Study on aggregate accumulation and growth mechanism in underground dynamic water cutting-off construction
-
摘要:
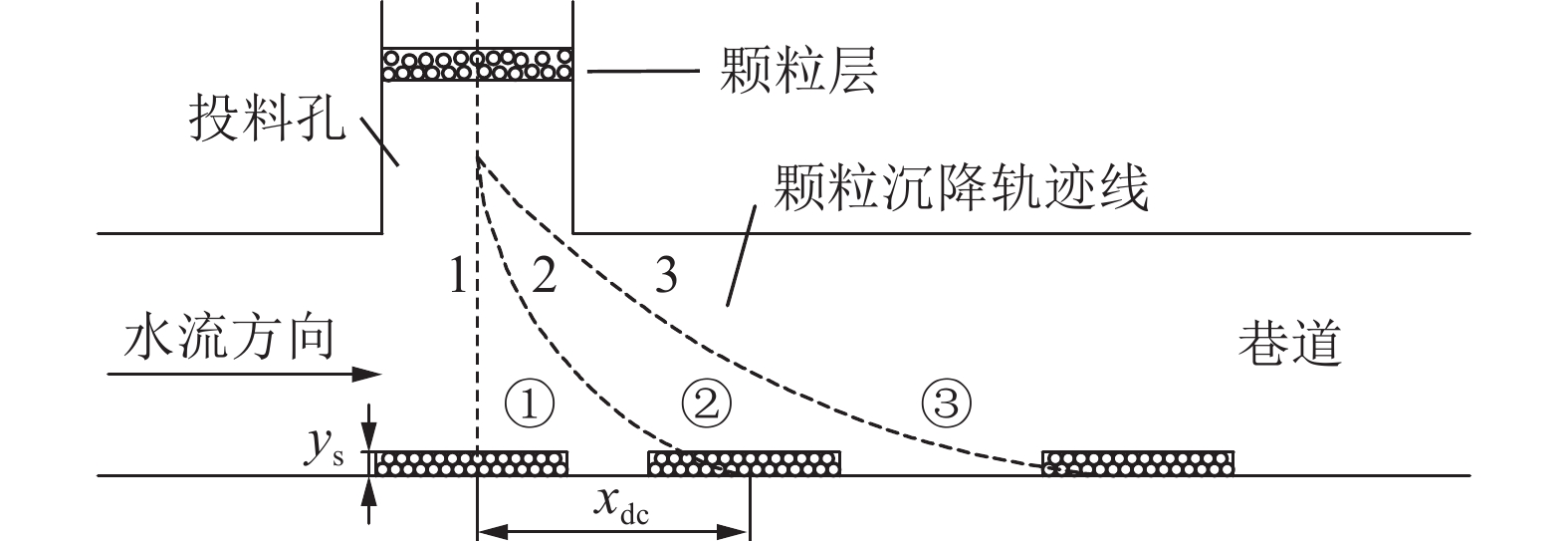
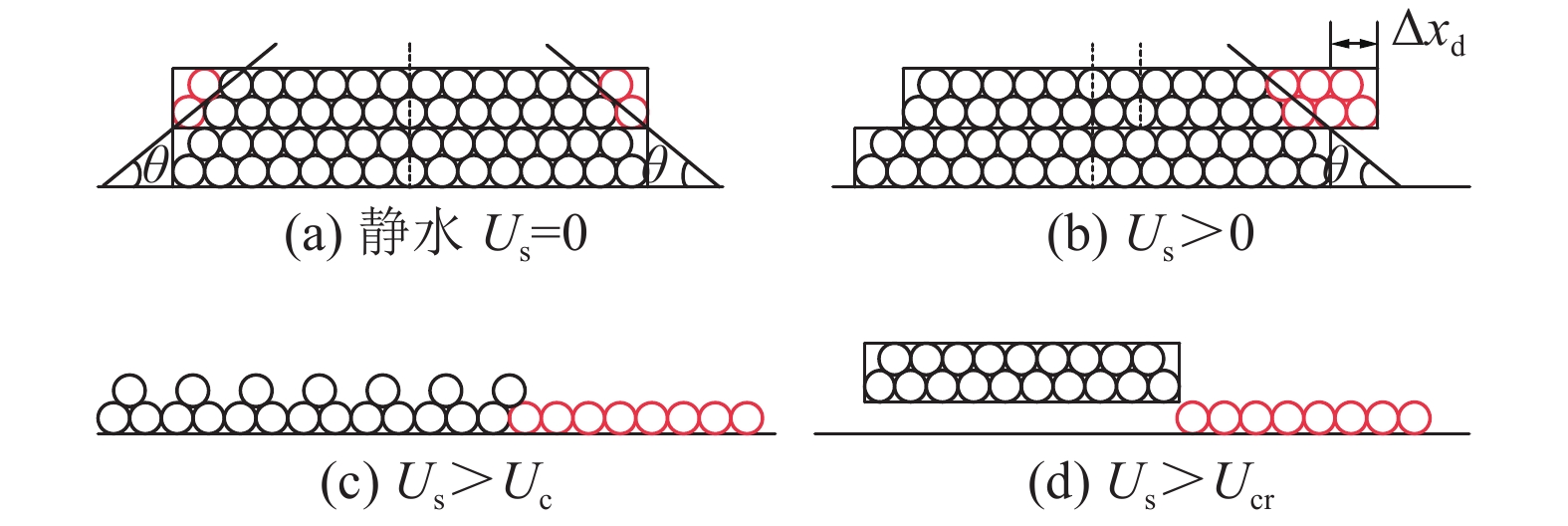
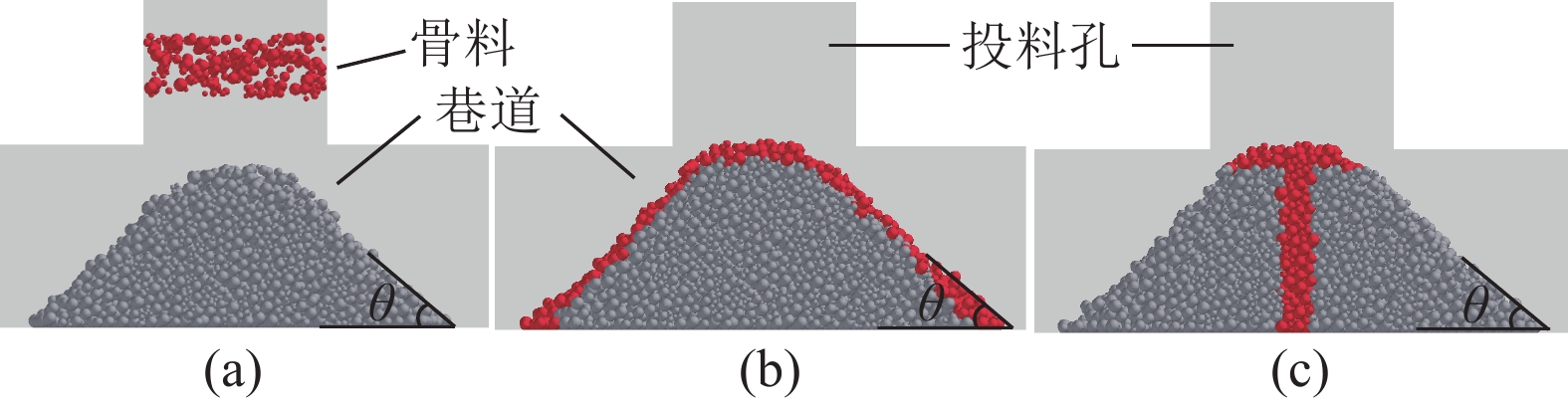
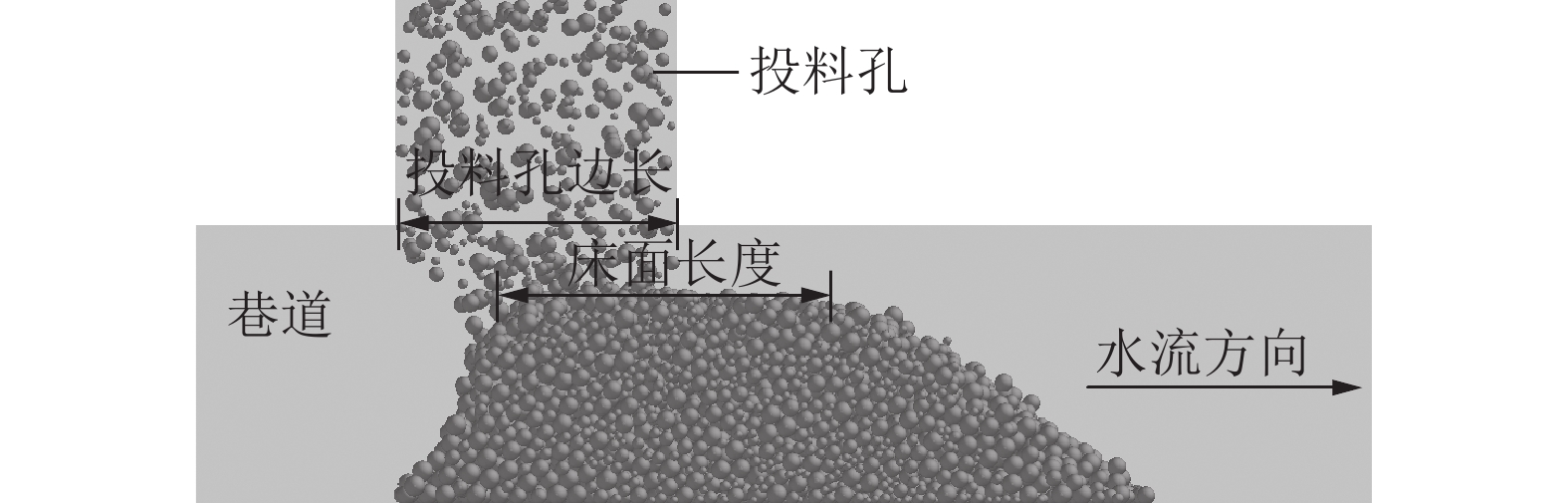
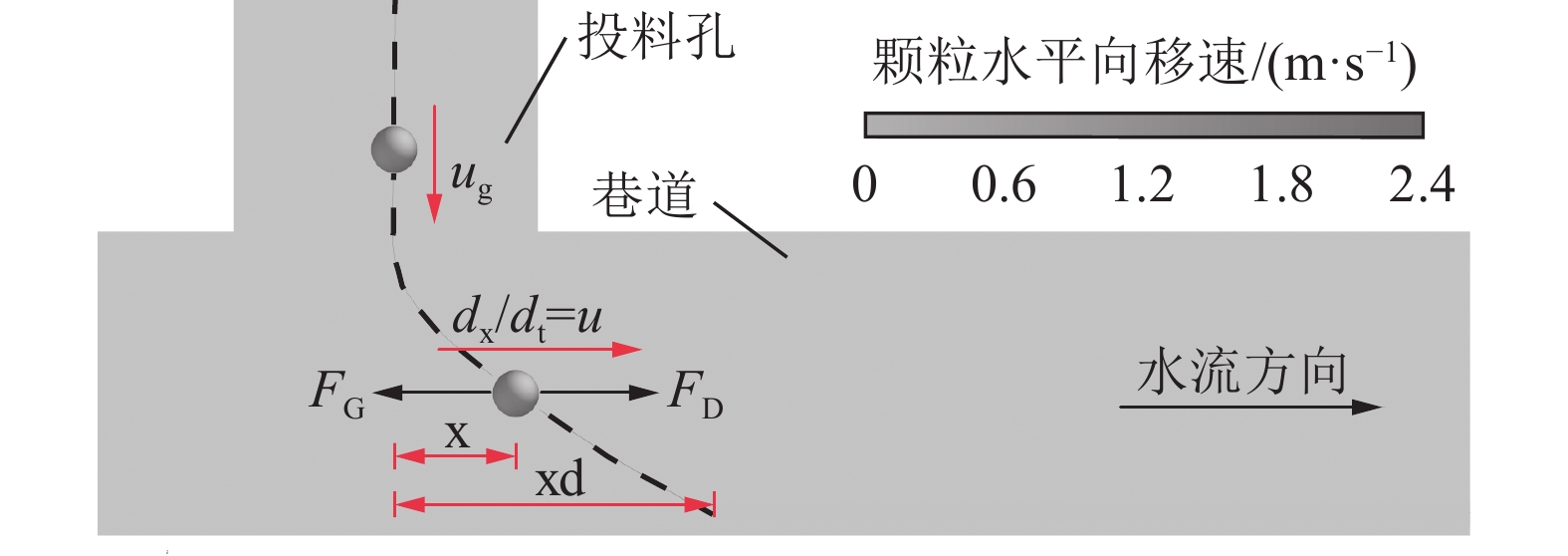
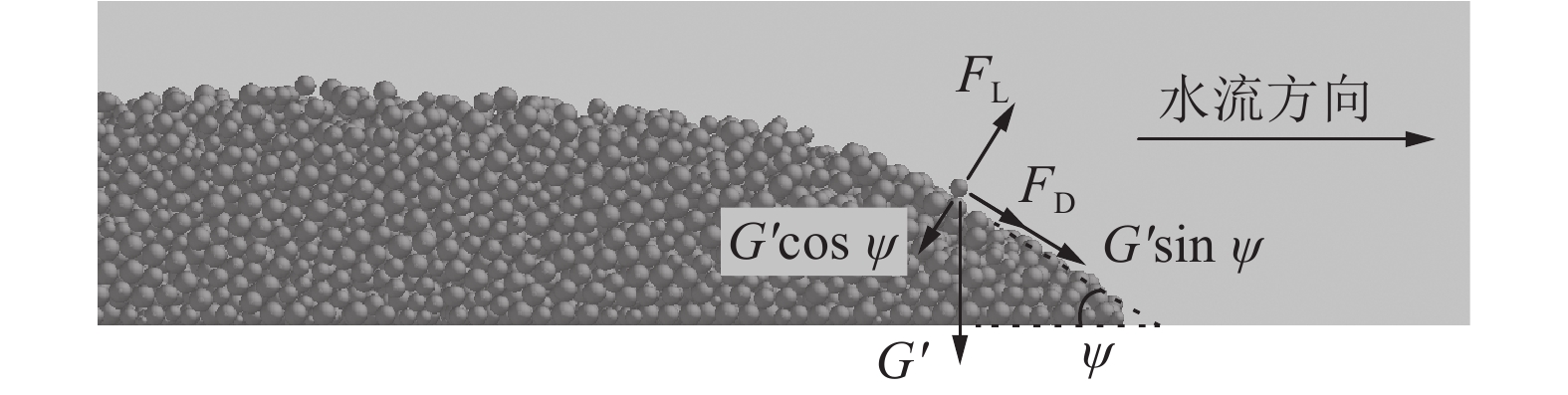
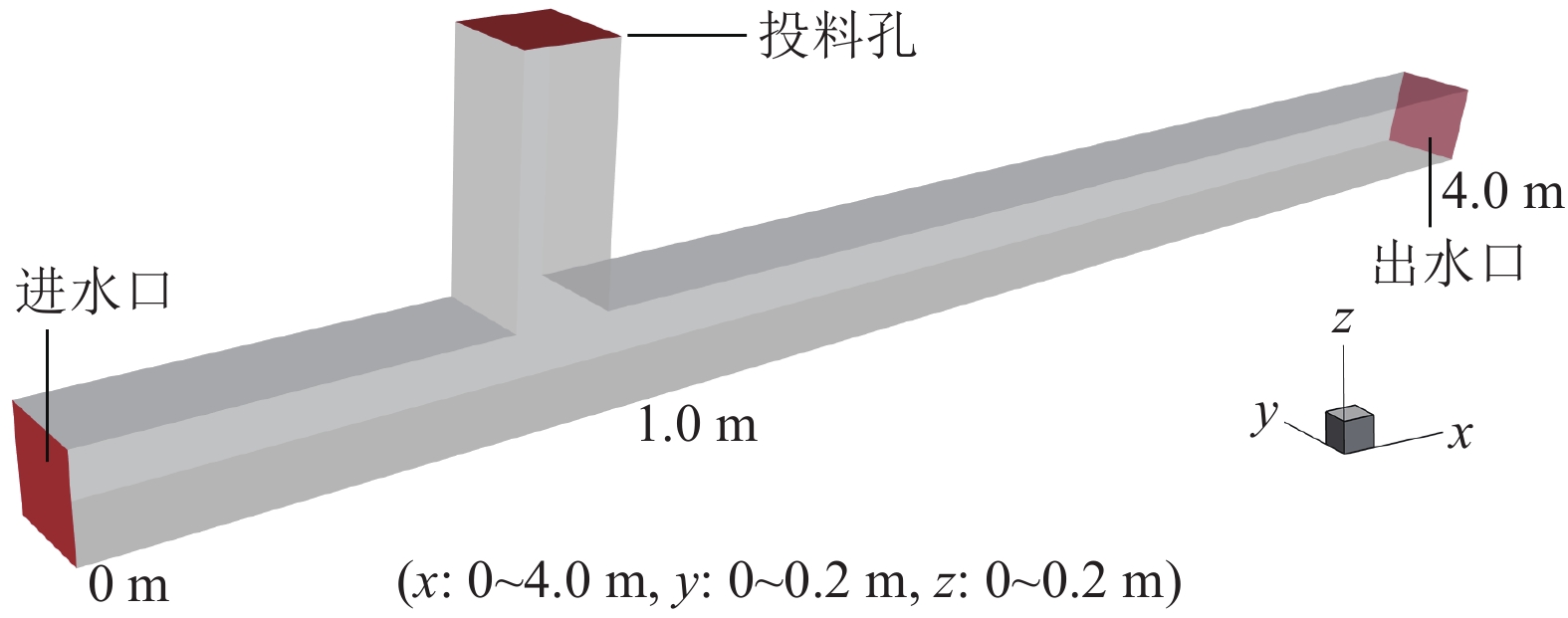
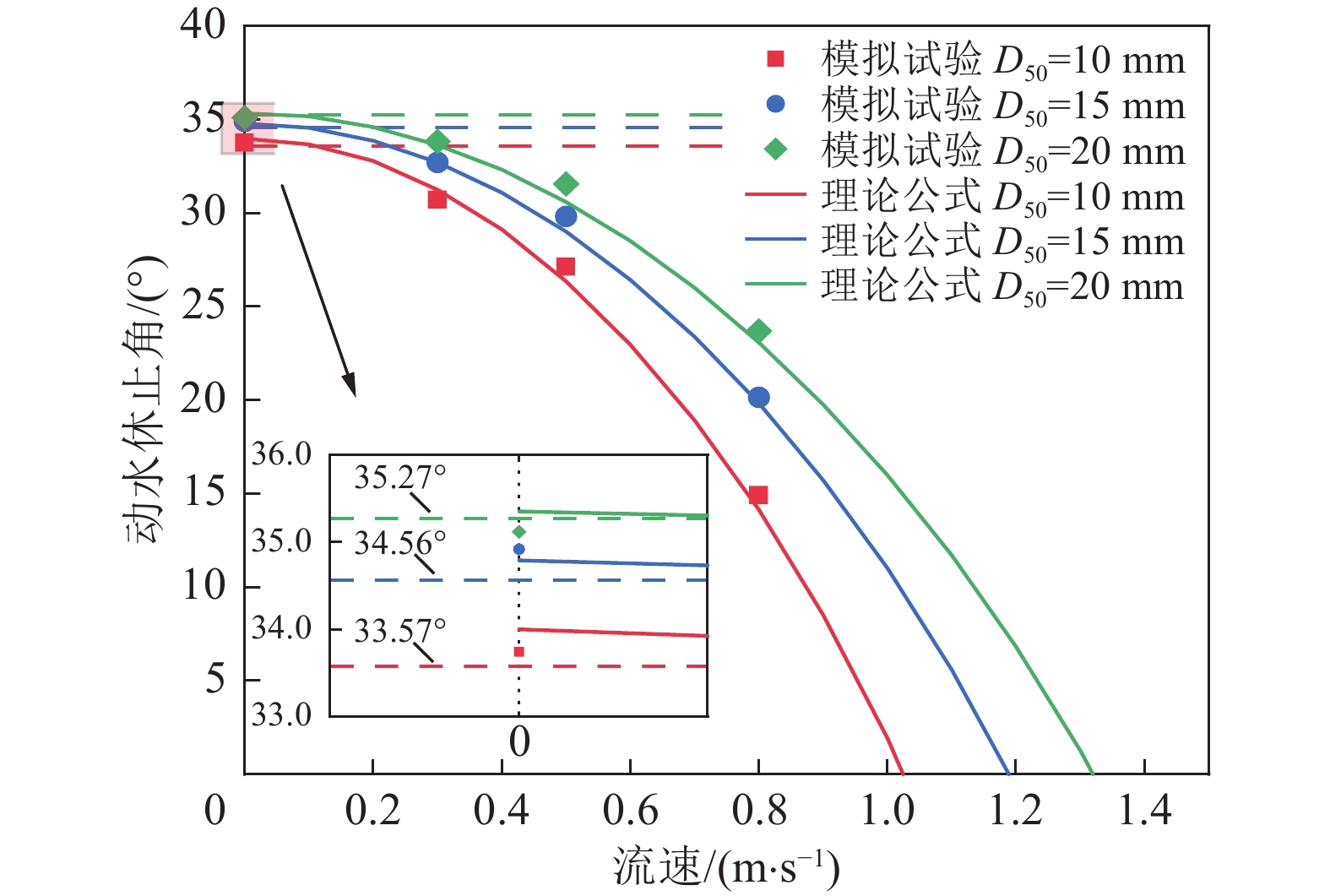
灌注骨料形成阻水屏障实现截流降速是井下治水工程的关键所在。为定量描述骨料堆积生长的时空演化机理,提出了将骨料沉降堆积过程切分为具有一定厚度的片状颗粒层堆叠过程的分析计算方法,以及动水环境中骨料灌注后从沉降到堆积全过程关键参量(颗粒水平移距xd,动水休止角ψ,未接顶区流速U,骨料留存临界流速Ucr)的理论计算公式,在此基础上构建了骨料堆积体生长预测模型。通过CFD-DEM双向耦合算法研究了骨料灌注期间流场分布演化特征和骨料堆积形态差异,并验证了预测模型合理性。研究表明:空间上,依据初始流速Us是否超过骨料起动流速Uc或骨料留存临界流速Ucr,可将截流初期骨料沉积主域的所在位置划分为3个区域,若沉积主域位于③区,则将其视为无效灌注;时间上,骨料堆积体生长过程可归结为3个阶段:高度快速增长阶段、高度长度同步生长阶段、仅水平向伸长阶段;初始流速决定了第1阶段的有无,而灌注条件(骨料粒径、灌注速度)主导着第1阶段所持续的时间;基于泥沙运动力学中推移质输沙率、起动流速等概念,得出了堵孔现象发生及骨料能否留存的临界判据;数值模拟试验结果表明,预测模型能够较好地刻画骨料灌注后的堆积生长规律,骨料堆积稳定后,理论计算值与模拟试验值相对误差小于10%。
Abstract:The key to inrush water control engineering in coal mine lies in forming a water-resistant barrier through the pouring of aggregate, which achieves flow interception and reduction. In order to quantitatively describe the spatiotemporal evolution mechanism of aggregate accumulation, an analytical calculation method is proposed to divide the process of aggregate settling and stacking into the process of particle layers superposition with a certain thickness and theoretical formulas for the entire process from settlement to pile after aggregate pouring in a dynamic water environment about critical parameters (horizontal displacement of particle xd, dynamic repose angle ψ, flow velocity in the topping zone U, critical flow velocity for aggregate retention Ucr) are proposed. Based on this, a prediction model about the growth of aggregate accumulation is constructed. The distribution characteristics of the flow field and the differences in aggregate accumulation morphology during the pouring period are studied with CFD-DEM, and the rationality of the prediction model is verified. The study reveals that spatially, the location of the main sedimentary domain during the initial interception phase can be divided into three regions, depending on whether the initial flow velocity Us exceeds the incipient flow velocity for particles Uc or the critical flow velocity for aggregate retention Ucr. That is considered ineffective pouring if the main sedimentary domain lies in region ③. Temporally, the growth process of aggregate accumulation can be summarized into three stages: a height rapid increase stage, a synchronous growth stage in height and length, and a stage with only horizontal elongation. The presence of the first stage is determined by the initial flow velocity, while the duration of the first stage is predominantly governed by the pouring conditions (particle size, pouring rate). A critical criterion for pore clogging and aggregate retention is derived based on sediment transport rate and incipient flow velocity from sediment dynamics. The numerical simulation experimental results indicate that the prediction model effectively characterizes the growth law of aggregate accumulation because the relative error between the theoretical calculation values and the simulated experiment values is less than 10% after the aggregate stacking stabilizes.
-
-
表 1 计算模型材料参数
Table 1 Material parameters used in the model
颗粒参数 流体参数 颗粒密度ρs /
(kg·m−3)弹性模量E /
(MN·m−2)泊松比v 恢复系数e 滑动摩擦因数μr 滚动摩擦因数μf 密度ρ/
(kg·m−3)动力黏度μf/
(kg·m−1·s−1)2 650 5 0.3 0.3 0.5 0.1 1 000 0.001 表 2 骨料堆积体内部孔隙率
Table 2 Porosity of aggregate accumulation
粒径/mm 初始流速/(m·s−1) 孔隙率/% 10 0 41.17 0.3 42.48 0.5 42.74 0.8 43.06 15 0 41.53 0.3 43.05 0.5 43.27 0.8 43.55 20 0 42.25 0.3 42.74 0.5 43.02 0.8 43.69 表 3 模拟试验方案
Table 3 Simulation test scheme
编号 初始流速/(m·s−1) 粒径/mm 灌注速度/(kg·s−1) 方案一 0.5 15 0.5、1.0、2.0 方案二 0.3、0.5、0.8 15 1.0 表 4 预测模型与模拟试验误差统计
Table 4 Statistical analysis of relative errors between prediction model and simulation test
t /s ey,max / % el,max / % 方案一 方案二 方案一 方案二 5 15.2 18.0 16.9 17.7 10 6.6 6.6 8.8 9.9 15 3.0 3.2 9.7 8.6 20 2.7 1.9 9.3 8.1 25 3.0 3.8 8.5 7.7 30 1.0 1.0 6.6 3.4 35 1.6 1.6 7.4 5.5 40 1.8 0.8 4.4 5.4 45 1.6 0.7 2.6 4.5 50 1.2 1.1 6.0 3.3 注:ey,max为堆积高度相对误差最大值;el,max为堆积长度相对误差最大值 -
[1] 姬中奎. 矿井大流量动水注浆细骨料截流技术[J]. 煤炭工程,2014,46(7):43−45. JI Zhongkui. Fine aggregate grouting closure technology of high flow running water in mine[J]. Coal Engineering,2014,46(7):43−45.
[2] 邵红旗,王 维. 双液注浆法快速建造阻水墙封堵突水巷道[J]. 煤矿安全,2011,42(11):40−43. SHAO Hongqi,WANG Wei. Rapid construction of water blocking wall by double liquid grouting method to block water inrush roadway[J]. Safety in Coal Mines,2011,42(11):40−43.
[3] 牟 林. 过水大断面截流堵巷工程若干关键技术问题的探讨[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(11):3525−3535. MOU Lin. Discussion on key technical problems of water cutting-off engineering in submerged roadway with large-cross section[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2021,46(11):3525−3535.
[4] 董书宁,牟 林. 突水淹没矿井动水巷道截流阻水墙建造技术研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2021,49(1):294−303. DONG Shuning,MOU Lin. Study on construction technology of water blocking wall in hydrodynamic pathway of submerged mine due to water inrush[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2021,49(1):294−303.
[5] 杨志斌,董书宁. 动水大通道突水灾害治理关键技术[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2018,46(4):110−116. YANG Zhibin,DONG Shuning. Key technology of water inrush disaster control under hydrodynamic large channel condition[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2018,46(4):110−116.
[6] 惠 爽. 矿井淹没巷道多孔灌注骨料封堵模拟试验[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2018:14-57. HUI Shuang. An experimental investigation on pouring aggregate to plug an inundated mine tunnel through boreholes[D]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology,2018:14-57.
[7] 李 军. 地铁突水抢险中粗骨料注浆快速封堵数值模拟研究[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2021:21-48. LI Jun. Numerical simulation study on rapid plugging of coarse aggregate grouting in subway water inrush rescue[D]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology,2021:21-48.
[8] 沈 淇,顾峰峰,万远扬,等. 基于泥沙随机交换过程及不同推移形式的推移质输沙公式[J]. 应用基础与工程科学学报,2023,31(3):599−610. SHEN Qi,GU Fengfeng,WAN Yuanyang,et al. A formula for bedload transport based on the stochastic sediment interchanges and the different motion patterns[J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering,2023,31(3):599−610.
[9] 牟 林,董书宁. 截流巷道骨料堆积体中浆液运移规律与阻水机制[J]. 地下空间与工程学报,2020,16(6):1891−1900. MOU Lin,DONG Shuning. Migration rule and water blocking mechanism of cement slurry in aggregate accumulation of underground tunnel closure[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering,2020,16(6):1891−1900.
[10] 陈光国,阳 宁,唐达生,等. 垂直管道颗粒及颗粒群沉降运动规律研究[J]. 泥沙研究,2010(4):16−21. CHEN Guangguo,YANG Ning,TANG Dasheng,et al. Study on the settling regularity of solid particles in vertical pipelines[J]. Journal of Sediment Research,2010(4):16−21.
[11] 苏东升. 基于CFD-DEM耦合模拟方法的水流泥沙运动研究[D]. 天津:天津大学,2015:8−21. SU Dongsheng. Study on flow and sediment movement based on CFD-DEM coupling simulation method[D]. Tianjin:Tianjin University,2015:8−21.
[12] 周宗青,李利平,石少帅,等. 隧道突涌水机制与渗透破坏灾变过程模拟研究[J]. 岩土力学,2020,41(11):3621−3631. ZHOU Zongqing,LI Liping,SHI Shaoshuai,et al. Study on tunnel water inrush mechanism and simulation of seepage failure process[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2020,41(11):3621−3631.
[13] 詹义正,寇树萍. 球体的移距及稳定移距公式[J]. 武汉水利电力大学学报,1996,29(2):85−90. ZHAN Yizheng,KOU Shuping. Equations of sphere’s falling distance[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Hydraulic and Electric Engineering,1996,29(2):85−90.
[14] 姚仕明,梁 兰,刘卫峰,等. 抛石移距规律初探[J]. 武汉水利电力大学学报,1997,30(6):24−27. YAO Shiming,LIANG Lan,LIU Weifeng,et al. Preliminary study of throwing distance of riprap[J]. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University,1997,30(6):24−27.
[15] 姚令侃,李仕雄,蒋良潍. 自组织临界性及其在散粒体研究中的应用[J]. 四川大学学报(工程科学版),2003,35(1):8−14. YAO Lingkan,LI Shixiong,JIANG Liangwei. Self-organized criticality and its application in granular mixtures[J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Engineering Science Edition),2003,35(1):8−14.
[16] 何文社,方 铎,曹叔尤,等. 泥沙起动判别标准探讨[J]. 水科学进展,2003,14(2):143−146. HE Wenshe,FANG Duo,CAO Shuyou,et al. Study on standards for incipient motion of sediment[J]. Advances In Water Science,2003,14(2):143−146.
[17] 牟 林. 动水条件巷道截流阻水墙建造机制与关键技术研究[D]. 北京:煤炭科学研究总院,2021:29−92. MOU Lin. Study on construction mechanism and key technology of water-blocking wall in hydrodynamic pathway[D]. Beijing:Chinese Institute of Coal Science,2021:29−92.
[18] 范 玉. 水沙两相流理论及引水工程管道输沙问题的研究[D]. 天津:天津大学,2014:88−110. FAN Yu. Study on the theory of water-sediment two-phase flow and the problem of sediment transport in the pipeline of water diversion project[D]. Tianjin:Tianjin University,2014:88−110.
[19] 陈 立,宋 涛,李东锋,等. 侧向水流作用下均匀沙休止角变化的试验研究[J]. 泥沙研究,2017,42(3):1−6. CHEN Li,SONG Tao,LI Dongfeng,et al. Experiment study on repose angle of uniform sand under influence of lateral flow[J]. Journal of Sediment Research,2017,42(3):1−6.
[20] 马子普,张宝森,邓 宇,等. 适用于明渠流及冰盖流的统一泥沙颗粒起动流速公式[J]. 水利学报,2021,52(8):969−978. MA Zipu,ZHANG Baosen,DENG Yu,et al. Unified incipient velocity formula of non-cohesive sediments for open channel flow and ice-cover flow[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2021,52(8):969−978.
[21] 张红武,汪家寅. 沙石及模型沙水下休止角试验研究[J]. 泥沙研究,1989(3):90−96. ZHANG Hongwu,WANG Jiayin. Experimental study on underwater angle of repose of sand and model sand[J]. Journal of Sediment Research,1989(3):90−96.
[22] 夏华永,廖世智,肖志建. 基于床面层能量平衡关系的推移质输沙率计算式[J]. 水利水运工程学报,2006(4):1−9. XIA Huayong,LIAO Shizhi,XIAO Zhijian. Formula for bedload sediment transport rate based on energy balance relationship within bed-surface layer[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering,2006(4):1−9.
[23] 张红武,张俊华,卜海磊,等. 试论推移质输沙率公式[J]. 南水北调与水利科技,2011,9(6):140−145. ZHANG Hongwu,ZHANG Junhua,BU Hailei,et al. Discussion of bed-load transport equations[J]. South-to-North Water Diversion and Water Science & Technology,2011,9(6):140−145.
[24] 张红武,张 清. 黄河水流挟沙力的计算公式[J]. 人民黄河,1992,14(11):7−9,61. ZHANG Hongwu,ZHANG Qing. Formula of sediment carrying capacity of the Yellow River[J]. Yellow River,1992,14(11):7−9,61.
[25] Bagnold. The flow of cohesionless grains in fluids[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London Series A,Mathematical and Physical Sciences,1956,249(964):235−297.
[26] 贺梦杨,尚海鑫,张宽地,等. 仿机翼形便携式量水槽水力特性试验与数值模拟[J]. 农业工程学报,2021,37(12):117−124. HE Mengyang,SHANG Haixin,ZHANG Kuandi,et al. Hydraulic performance experiments and numerical simulation of portable water measuring flume of imitating airfoil shape[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2021,37(12):117−124.
[27] BAGNOLD. The nature of saltation and of ‘bed-load’ transport in water[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London A Mathematical and Physical Sciences,1973,332(1591):473−504. doi: 10.1098/rspa.1973.0038
[28] 张红武,张罗号,彭 昊,等. 冲积河流糙率由来与计算方法研究[J]. 水利学报,2020,51(7):774−787. ZHANG Hongwu,ZHANG Luohao,PENG Hao,et al. Research on cognition and calculation method of alluvial river roughness[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2020,51(7):774−787.
[29] 何文社,方 铎,杨具瑞,等. 泥沙起动流速研究[J]. 水利学报,2002,33(10):51−56. HE Wenshe,FANG Duo,YANG Jurui,et al. Study on incipient velocity of sediment[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2002,33(10):51−56.
[30] 牟 林,董书宁,郑士田,等. 基于CFD-DEM耦合模型的阻水墙建造过程数值模拟[J]. 岩土工程学报,2021,43(3):481-491,F0002,F0003. MOU Lin,DONG Shuning,ZHENG Shitian,et al. Numerical simulation of construction of water-blocking wall based on CFD-DEM coupling method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2021,43(3):481-491,F0002,F0003.
[31] 王 胤,艾 军,杨 庆. 考虑粒间滚动阻力的CFD-DEM流–固耦合数值模拟方法[J]. 岩土力学,2017,38(6):1771−1780. WANG Yin,AI Jun,YANG Qing. A CFD-DEM coupled method incorporating soil inter-particle rolling resistance[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2017,38(6):1771−1780.
[32] 刘巨保,王 明,王雪飞,等. 颗粒群碰撞搜索及CFD-DEM耦合分域求解的推进算法研究[J]. 力学学报,2021,53(6):1569−1585. LIU Jubao,WANG Ming,WANG Xuefei,et al. Research on particle swarm collision search and advancement algorithm for cfd-Dem coupling domain solving[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics,2021,53(6):1569−1585.
[33] TSUJI Y,TANAKA T,ISHIDA T. Lagrangian numerical simulation of plug flow of cohesionless particles in a horizontal pipe[J]. Powder Technology,1992,71(3):239−250. doi: 10.1016/0032-5910(92)88030-L
[34] GIDASPOW D. Hydrodynamics of fiuidizatlon and heat transfer:supercomputer modeling[J]. Applied Mechanics Reviews,1986,39(1):1−23. doi: 10.1115/1.3143702
[35] 蒋勤明. 大埋深突水巷道“阻水段”骨料灌注技术[C]//2017年钻探工程学术研讨会论文集. 鄂尔多斯:中国煤炭学会钻探工程专业委员会,2017:210−212. JIANG Qinming. Aggregate pouring technology for "water blocking section" of deep water inrush pathway[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 Symposium on Drilling Engineering. Ordos:Drilling Engineering Professional Committee of China Coal Society,2017:210−212.





 下载:
下载: