Microscopic pore characteristics of coal seam and the controlling effect of sedimentary environment on pore structure in No.8 coal seam of the Ordos Basin
-
摘要:
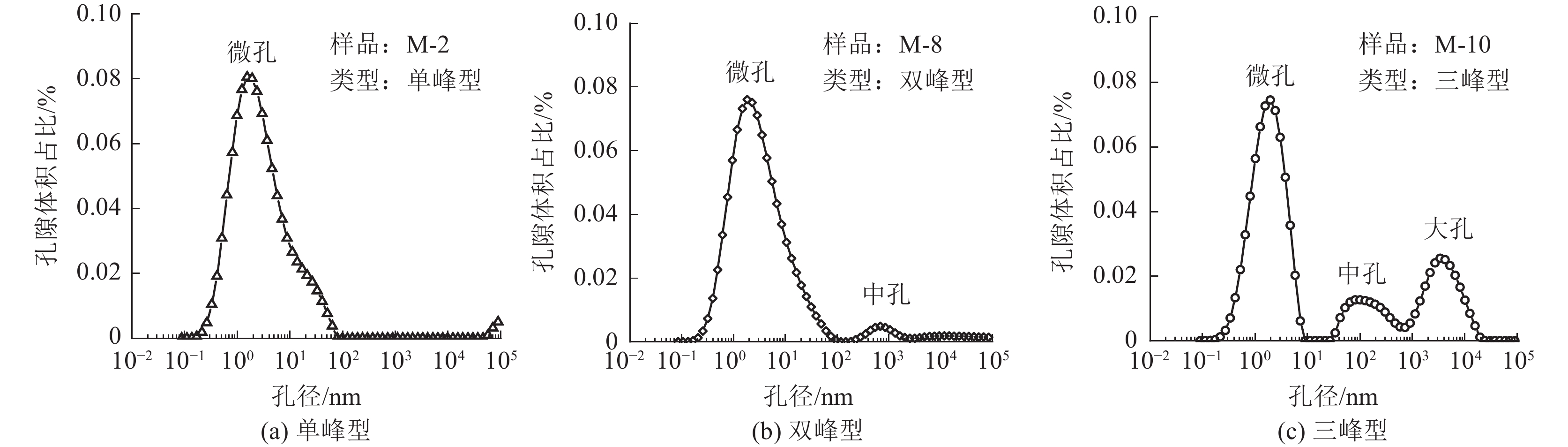
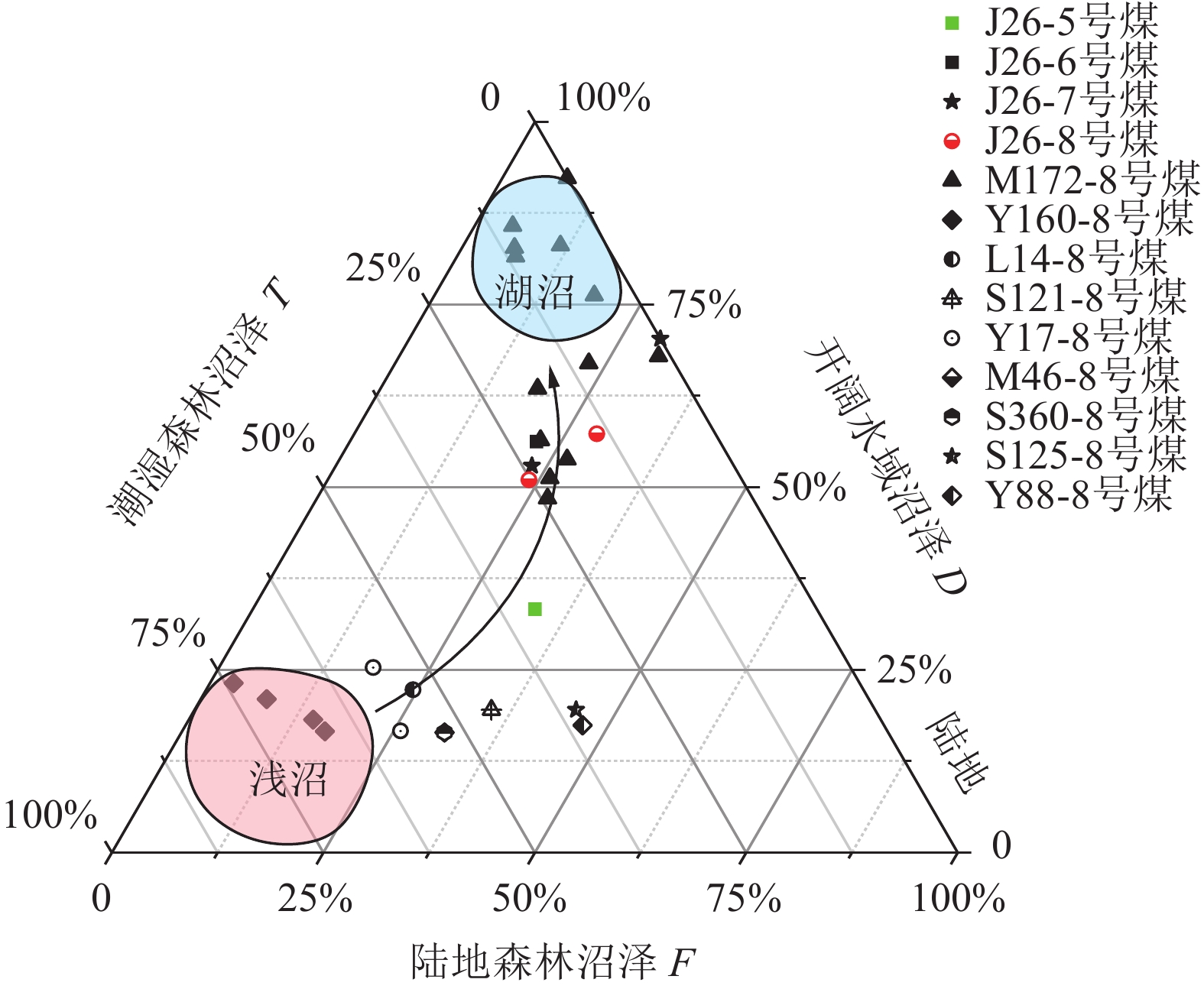
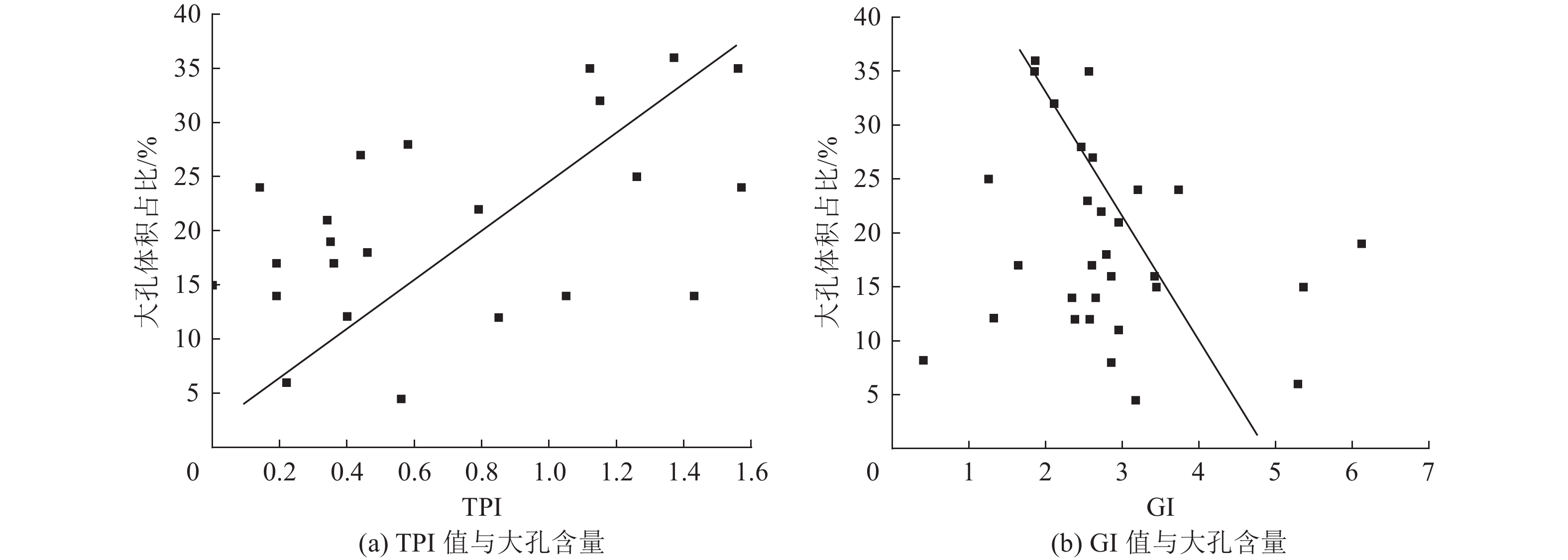
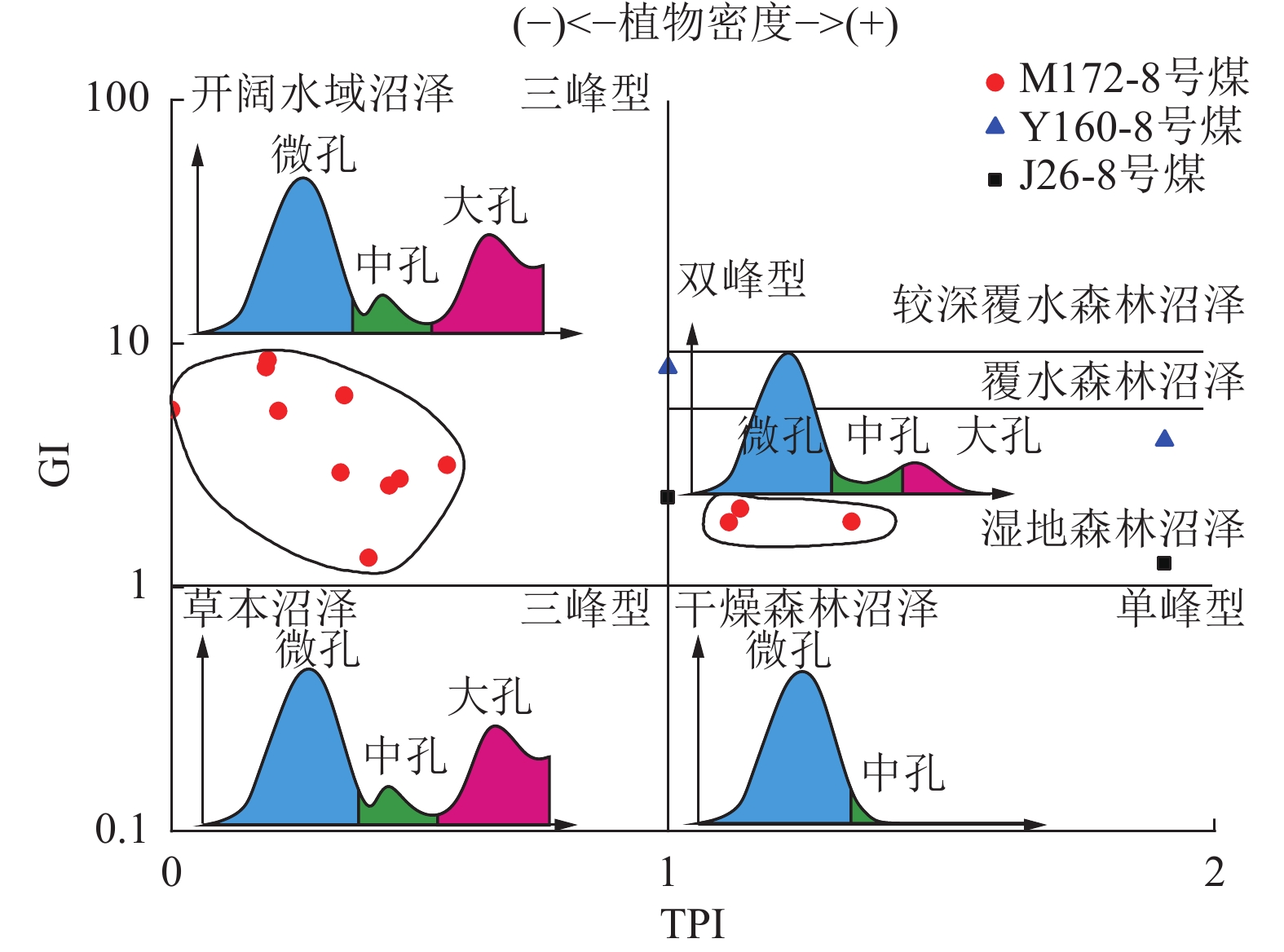
寻找深部煤层气资源分布,亟待查明深部煤储层沉积环境和孔隙分布特征。为此,在开展鄂尔多斯盆地煤岩显微组分、核磁共振孔隙和电镜分析的基础上,查明了煤岩显微组分和孔隙分布特征,评价了鄂尔多斯盆地8号煤的煤沉积环境和孔隙结构特征之间的关系。结果表明:①研究区8煤层煤岩有机显微组分以镜质组为主,成煤早期植物类型应主要为木本植物,后期随着覆水程度增大而逐渐转变为木本+草本混生植物为主;②本溪期8号煤由早期为湿地森林沼泽逐步演化为后期开阔水域沼泽,沼泽水体相对滞留,沼泽环境稳定,利于有机质富集和煤层结构稳定;③研究区8煤大孔占比与结构保存指数(TPI)两者呈正相关,而与凝胶化指数(GI)呈负相关;④基质镜质体发育密集气孔群或稀疏带状气孔群,团块镜质体中发育少量气孔,结构镜质体中发育原始组织孔,多为矿物充填,均质镜质体气孔不发育。研究认为榆林地区煤层孔隙分布受到煤沉积环境和显微组分控制,开阔水域沼泽相的煤层孔隙结构呈现三峰,其中微孔和大孔发育最好,湿地森林沼泽相煤层孔隙结构呈现双峰,微孔发育好,大孔发育较差。
Abstract:To accurately evaluate the distribution and potential of deep coalbed methane resources, it is critical to identify the coal sedimentary and pore distribution characteristics of deep coal reservoirs. Therefore, based on the analysis of coal macerals, nuclear magnetic resonance porosity, and electron microscopy, the characteristics of coal macerals and pore distribution in the Yulin area were identified, as well as the relationship between the coal sedimentary and pore structure characteristics of No.8 coal was evaluated. The results indicated that: ① The organic macerals of No.8 coal seam in the study area were predominantly composed of vitrinite, indicating a predominance of woody plants during the early stages of coal formation. As the degree of water cover increases, it gradually transitions into a mixture of woody and herbaceous plants. ② During the Benxi period, No. 8 coal evolved from an early wetland forest swamp to a later open water swamp with stagnant swamp water, creating a stable environment conducive to organic matter enrichment and coal seam stability. ③ The proportion of macropores in No.8 coal seam was negatively correlated with the structure preservation index (TPI), while it was positively correlated with the gel index (GI). ④ Matrix vitrinite developed dense or sparse banded pores, mass vitrinite developed few pores, and the structure vitrinite developed original tissue pores, mostly filled with minerals, while the homogeneous vitrinite did not develop pores. In conclusion, pore distribution in Yulin's coal seams was controlled by sedimentation and macerals. The pore structure of coal seams in the open water swamp sedimentary presented three peaks, with micropores and macropores developing best, which can simultaneously enrich free gas and adsorbed gas. The pore structure of coal seams in the wetland forest swamp sedimentary presented two peaks, with micropores developing well and macropores developing poorly, mainly enriching adsorbed gas.
-
Keywords:
- deep coalbed methane /
- coal sedimentary /
- pore structure /
- coal macerals /
- Ordos basin
-
-
图 3 榆林地区8号反射光与荧光条件下煤岩显微组分特征
注:图3a丝质体(F)胞腔呈椭圆−圆状,保存程度较好,充填渗出沥青体(Ex)和黏土矿物;图3b与图3a为同一视域下的荧光图像,渗出沥青体发橘黄色荧光;图3c为基质镜质体(C1)和惰屑体(Id);图3d与图3c为同一视域下的荧光图像;图3e 为丝质体(F),胞腔呈椭圆−圆状,保存好,充填渗出沥青体(Ex)和黏土矿物;图3f与图3e为同一视域下的荧光图像,渗出沥青体橘黄色荧光;图3g基质镜质体(C1)和均质镜质体(T2)呈条带式分布;图3h与图3g为同一视域下的荧光图像,渗出沥青体发橘黄色荧光,均质镜质体发出很弱的褐色荧光,惰质体不发荧光;图3i为基质镜质体(C1)胶结惰屑体(Id)和矿物(Ca); 图3j与图3i为同一视域下的荧光图像,矿物(Ca)呈现浅绿色荧光; 图3k均质镜质体(C1)、结构镜质体(T2)呈条带式展布,胞腔中充填渗出沥青体;图3m与图3k为同一视域下的荧光图像,渗出沥青体发橘黄−黄色荧光。
Figure 3. Microscopic composition characteristics of coal and rock under No. 8 reflected light and fluorescence conditions in Yulin area
图 9 榆林地区8号煤中常见组分中气泡孔和组织孔
注:图9b为图9a中局部放大(红框);部分样品基质镜质体(C1)也可见稀疏带状气孔群(图9c、9d),图9d为图9c中局部放大(红框),丝质体(F)中发育植物原始孔隙,多为黏土矿物充填(图9e、9f),图9f为图9e中局部放大(红框);团块镜质体(C2)中发育少量气孔(图9g、图9h),图9h为图9g中局部放大(红框);结构镜质体(T1)中发育原始组织孔,充填严重(图9i、图9j),图9j为图9i中局部放大(红框);均质镜质体(T2)基本看不到气孔(图9k、图9l),图9l为图9k中均质镜质体(T2)局部放大(红框);BSE为背散射成像模式。
Figure 9. Typical pores and plant tissue pores of No. 8 coal seam in Yulin area
表 1 榆林地区8号煤储层显微组分与工业分析
Table 1 Microscopic composition and industrial analysis of No. 8 coal reservoir in Yulin area
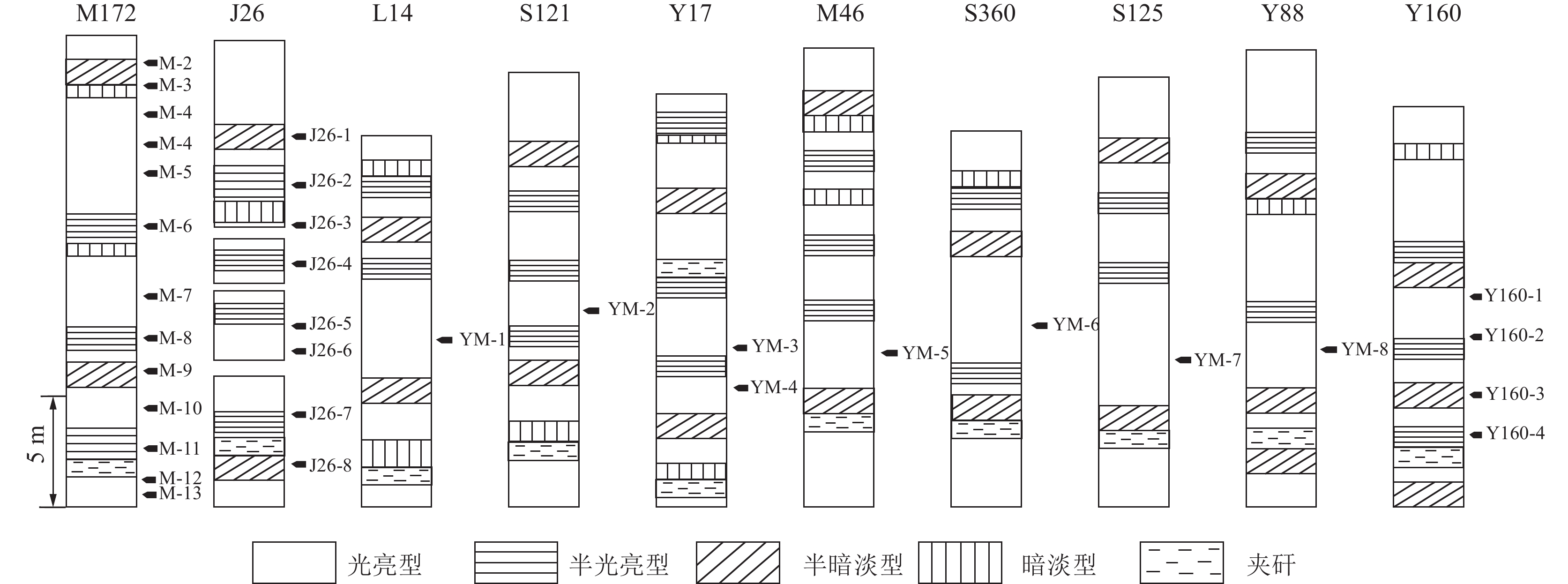
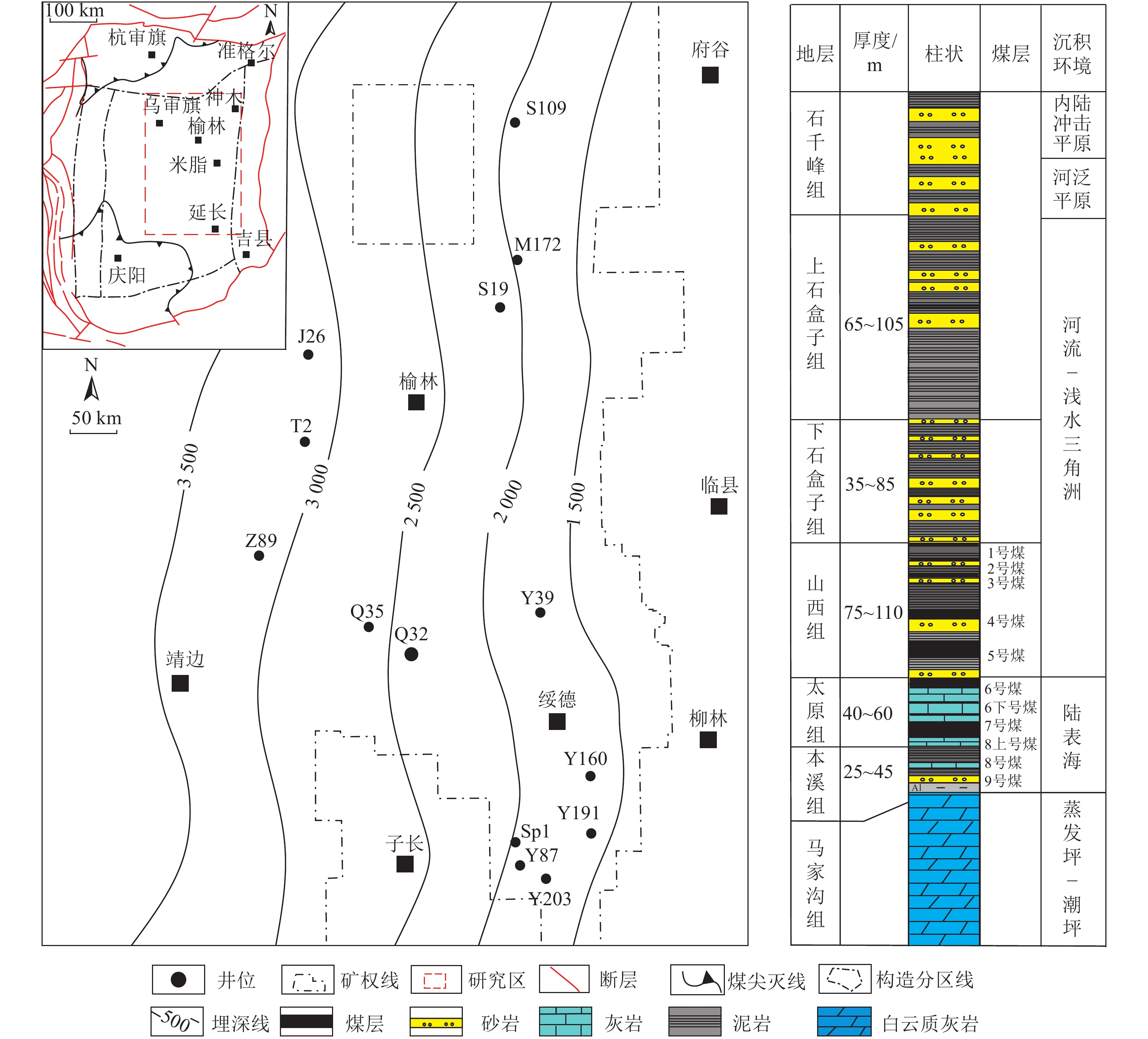
编号 煤层 井深/m 镜质组/% 惰性组 /% 壳质组/% Ro,max/% Mad/% Aad/% Vad/% FCad/% Gc/(m3·t−1) 井位 M-2 8号煤 2 426.22 47.22 20.48 32.30 1.76 0.65 22.84 12.75 63.76 14.85 M172 M-3 8号煤 2 427.27 50.51 31.96 17.53 1.77 0.98 12.69 12.16 74.17 15.40 M172 M-4 8号煤 2 427.89 65.55 31.76 2.69 1.77 0.65 17.38 15.70 66.27 23.63 M172 M-5 8号煤 2 428.65 54.88 41.13 3.99 1.77 0.65 12.23 11.95 75.17 18.05 M172 M-6 8号煤 2 429.29 59.80 40.20 0 1.83 0.79 21.46 11.81 65.94 21.48 M172 M-7 8号煤 2 429.90 34.15 49.82 16.03 1.77 1.09 11.04 11.54 76.33 20.07 M172 M-8 8号煤 2 430.55 60.20 30.51 9.29 1.76 0.66 42.17 11.93 45.24 22.85 M172 M-9 8号煤 2 431.01 61.18 36.25 2.57 1.76 0.98 35.42 11.88 51.72 12.97 M172 M-10 8号煤 2 431.69 43.59 30.76 25.65 1.76 0.93 16.46 11.89 70.72 17.30 M172 M-11 8号煤 2 432.60 60.76 34.72 4.52 1.76 0.79 19.43 11.96 67.82 22.55 M172 M-12 8号煤 2 433.25 47.31 34.05 18.64 1.74 0.70 17.47 12.84 68.99 17.50 M172 M-13 8号煤 2 434.08 41.45 41.46 17.09 1.75 0.72 17.63 13.13 68.52 16.73 M172 J26-1 5号煤 3 031.44 59.44 31.81 8.75 1.83 0.65 28.86 12.21 58.28 16.93 J26 J26-2 5号煤 3 032.86 28.61 70.71 0.68 1.81 0.73 26.28 12.70 60.29 11.01 J26 J26-3 5号煤 3 033.81 48.59 37.24 14.17 1.75 0.68 27.85 12.53 58.94 9.82 J26 J26-4 6号煤 3 066.10 52.47 36.12 11.41 1.79 0.64 32.44 11.76 55.16 14.59 J26 J26-5 7号煤 3 083.45 58.82 40.13 1.05 1.74 0.77 7.95 9.96 81.32 12.89 J26 J26-6 7号煤 3 094.36 39.58 46.99 13.43 1.76 0.68 38.29 9.17 51.86 16.93 J26 J26-7 8号煤 3 101.17 51.36 39.79 8.85 1.73 0.89 9.66 10.09 79.36 15.25 J26 J26-8 8号煤 3 110.14 37.07 38.13 24.80 1.73 0.69 26.28 10.25 62.78 — J26 Y-M1 8号煤 4 101.00 95.80 0.30 0.60 1.65 0.65 11.23 14.34 73.78 — L14 Y-M2 8号煤 2 737.26 95.40 0 3.80 1.75 0.64 11.44 14.04 73.88 — S121 Y-M3 8号煤 2 508.45 92.90 3.10 0 1.63 0.68 5.66 11.32 82.34 — Y17 Y-M4 8号煤 2 509.60 81.00 13.90 0 1.86 0.45 7.44 15.40 76.71 — Y17 Y-M5 8号煤 2 230.34 92.10 1.80 0.10 1.56 0.65 12.23 12.43 74.69 — M46 Y-M6 8号煤 2 942.02 95.40 0.50 3.20 1.58 0.76 7.11 11.34 80.79 — S360 Y-M7 8号煤 2 472.60 96.00 1.40 0.20 1.66 0.87 6.44 14.49 78.2 — S125 Y-M8 8号煤 2 506.02 96.60 0.70 0.20 1.64 0.97 5.90 14.95 78.18 — Y88 Y160-1 8号煤 2 670.00 75.50 17.70 6.80 1.87 0.78 11.23 15.64 72.35 — Y160 Y160-2 8号煤 2 720.00 71.20 28.60 0.20 1.85 0.73 13.42 16.75 69.10 — Y160 Y160-3 8号煤 2 770.00 67.10 31.90 1.00 1.86 0.94 12.64 17.54 68.88 — Y160 Y160-4 8号煤 2 820.00 66.50 24.51 8.99 1.85 0.84 10.40 15.50 73.26 — Y160 注:Ro,max为油浸下镜质体最大反射率;Gc为含气量。 表 2 榆林地区8号煤主要煤相参数
Table 2 Main coal facie parameters of No. 8 coal in Yulin area
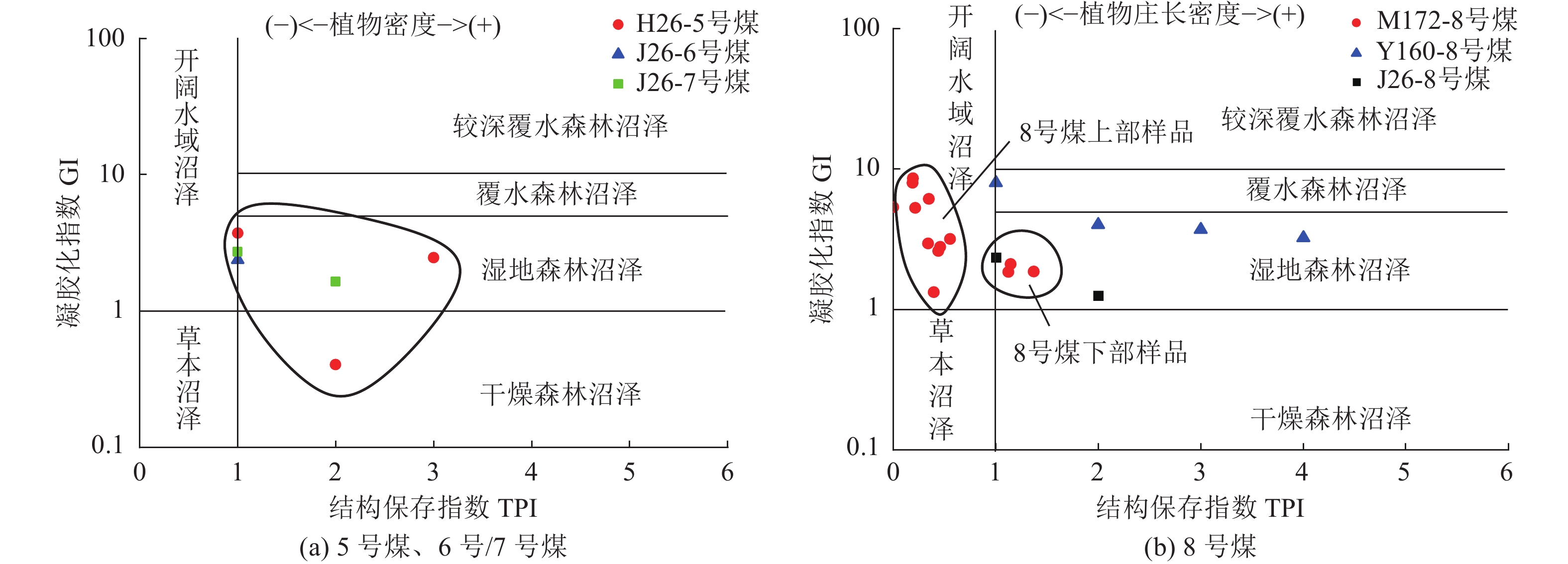
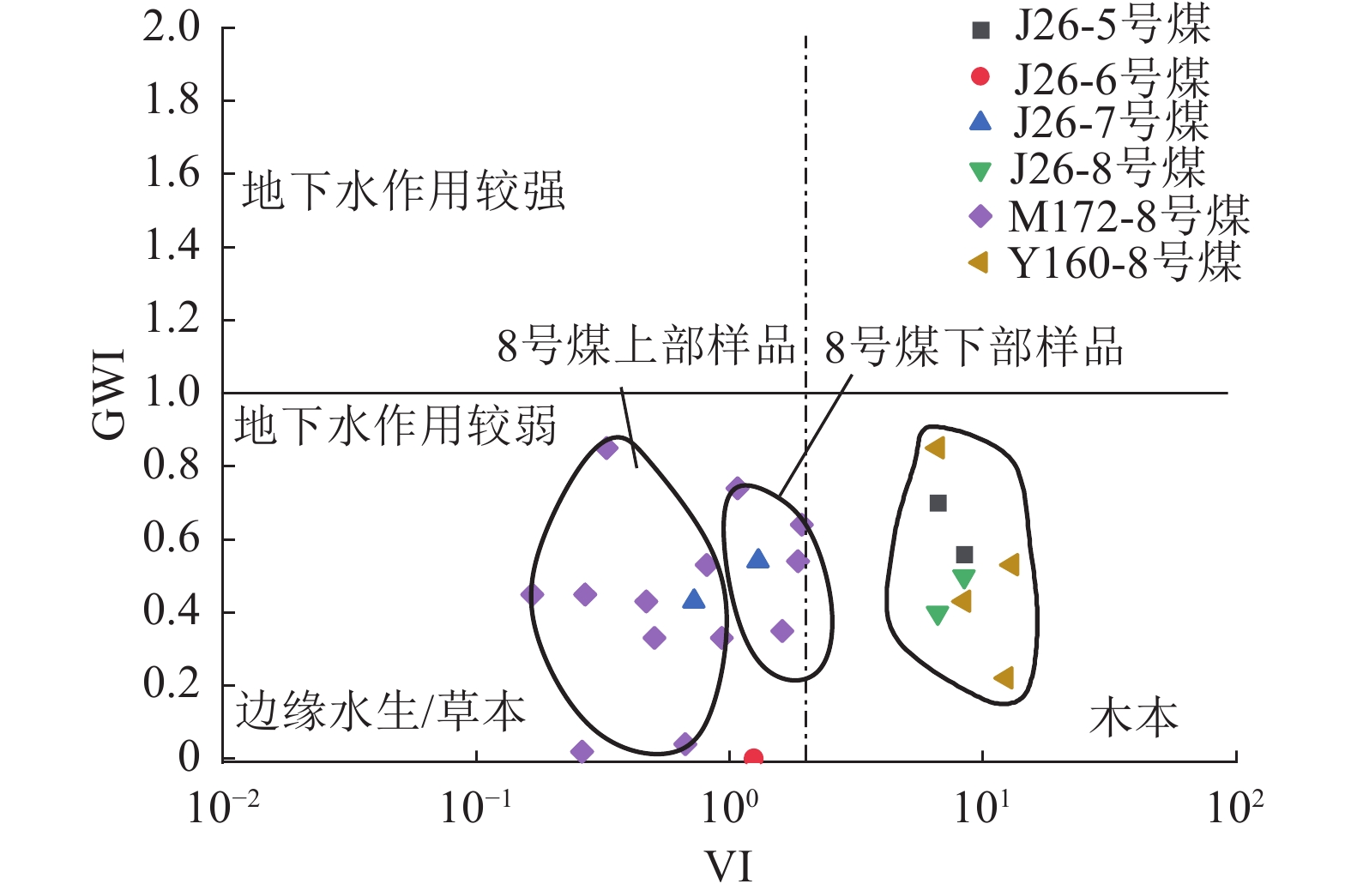
编号 煤层 井深/m 镜质组/% 惰性组/% 壳质组/% GI TPI V/I F/% D/% T/% F/M GWI VI 井号 M-1 8号煤 2425.45 60.62 31.09 8.29 2.79 0.46 1.90 22.90 66.99 10.11 0.30 0.04 0.67 M172 M-2 8号煤 2426.22 47.22 20.48 32.30 6.12 0.35 2.30 6.94 81.60 11.46 0.07 0.43 0.47 M172 M-3 8号煤 2427.27 50.51 31.96 17.53 2.95 0.34 1.60 18.90 76.29 4.81 0.42 0.33 0.50 M172 M-4 8号煤 2427.89 65.55 31.76 2.69 5.29 0.22 2.10 11.49 83.10 5.41 0.23 0.45 0.27 M172 M-5 8号煤 2428.65 54.88 41.13 3.99 2.11 1.15 1.30 27.28 48.48 24.24 1.31 0.35 1.61 M172 M-6 8号煤 2429.29 59.80 40.20 0.00 3.17 0.56 1.50 18.58 63.51 17.91 0.66 0.53 0.81 M172 M-7 8号煤 2429.90 34.15 49.82 16.03 1.32 0.40 0.70 30.66 67.94 1.40 0.73 0.33 0.93 M172 M-8 8号煤 2430.55 60.20 30.51 9.29 2.61 0.44 2.00 22.45 56.47 21.08 0.85 0.74 1.08 M172 M-9 8号煤 2431.01 61.18 36.25 2.57 8.55 0.19 1.70 6.22 82.78 11.00 0.25 0.85 0.33 M172 M-10 8号煤 2431.69 43.59 30.76 25.65 5.36 0.00 1.40 7.69 92.31 0.00 0.13 0.45 0.17 M172 M-11 8号煤 2432.60 60.76 34.72 4.52 7.97 0.19 1.80 4.51 85.77 9.72 0.20 0.02 0.26 M172 M-12 8号煤 2433.25 47.31 34.05 18.64 1.86 1.37 1.40 26.17 51.25 22.58 1.62 0.54 1.86 M172 M-13 8号煤 2434.08 41.45 41.46 17.09 1.85 1.12 1.00 26.91 53.82 19.27 1.30 0.64 1.92 M172 J26-1 5号煤 3031.44 59.44 31.81 8.75 3.73 0.14 1.90 15.73 84.27 0.00 0.22 0.56 0.25 J26 J26-2 5号煤 3032.86 28.61 70.71 0.68 0.40 3.52 0.40 69.03 29.96 1.01 4.00 0.70 4.00 J26 J26-3 5号煤 3033.81 48.59 37.24 14.17 2.46 0.58 1.30 23.05 68.08 8.87 0.73 0.09 0.89 J26 J26-4 6号煤 3066.10 52.47 36.12 11.41 2.38 0.85 1.50 22.05 56.28 21.67 0.97 0.43 1.25 J26 J26-5 7号煤 3083.45 58.82 40.13 1.05 2.72 0.79 1.50 23.18 52.95 23.87 1.03 0.54 1.30 J26 J26-6 7号煤 3094.36 39.58 46.99 13.43 1.64 0.36 0.80 29.68 70.32 0.00 0.57 0.43 0.72 J26 J26-7 8号煤 3101.17 51.36 39.79 8.85 2.34 1.05 1.30 23.81 51.02 25.17 1.20 0.50 1.80 J26 J26-8 8号煤 3110.14 37.07 38.13 24.80 1.25 1.26 1.00 28.68 57.33 13.99 1.38 0.40 1.63 J26 Y-M1 8号煤 4101.00 55.80 43.60 0.60 2.56 1.56 1.30 24.47 22.30 53.23 2.32 0.12 2.54 L14 Y-M2 8号煤 2737.26 55.40 40.80 3.80 3.20 1.57 1.40 35.12 19.54 45.34 1.43 0.63 3.54 S121 Y-M3 8号煤 2508.45 62.90 37.10 0.00 3.42 1.98 1.70 18.23 25.33 56.44 1.42 0.54 3.75 Y17 Y-M4 8号煤 2509.60 81.20 18.80 0.00 2.65 1.43 4.30 25.81 16.65 57.54 1.53 0.43 3.98 Y17 Y-M5 8号煤 2230.34 74.30 25.60 0.10 2.55 2.53 2.90 31.12 16.45 52.43 1.43 0.43 4.63 M46 Y-M6 8号煤 2942.02 75.40 21.40 3.20 3.44 2.43 3.50 37.24 17.54 45.22 1.63 0.54 4.86 S360 Y-M7 8号煤 2472.60 76.40 23.40 0.20 2.95 2.45 3.30 45.12 19.54 35.34 0.54 0.89 4.65 S125 Y-M8 8号煤 2506.02 74.40 25.40 0.20 2.85 2.64 2.90 46.92 17.44 35.64 0.55 0.43 5.54 Y88 Y160-1 8号煤 2670.00 75.50 43.60 6.80 2.57 1.87 4.30 2.80 23.20 74.00 0.43 0.43 5.74 Y160 Y160-2 8号煤 2720.00 71.20 43.60 0.20 2.85 2.53 2.50 7.80 21.00 71.20 0.54 0.85 5.34 Y160 Y160-3 8号煤 2770.00 67.10 43.60 1.00 2.60 2.75 2.10 14.70 18.20 67.10 0.53 0.22 4.54 Y160 Y160-4 8号煤 2820.00 66.50 43.60 8.99 2.75 2.95 2.70 16.90 16.60 66.50 0.64 0.53 3.23 Y160 注:GI为凝胶化指数;TPI为结构保存指数;V/I为镜惰比;T、F、D分别为结构镜质体、丝质体、分散组分体积分数;F/M为骨基比;GWI为地下水活跃指数;VI为植被指数。 表 3 榆林地区与邻区8号煤储层参数对比
Table 3 Comparison of reservoir parameters of No. 8 coal in Yulin area and neighboring areas
地区 深度/m 镜质组
体积分数/%惰性组
体积分数/%壳质组
体积分数/%Ro,max/% Mad/% Aad/% Vad/% FCad/% 来源 榆林地区 2 500~3 200 52.22 35.26 12.53 1.77 0.80 20.52 12.46 66.22 本文测试 大宁—吉县地区 1 200~2 300 84.22 10.26 5.52 2.15 0.79 17.97 10.17 71.07 文献[31] 延川南地区 1 500~1 800 71.28 27.62 1.10 2.35 0.61 8.94 13.78 76.68 文献[18,20,26] 保德地区 1 000~1 200 75.03 24.04 0.93 1.11 0.81 7.92 13.30 77.97 文献[31] -
[1] 徐凤银,王成旺,熊先钺,等. 深部(层)煤层气成藏模式与关键技术对策:以鄂尔多斯盆地东缘为例[J]. 中国海上油气,2022,34(4):30−42,262. XU Fengyin,WANG Chengwang,Xiong Xianyue ,et al. Deep (layer) coalbed methane reservoir forming modes and key technical countermeasures:taking the eastern margin of Ordos Basin as an example[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas,2022,34(4):30−42,262.
[2] 秦勇,申建,沈玉林. 叠置含气系统共采兼容性—煤系“三气”及深部煤层气开采中的共性地质问题[J]. 煤炭学报,2016,41(1):14−23. QIN Yong,SHEN Jian,SHEN Yulin. Joint mining compatibility of superposed gas-bearing systems:a general geological problem for extraction of three natural gases and deep CBM in coal series[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2016,41(1):14−23.
[3] 秦勇,申建,王宝文,等. 深部煤层气成藏效应及其耦合关系[J]. 石油学报,2012,33(1):48−54. doi: 10.7623/syxb201201006 QIN Yong,SHEN Jian,WANG Baowen,et al. Accumulation effects and coupling relationship of deep coalbed methane[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2012,33(1):48−54. doi: 10.7623/syxb201201006
[4] 申建,秦勇,傅雪海,等. 深部煤层气成藏条件特殊性及其临界深度探讨[J]. 天然气地球科学,2014,25(9):1470−1476. SHEN Jian,QIN Yong,FU Xuehai,et al. Properties of deep coalbed methane reservoir forming conditions and critical depth discussion[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience,2014,25(9):1470−1476.
[5] 何发岐,董昭雄,赵兰,等. 深部煤层游离气形成机理及资源意义[J]. 断块油气田,2021,28(5):604−608,613. HE Faqi,DONG Zhaoxiong,ZHAO Lan,et al. Formation mechanism and resource significance of free gas in deep coalbed[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field,2021,28(5):604−608,613.
[6] 何发岐,董昭雄. 深部煤层气资源开发潜力:以鄂尔多斯盆地大牛地气田为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2022,43(2):277−285. doi: 10.11743/ogg20220203 HE Faqi,DONG Zhaoxiong. Development potential of deep coalbed methane:a case study in the Daniudi gas field,Ordos Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology,2022,43(2):277−285. doi: 10.11743/ogg20220203
[7] 陈贞龙,郭涛,李鑫,等. 延川南煤层气田深部煤层气成藏规律与开发技术[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2019,47(9):112−118. CHEN Zhenlong,GUO Tao,LI Xin,et al. Enrichment law and development technology of deep coalbed methane in South Yanchuan Coalbed Methane Field[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2019,47(9):112−118.
[8] 姚红生,陈贞龙,何希鹏,等. 深部煤层气“有效支撑”理念及创新实践:以鄂尔多斯盆地延川南煤层气田为例[J]. 天然气工业,2022,42(6):97−106. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2022.06.009 YAO Hongsheng,CHEN Zhenlong,HE Xipeng,et al. "Effective support" concept and innovative practice of deep CBM in south Yanchuan gas field of the Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2022,42(6):97−106. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2022.06.009
[9] 刘玉龙,汤达祯,许浩,等. 煤岩类型控制下的微观孔隙结构及吸附特征研究[J]. 煤炭工程,2016,48(11):107−110. doi: 10.11799/ce201611031 LIU Yulong,TANG Dazhen,XU Hao,et al. Study on microscopic pores structure and adsorption characteristics of different lithotypes[J]. Coal Engineering,2016,48(11):107−110. doi: 10.11799/ce201611031
[10] 王博洋,秦勇,申建,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地紫金山地区煤孔隙分形规律及其主控地质因素分析[J]. 高校地质学报,2017,23(3):499−510. WANG Boyang,QIN Yong,SHEN Jian,et al. The fractal regularity of coal porosity and its controlling geological factors in Zijinshan area[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities,2017,23(3):499−510.
[11] 王 锐,夏玉成,马丽. 榆神矿区富油煤赋存特征及其沉积环境研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2020,48(12):192−197. WANG Rui,XIA Yucheng,MA Li. Study on oil-rich coal occurrence characteristics and sedimentary environment in Yushen Mining Area[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2020,48(12):192−197.
[12] 秦勇,申建. 论深部煤层气基本地质问题[J]. 石油学报,2016,37(1):125−136. QIN Yong,SHEN Jian. On the fundamental issues of deep coalbed methane geology[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2016,37(1):125−136.
[13] STACH E,MACKOWSKY M,TEICHMÜLLER M,et al. 斯塔赫煤岩学教程[M]. 杨起,李宝芳,黄家福,译. 北京:煤炭工业出版社,1990. [14] DIESSEL C. Utility of coal petrology for sequence-stratigraphic analysis[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology,2007,70(1/2/3):3−34.
[15] CALDER J H,GIBBING M R,MUKHOPADHAY P K. Peat formation in a Westphalian B pidemont setting. Cumberland Basin,Nova Scotia:implication for the maceral-based interpretation of rheotrophic and raised Paleomires[J]. BullSocGeol Fr,1991,162(2):283−298.
[16] MARQUES M. Coal facies and depositional environments of the Aurora and Cabeza de Vaca Units,Peñarroya–Belmez–Espiel Coalfield (Cordoba,Spain)[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology,2002,48(34):197−216.
[17] HARVEY R D,DILLON J W. Maceral distributions in Illinois coals and their paleoenvironmental implications[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology,1985,5(12):141−165.
[18] 李清. 山西延川南煤层气田2号煤层煤相研究:煤层气开发选区意义[J]. 石油实验地质,2014,36(2):245−248,256. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201402245 LI Qing. Coal facies of No. 2 coal in Yanchuannan coal field of Shanxi:Significance for constituencies of coalbed methane exploitation[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment,2014,36(2):245−248,256. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201402245
[19] 桑树勋,皇凡生,单衍胜,等. 碎软低渗煤储层强化与煤层气地面开发技术进展[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2024,52(1):196−210. SANG Shuxun,HUANG Fansheng,SHAN Yansheng,et al. Technology processes of enhancement of broken soft and low permeability coal reservoir and surface development of coalbed methane[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2024,52(1):196−210.
[20] 申艳军,王旭,师庆民,等. 榆神府矿区富油煤煤相及孔隙结构特征试验研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2021,52(10):30−37,44. SHEN Yanjun,WANG Xu,SHI Qingmin,et al. Coal facies characteristics and pore structure response of oil-rich coal in Yushenfu Mining Area[J]. Safety in Coal Mines,2021,52(10):30−37,44.
[21] 陈瑞银,罗晓容,陈占坤,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地埋藏演化史恢复[J]. 石油学报,2006,27(2):43−47. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2006.02.009 CHEN Ruiyin,LUO Xiaorong,CHEN Zhankun,et al. Restoration of burial history of four periods in Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2006,27(2):43−47. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2006.02.009
[22] MARCHIONI D,KALKREUTH W. Coal facies interpretations based on lithotype and maceral variations in Lower Cretaceous (Gates Formation) coals of Western Canada[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology,1991,18(12):125−162.
[23] OBAJE N G,LIGOUIS B. Petrographic evaluation of the depositional environments of the Cretaceous Obi/Lafia coal deposits in the Benue Trough of Nigeria[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences,1996,22(2):159−171. doi: 10.1016/0899-5362(96)00003-6
[24] 许福美,方爱民. 山东兖州矿区太原组16号煤层煤相研究[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2005,33(4):10−13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2005.04.003 XU Fumei,FANG Aimin. Coal facies analysis upon No. 16 coal seam in Yanzhou coal mining area of Shangdong Province[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2005,33(4):10−13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2005.04.003
[25] 代世峰,任德贻,李生盛,等. 内蒙古准格尔黑岱沟主采煤层的煤相演替特征[J]. 中国科学(D辑:地球科学),2007(S1):119−126. DAI Shifeng,REN Deyi,LI Shengsheng,et al. Coal facies succession characteristics of main coal seam in Heidaigou,Zhungeer,Inner Mongolia[J]. Science China:Earth Sciences,2007(S1):119−126.
[26] 马伟竣. 鄂尔多斯盆地延川南2号煤层煤相分析[J]. 中国煤层气,2014,11(2):25−29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3074.2014.02.006 MA Weijun. Analysis of Coal Facies of No. 2 Coal Seam in Yanchuannan Block of Erdos Basin[J]. China Coalbed Methane,2014,11(2):25−29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3074.2014.02.006
[27] 武志威,郑刘根,韩必武,等. 张集矿山西组1煤层煤相及泥炭沼泽演化特征[J]. 安徽理工大学学报(自然科学版),2022,42(3):65−77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1098.2022.03.010 WU Zhiwei,ZHENG Liugen,HAN Biwu et al. Coal facies and peat swamp evolution of NO. 1 coal seam in Shanxi Formation in Zhangji Mine[J]. Journal of Anhui University of Science and Technology:Natural Science,2022,42(3):65−77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1098.2022.03.010
[28] 姚艳斌,刘大锰,蔡益栋,等. 基于NMR和X-CT的煤的孔裂隙精细定量表征[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,2010,40(11):1598−1607. YAO Yanbin,LIU Dameng,CAI Yidong,et al. Advanced characterization of pores and fractures in coals by nuclear magnetic resonance and X-ray computed tomography[J]. Sci China Earth Sci,2010,40(11):1598−1607.
[29] 刘彦飞,汤达祯,许浩,等. 基于核磁共振的煤岩孔裂隙应力变形特征[J]. 煤炭学报,2015,40(6):1415−1421. LIU Yanfei,TANG Dazhen,XU Hao,et al. Characteristics of the stress deformation of pore-fracture in coal based on nuclear magnetic resonance[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2015,40(6):1415−1421
[30] ZHENG S J, YAO Y, LIU D M, et al. Nuclear magnetic resonance surface relaxivity of coals[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology,2019,205:1−13.
[31] 田文广. 鄂尔多斯盆地东缘煤层气富集规律与控制机制研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2012. TIAN Wenguang. CBM enrichment rules of eastern Ordos basin and controlling mechanism[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences (Beijing),2012.
[32] 任会康,王安民,李昌峰,等. 基于核磁共振技术的低阶煤储层孔隙特征研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2017,45(4):143−148. REN Huikang,WANG Anmin,LI Changfeng,et al. Study on porosity characteristics of low-rank coal reservoirs based on nuclear magnetic resonance technology[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2017,45(4):143−148.
[33] 胡社荣,潘响亮,张喜臣,等. 煤相研究方法综述[J]. 地质科技情报,1998,17(1):63−67. HU Rongshe,PAN Xiangliang,ZHANG Xichen,et al. Overview of research methods of coal facies[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,1998,17(1):63−67.
[34] 李静琴,李明培,樊俊雷. 吐哈盆地三道岭剖面西山窑组煤层煤相分析[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2018,46(2):97−102. LI Jingqin,LI Mingpei,FAN Junlei. Analysis on coal facies of seam in Xishanyao Formation of Sandaoling Section in Turpan-Hami Basin[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2018,46(2):97−102.
[35] 雷国明,周继兵,张东亮,等. 准东煤田五彩湾矿区西山窑组巨厚煤层煤相研究[J]. 新疆地质,2012,30(3):347−349. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2012.03.021 LEI Guoming,ZHOU Jibing,ZHANG Dongliang,et al. The coal facies research on the Xishanyan formation in the Wucaiwan coalfield Eastern Junggar Basin,Xinjiang[J]. Xinjiang Geology,2012,30(3):347−349. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2012.03.021
[36] 李玉坤,李广. 吐哈盆地沙尔湖煤田煤质煤岩特征及煤相分析[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2019,47(5):198−205. LI Yukun,LI Guang. Analysis on quality,Petrography and facies of coal seam in Shaerhu Coalfield of Turpan-Hami Basin[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2019,47(5):198−205.
[37] 张慧,吴静,袁立颖,等. 煤中气孔的发育特征与影响因素浅析[J]. 煤田地质与勘探2019,47 (1):78−85,91. ZHANG Hui,WU Jing,YUAN Liying,et al. Analysis on the development characteristics and influencing factors of gas pores in coal[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2019,47(1):78−85,91.




 下载:
下载: