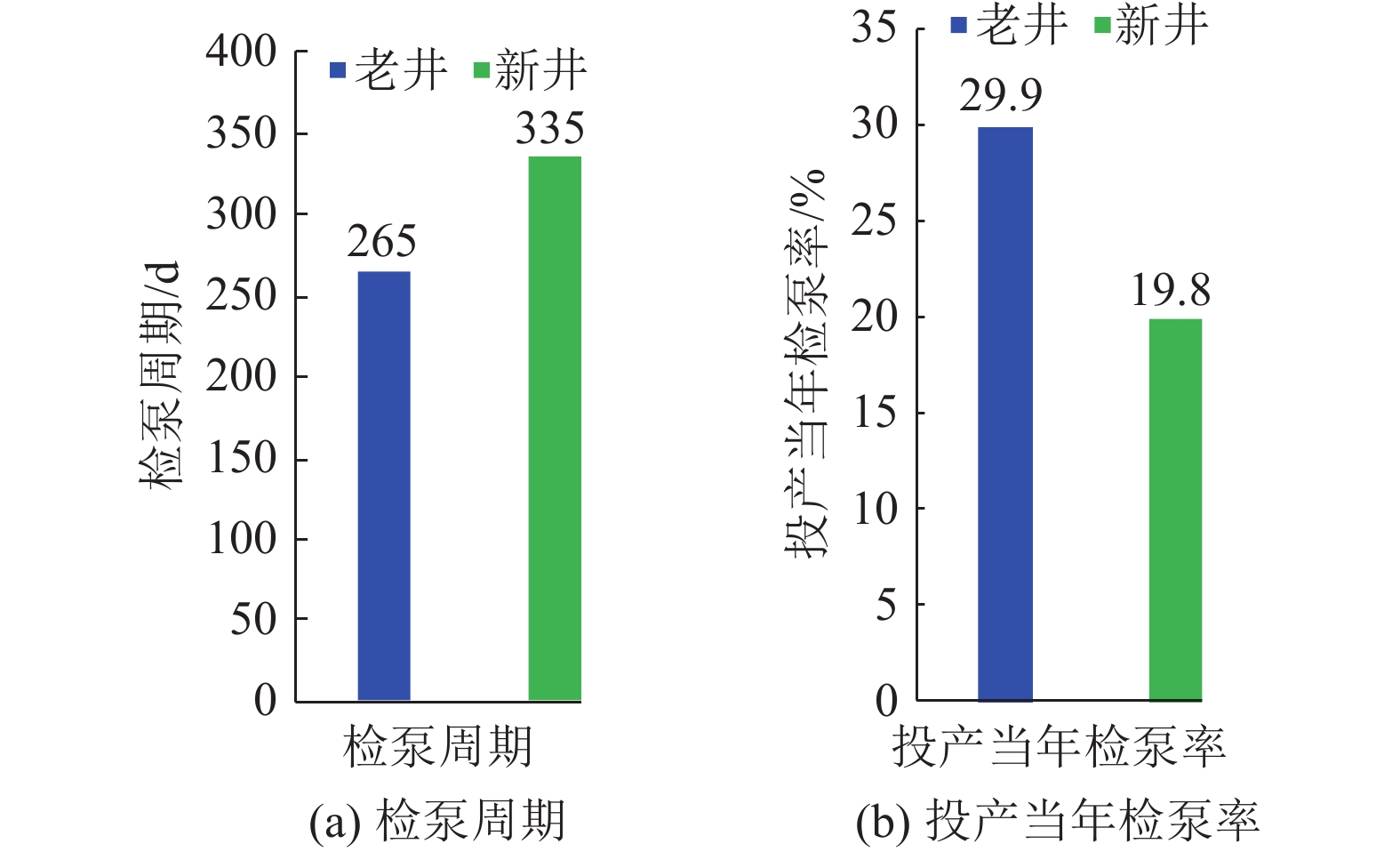
随着L型水平井成为煤层气主要开发井型,传统煤层气井排采工艺不能满足需要,为了形成适用于L型水平井的排采工艺技术,基于沁水盆地南部马必合作区块L型水平井排采实践,分析了2类有杆排采工艺和3类无杆排采工艺的工作原理、工艺改进及其对L型水平井的适应性,并研究了相关防砂、防气配套工艺,形成了系统的水平井排采工艺。结果表明:① 2类有杆排采工艺通过管柱结构优化、泵结构优化等可以有效减轻杆管偏磨,能够适应L型水平井排采。抽油机+管式泵排采工艺通过优化管柱结构加装扶正器,能够减缓杆管偏磨,通过采用双固定阀长柱塞管式泵能够提升固体颗粒适应性;顶驱螺杆泵排采工艺通过在管柱结构不同部位差异化安装弹簧式扶正器,采用加厚油管,并在狗腿度大的位置加装导向器和双保接箍,能够减轻杆管偏磨。② 无杆管式泵、射流泵、电潜螺杆泵等无杆工艺从本质上消除了杆管偏磨问题,对L型水平井适应性更强,射流泵对固体颗的粒适应性最强,电潜螺杆泵的排量可达50~60 m3/d,无杆管式泵排量一般在20~30 m3/d,射流泵的排量一般在30~40 m3/d。③ 提出的分级下泵、气液分离及循环洗井3项配套工艺,能够有效防砂、防气,提升了主体工艺的适应性。其中,分级下泵工艺即在排采前期将泵挂位置设计在井斜65°~75°处,保留足够的沉砂空间,在排采后期,出砂量减少时,进一步下放管柱,充分释放单井产能;循环洗井工艺即在排采后期,通过循环洗井增加产出液体排量,提升携砂能力;重力分离式气锚可有效实现气液分离,减缓窜气对泵效影响。上述工艺技术在研究区应用后,能够满足埋深1 500 m中深层煤层气水平井的排采需求,L型水平井平均检泵周期由265 d延长至335 d,投产第1年检泵率由29.9%下降至19.8%,实现了L型水平井平稳高效排采。
Abstract:As L-shaped horizontal wells have become the main well type for Coalbed Methane (CBM) development, the traditional CBM wells’ drainage technologies can no longer meet the drainage requirements. In order to develop a series of drainage technologies applicable to L-shaped horizontal wells, this article, based on the drainage practices of L-shaped horizontal wells in the Mabi Cooperative Block in Southern Qinshui Basin, analyzes the working principles, process improvements, and technological adaptability to L-shaped horizontal wells of two types of rod-pumping drainage technologies and three types of rodless-pumping drainage technologies. It also studies the relevant supporting processes for sand control and gas prevention, and forms a systematic horizontal well production technology. The results show that: ① Through the optimization of the string structure and the pump structure, the eccentric wear between the rods and the pipes of the two types of rod-pumping drainage technologies can be effectively reduced, which can adapt to the drainage of L-shaped horizontal wells. For the oil pumping unit process, the eccentric wear can be alleviated by installing centralizers optimize the string structure and using a long plunger tubing pump with double fixed valves to improve the adaptability to solid particles. For the top drive screw pump process, by installing spring centralizers differently at different parts of the string structure, using thickened tubing, and installing a deflector and double protect collars at the positions with large dogleg degrees, the eccentric wear can be reduced. ② Rodless processes such as rodless tubing pumps, jet pumps, and electric submersible screw pumps essentially eliminate the problem of eccentric wear between the rods and the pipes, and have a much stronger adaptability to L-shaped horizontal wells than rod-pumping drainage technologies. Jet pumps have the strongest adaptability to solid particles. The maximum displacement of electric submersible screw pumps can reach 50−60 m3/d, the maximum displacement of rodless tubing pumps is generally 20−30 m3/d, and the maximum displacement of jet pumps is generally 30−40 m3/d. ③ The three supporting processes proposed in this article, namely, the graded pump setting process, gas-liquid separation process, and circulating well cleaning process, can effectively reduce the influence from sand particles and CBM gas, and improve the adaptability of the main processes. Among them, the graded pump setting process is that the pump setting position is designed at the well deviation of 65°−75°in the early stage of production to reserve sufficient sand settling space,while the pump setting position is further lowered to fully release the productivity of a single well,in the later stage of production, when the sand production decreases.The circulating well cleaning process improves the sand carrying capacity by injecting water to increase the production rate in the later stage of production. The gravity separation gas anchor can effectively realize gas-liquid separation and reduce the impact of gas channeling on the pump efficiency. After the above process technologies are applied in the study area, they can meet the production requirements of horizontal CBM wells in the middle-deep layer with a burial depth of
1500 m. The average pump inspection cycle of L-shaped horizontal wells has been extended from 265 days to 335 days, and the pump inspection rate in the first year of production has decreased from 29.9% to 19.8%, achieving stable and efficient production of L-shaped horizontal wells. -
-
表 1 水平井排采工艺对比
Table 1 Comparison of horizontal well production techniques
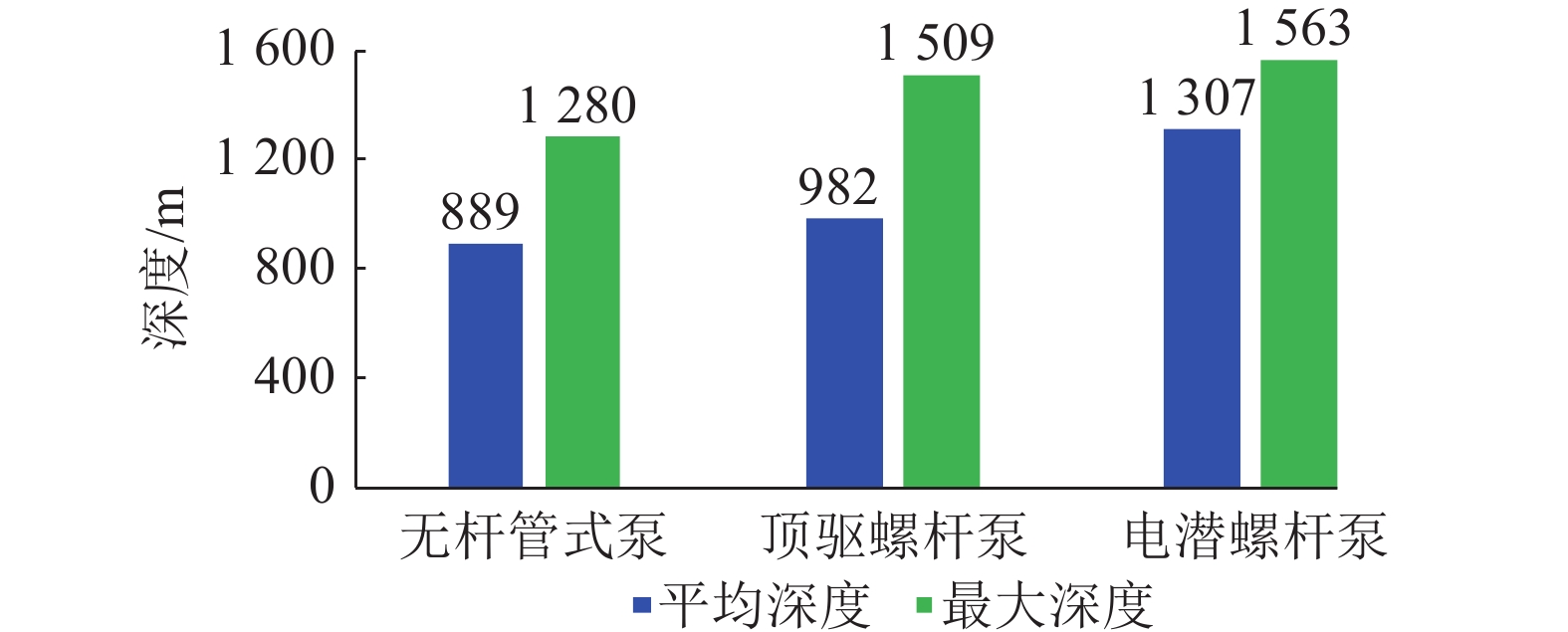
项目 条件 有杆泵 无杆泵 管式泵 螺杆泵 电潜螺杆泵 射流泵 水力管式泵 基本情况 复杂程度 简单 简单 井下复杂 地面复杂 地面复杂 一次投资 低 低 较高 中等 中等 运行能耗 低 较高 低 高 低 排量/(m3·d−1) 正常范围 0.1~100.0 0.5~250.0 0.1~100.0 10.0~130 0.1~30.0 泵深/m 正常范围 <3 000 <1 500 <1 200 <1 500 <1 000 井身结构 大斜度井或水平井 差 差 一般 适宜 适宜 操作问题 高气水比 较好 一般 一般 一般 较好 出砂 适宜 适宜 一般 一般 适宜 煤灰 适宜 适宜 适宜 配套筛管 较好 维修管理 检泵工作 较大 较大 大 大 大 免修期 3 2 2 1 1 自动控制 适宜 一般 适宜 适宜 适宜 灵活性 适宜 一般 适宜 适宜 适宜 表 2 水平井高效排采工艺技术模板
Table 2 Template for efficient drainage technology of horizontal well
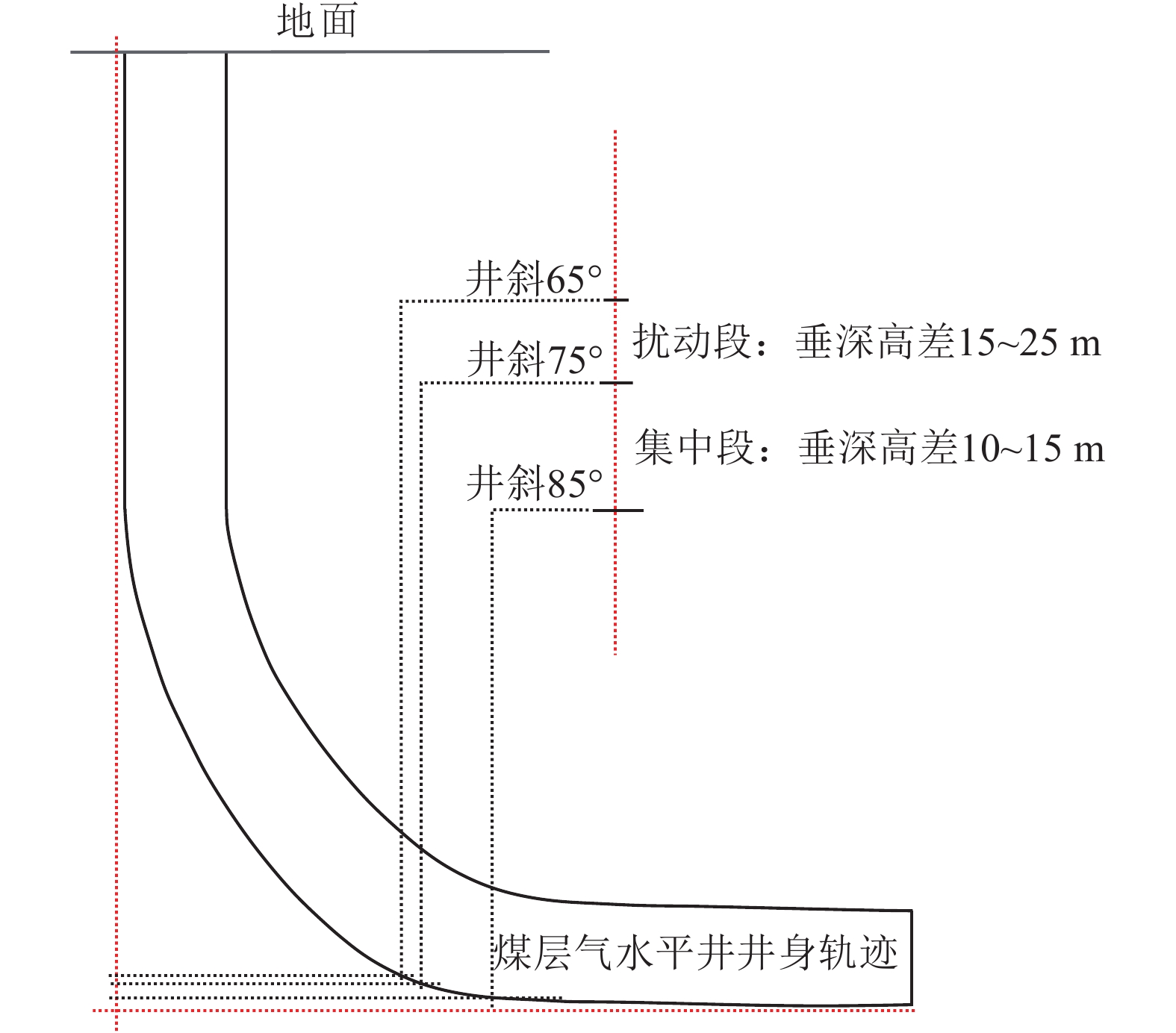
时段 原则 排采设备 下泵位置/管柱优化 日排采强度/m3 完井 前期疏导扩面,安全排出煤粉 电潜螺杆泵、顶驱螺杆泵、射流泵 井斜65°左右,15~20 m稳斜段 15~20 见气 根据解吸压力和井底压力,可适当加深管柱(适量多次) 5~10 提产 中期清理井筒,优化设备和管柱 水量变小则更换为水力无杆泵,同时加深、优化泵挂(防窜气防煤粉) 根据水量变化,考虑更换排采设备或优化管柱(此时清理井筒) 3~5 稳产 后期保证足够流压、安全空间 保证足够流压的前提下稳定产水 0.5~1.0 表 3 不同气液分离装置条件下最大排液速度
Table 3 Suggested drainage speed for efficient gas-liquid separation in horizontal well
井斜角度/(°) 73 mm油管,
32 mm中心管/
(m3·d−1)89 mm油管,
48 mm中心管/
(m3·d−1)89 mm油管,
32 mm中心管/
(m3·d−1)65 43.6 53.7 73.5 70 35.3 43.4 59.4 75 26.7 32.9 45.0 80 17.9 22.1 30.2 85 9.0 11.0 15.1 -
[1] 刘大锰,贾奇锋,蔡益栋. 中国煤层气储层地质与表征技术研究进展[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(1):196−203. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2336.2022.1.mtkxjs202201019 LIU Dameng,JIA Qifeng,CAI Yidong. Research progress on coalbed methane reservoir geology and characterization technology in China[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2022,50(1):196−203. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2336.2022.1.mtkxjs202201019
[2] 张道勇,朱杰,赵先良,等. 全国煤层气资源动态评价与可利用性分析[J]. 煤炭学报,2018,43(6):1598−1604. ZHANG Daoyong,ZHU Jie,ZHAO Xianliang,et al. Dynamic assessment of coalbed methane resources and availability in China[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2018,43(6):1598−1604.
[3] 熊先钺,闫霞,徐凤银,等. 深部煤层气多要素耦合控制机理、解吸规律与开发效果剖析[J]. 石油学报,2023,44(11):1812−1826,1853. doi: 10.7623/syxb202311005 XIONG Xianyue,YAN Xia,XU Fengyin,et al. Analysis of multi-factor coupling control mechanism,desorption law and development effect of deep coalbed methane[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2023,44(11):1812−1826,1853. doi: 10.7623/syxb202311005
[4] 米立军,朱光辉. 鄂尔多斯盆地东北缘临兴−神府致密气田成藏地质特征及勘探突破[J]. 中国石油勘探,2021,26(3):53−67. MI Lijun,ZHU Guanghui. Geological characteristics and exploration breakthrough in Linxing-Shenfu tight gas field,northeastern Ordos Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration,2021,26(3):53−67.
[5] 张聪,李梦溪,胡秋嘉,等. 沁水盆地南部中深部煤层气储层特征及开发技术对策[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2024,52(2):122−133. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.10.0624 ZHANG Cong,LI Mengxi,HU Qiujia,et al. Moderately deep coalbed methane reservoirs in the southern Qinshui Basin:Characteristics and technical strategies for exploitation[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2024,52(2):122−133. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.10.0624
[6] 王红岩,段瑶瑶,刘洪林,等. 煤层气水平井开发的理论技术初探:兼论煤层气和页岩气开发条件对比[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2024,52(4):47−59. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.11.0794 WANG Hongyan,DUAN Yaoyao,LIU Honglin,et al. Preliminarily exploring the theories and technologies for coalbed methane production using horizontal wells:Comparison of conditions for coalbed methane and shale gas exploitation[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2024,52(4):47−59. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.11.0794
[7] 高德利,毕延森,鲜保安. 中国煤层气高效开发井型与钻完井技术进展[J]. 天然气工业,2022,42(6):1−18. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2022.06.001 GAO Deli,BI Yansen,XIAN Baoan. Technical advances in well types and drilling & completion for high-efficient development of coalbed methane in China[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2022,42(6):1−18. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2022.06.001
[8] 胡秋嘉,李梦溪,贾慧敏,等. 沁水盆地南部高煤阶煤层气水平井地质适应性探讨[J]. 煤炭学报,2019,44(4):1178−1187. HU Qiujia,LI Mengxi,JIA Huimin,et al. Discussion of the geological adaptability of coal-bed methane horizontal wells of high-rank coal formation in southern Qinshui Basin[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2019,44(4):1178−1187.
[9] 韩文龙,李勇,陈湘生,等. 煤层气排采非饱和流阶段煤粉–气泡耦合作用机理[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2023,51(3):46−53. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.22.09.0683 HAN Wenlong,LI Yong,CHEN Xiangsheng,et al. Mechanism of coal fine-bubble coupling in the unsaturated flow stage of coalbed methane drainage[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2023,51(3):46−53. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.22.09.0683
[10] 章朋,孟雅,刘超英,等. 煤层气井排采中煤储层稳定性分析方法与应用:以郑庄区块为例[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(4):1620−1628. ZHANG Peng,MENG Ya,LIU Chaoying,et al. Stability analysis method of CBM reservoir during depletion and its application:A case study of Zhengzhuang Block[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2022,47(4):1620−1628.
[11] 朱庆忠. 我国高阶煤煤层气疏导式高效开发理论基础—以沁水盆地为例[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2022,50(3):82−91. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.21.12.0845 ZHU Qingzhong. Theoretical basis of dredging and efficient development of high−rank coalbed methane in China:A case study of the Qinshui Basin[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2022,50(3):82−91. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.21.12.0845
[12] 刘展,张群霞,耿宇欣,等. 煤层气L型水平井防窜气排采控制方法研究[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2024,52(5):77−87. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.10.0660 LIU Zhan,ZHANG Qunxia,GENG Yuxin,et al. Anti-channeling methods for coalbed methane production using L-type horizontal wells[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2024,52(5):77−87. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.10.0660
[13] 原红超, 安玉敏, 张慧, 等. 煤层气L型水平井无杆泵油水分离装置研发与应用[J]. 中国煤层气,2020,17(5):28−30. YUAN Hongchao, AN Yumin, ZHANG Hui, et al. Development and application of oil-water separation unit for rodless pump drainage technology in L-type horizontal well for coalbed methane[J]. China Coalbed Methane,2020,17(5):28−30.
[14] 冯常青. 井筒内煤粉颗粒的运移规律研究[D]. 太原:中北大学,2020:32−38. FENG Changqing. Study on the migration law of pulverized coal in wellbor[D]. Taiyuan:North University of China,2020:32−38.
[15] 唐松磊. 煤层气排采井地层液-煤粉颗粒耦合运移规律研究[D]. 北京:中国矿业大学(北京),2021. TANG Songlei. Study on coupling law of formation fluid and pulverized coal particles in coalbed methane drainage[D]. Beijing:China University of Mining&Technology-Beijing,2021.
[16] 魏迎春,李超,曹代勇,等. 煤层气开发中煤粉产出机理及管控措施[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2018,46(2):68−73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2018.02.011 WEI Yingchun,LI Chao,CAO Daiyong,et al. The output mechanism and control measures of the pulverized coal in coalbed methane development[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2018,46(2):68−73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2018.02.011
[17] 鲜保安,高德利,徐凤银,等. 中国煤层气水平井钻完井技术研究进展[J]. 石油学报,2023,44(11):1974−1992. doi: 10.7623/syxb202311017 XIAN Baoan,GAO Deli,XU Fengyin,et al. Research progress of coalbed methane horizontal well drilling and completion technology in China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2023,44(11):1974−1992. doi: 10.7623/syxb202311017
[18] 朱庆忠,李志军,李宗源,等. 复杂地质条件下煤层气高效开发实践与认识:以沁水盆地郑庄区块为例[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2023,51(1):131−138. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.22.10.0768 ZHU Qingzhong,LI Zhijun,LI Zongyuan,et al. Practice and cognition of efficient CBM development under complex geological conditions:A case study of Zhengzhuang Block,Qinshui Basin[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2023,51(1):131−138. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.22.10.0768
[19] 叶建平. 中国煤层气勘探开发及其科技进步历程回顾与思考[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2025,53(1):114−127. YE Jianping. China’s CBM exploration and production and associated technological advancements: A review and reflections[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2025,53(1):114−127.
[20] 祖海英,孙金山,叶卫东,等. 采油单螺杆泵动态力学特性及疲劳寿命预测研究[J]. 中国机械工程,2024,35(8):1358−1365. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2024.08.003 ZU Haiying,SUN Jinshan,YE Weidong,et al. Study on dynamic mechanics characteristics and fatigue life prediction of single PCPs[J]. China Mechanical Engineering,2024,35(8):1358−1365. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2024.08.003
[21] 董子龙,董世民,具自强. 螺杆泵采油杆柱受径向力激励的横向振动[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版),2023,47(1):156−163. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2023.01.017 DONG Zilong,DONG Shimin,JU Ziqiang. Transverse vibration driven by radial force of sucker rod string in screw pump production system[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science),2023,47(1):156−163. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2023.01.017
[22] 秦绍锋,王若仪. 潘河区块煤层气L型水平井排采工艺及配套技术研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2019,47(9):132−137. QIN Shaofeng,WANG Ruoyi. Study on gas drilling technology and supporting technology for L-type horizontal well in Panhe Block[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2019,47(9):132−137.
[23] 梅永贵,郭简,苏雷,等. 无杆泵排采技术在沁水煤层气田的应用[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2016,44(5):64−67. MEI Yonggui,GUO Jian,SU Lei,et al. Appfication of rodless pump drainage technology to Qinshui Coalbed Methane Field[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2016,44(5):64−67.
[24] 马文涛,刘印华,吴建军,等. 煤层气井无杆排采工艺应用与改进方向:以鄂尔多斯盆地东缘为例[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2022,50(9):22−31. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.21.12.0763 MA Wentao,LIU Yinhua,WU Jianjun,et al. Application and improvement directions of rodless drainage technology in coalbed methane wells:A case study from east margin of Ordos Basin[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2022,50(9):22−31. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.21.12.0763
[25] 曾雯婷,徐凤银,张雷,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东缘深部煤层气排采工艺技术进展与启示[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2024,52(2):23−32. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.10.0698 ZENG Wenting,XU Fengyin,ZHANG Lei,et al. Deep coalbed methane production technology for the eastern margin of the Ordos Basin:Advances and their implications[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2024,52(2):23−32. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.10.0698
[26] 郝忠献,朱世佳,裴晓含,等. 井下直驱螺杆泵无杆举升技术[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2019,46(3):594−601. doi: 10.11698/PED.2019.03.18 HAO Zhongxian,ZHU Shijia,PEI Xiaohan,et al. Submersible direct-drive progressing cavity pump rodless lifting technology[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2019,46(3):594−601. doi: 10.11698/PED.2019.03.18
[27] 刘新福,刘春花,何鸿铭,等. 大斜度井段排采泵三层流场低速液流携粉运移特性[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(7):2313−2320. LIU Xinfu,LIU Chunhua,HE Hongming,et al. Characteristics of pulverized coal with water of low rate in three-layer flow field of high-inclined pumps[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2021,46(7):2313−2320.
[28] 邢雷,关帅,蒋明虎,等. 高气液比井下气液旋流分离器结构设计与性能分析[J]. 化工学报,2024,75(3):900−913. XING Lei,GUAN Shuai,JIANG Minghu,et al. Study on structure optimization and performance of downhole gas-liquid hydrocyclone under high gas-liquid ratio[J]. CIESC Journal,2024,75(3):900−913.
[29] 苗志国. 深井泵气锚分气效率计算方法研究[D]. 东营:中国石油大学(华东),2008:19−31. MIAO Zhiguo. Study on separation efficiency calculation method of deep well pump gas anchor[D]. Dongying:China University of Petroleum (Huadong),2008:19−31.
[30] 李勇,徐凤银,唐书恒,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地煤层(岩)气勘探开发进展及发展方向[J]. 天然气工业,2024,44(10):63−79. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2024.10.005 LI Yong,XU Fengyin,TANG Shuheng,et al. Progress and development direction of coalbed methane(coal-rock gas)exploration and development in the Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2024,44(10):63−79. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2024.10.005




 下载:
下载: