Mine water inrush risk identification method based on MRAU video segmentation model
-
摘要:
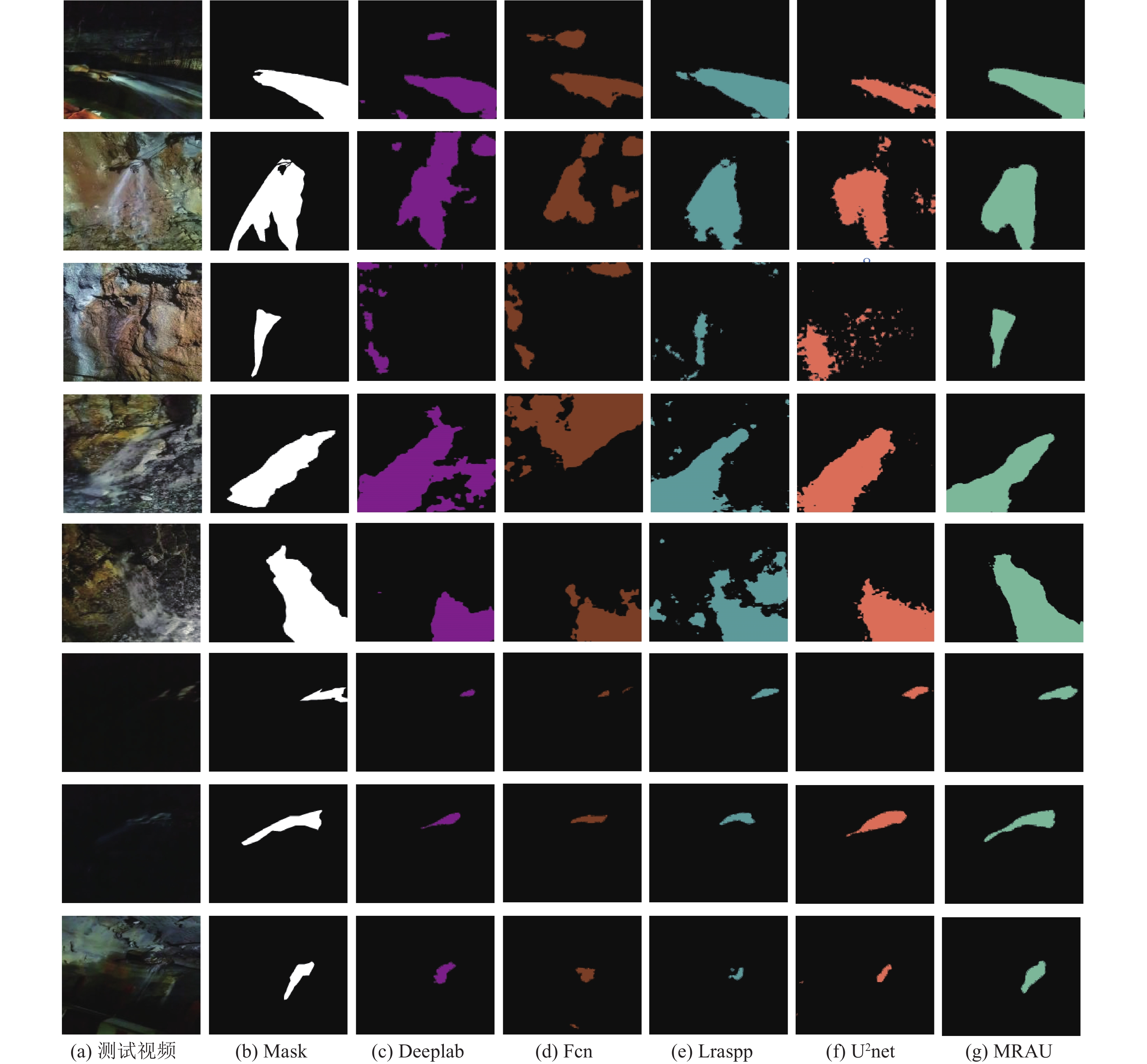
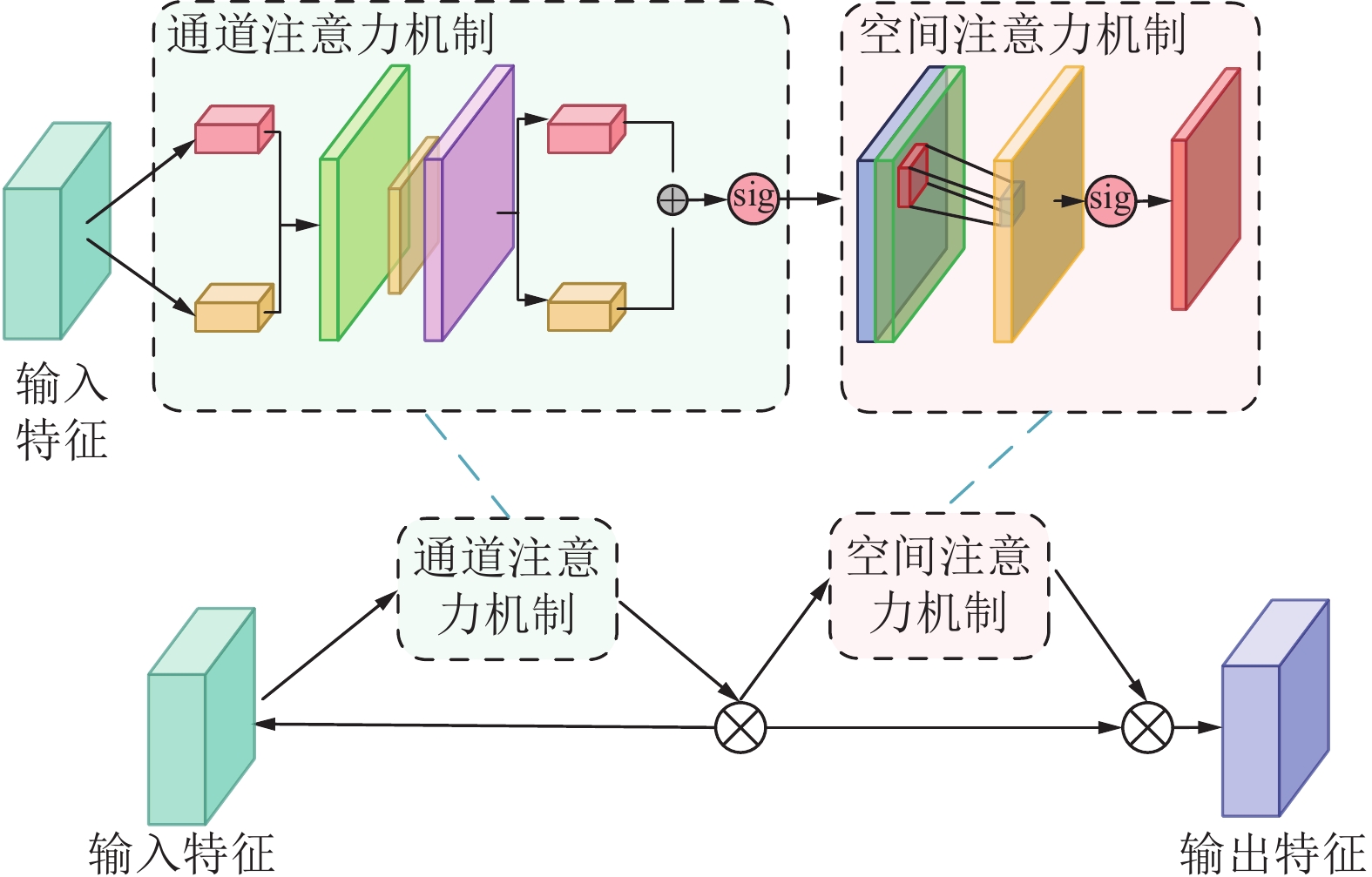
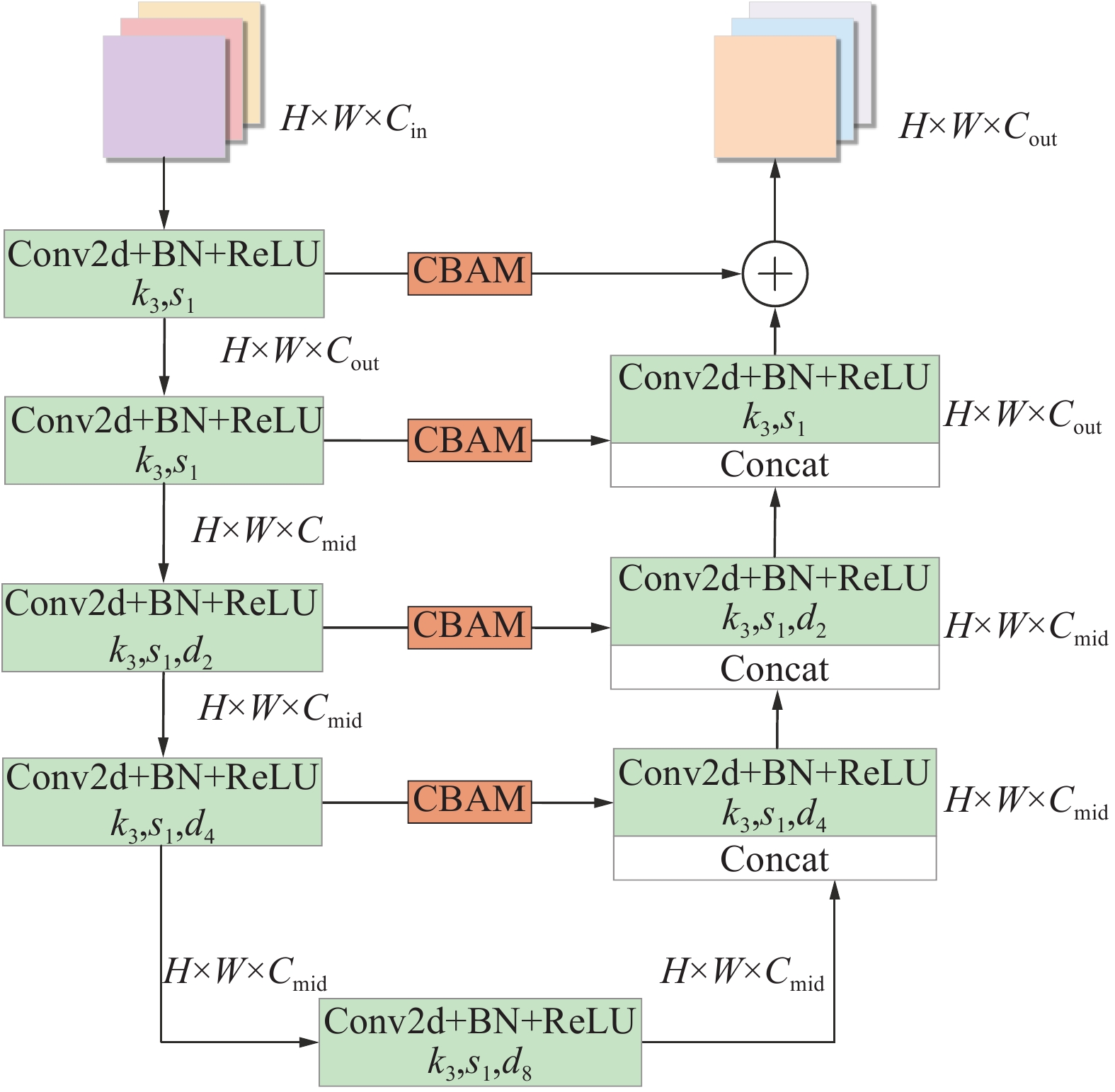
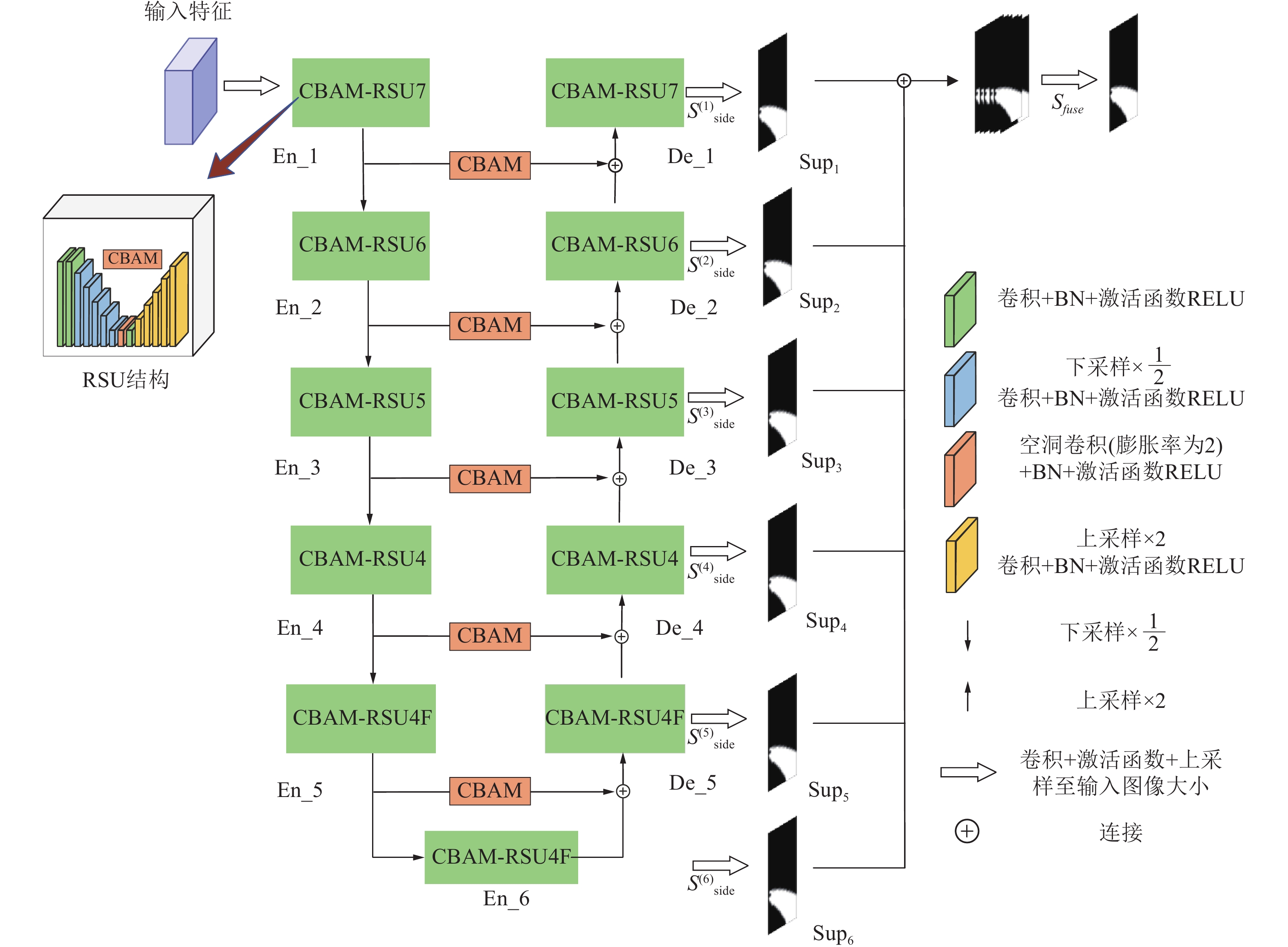
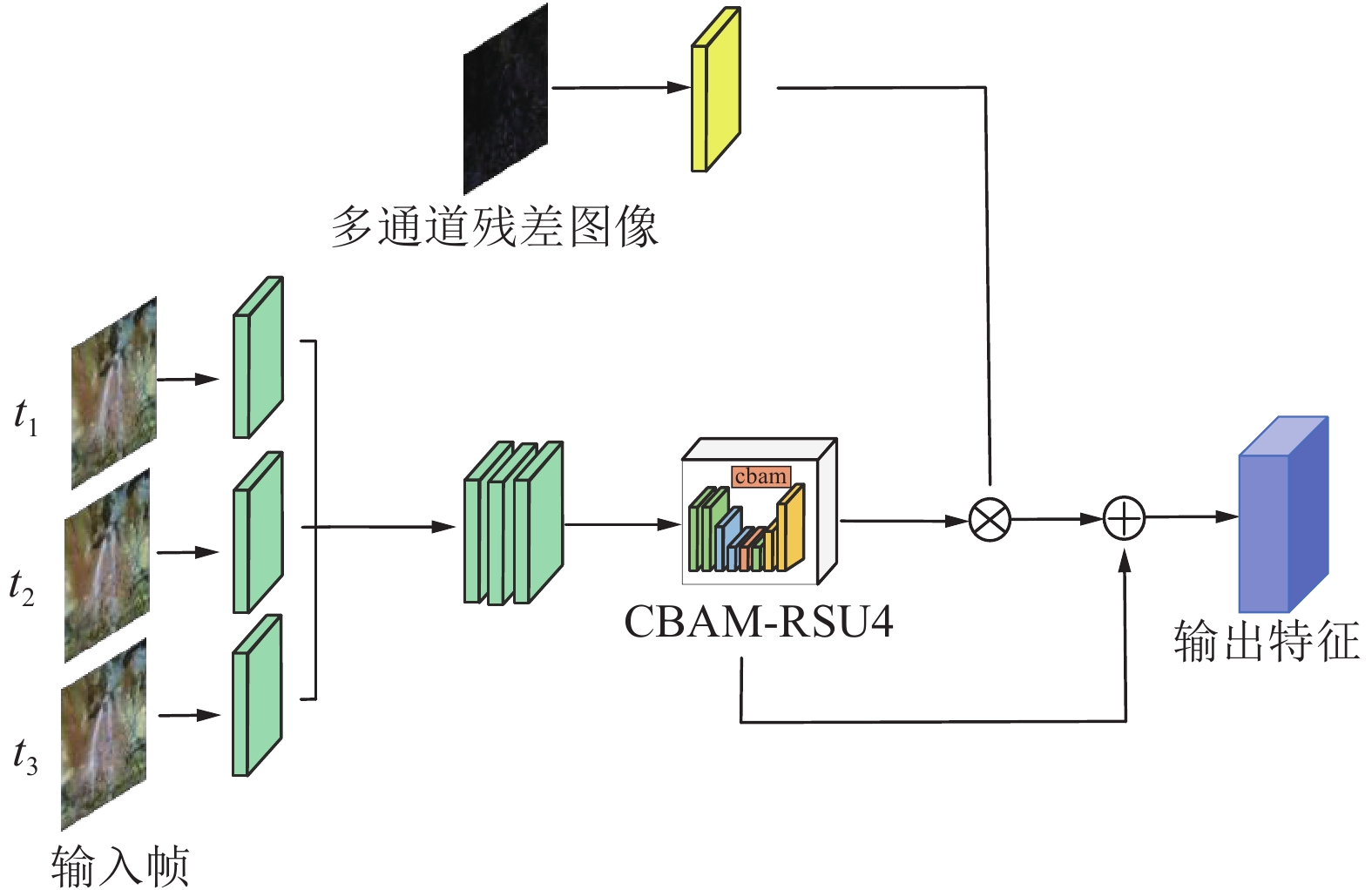
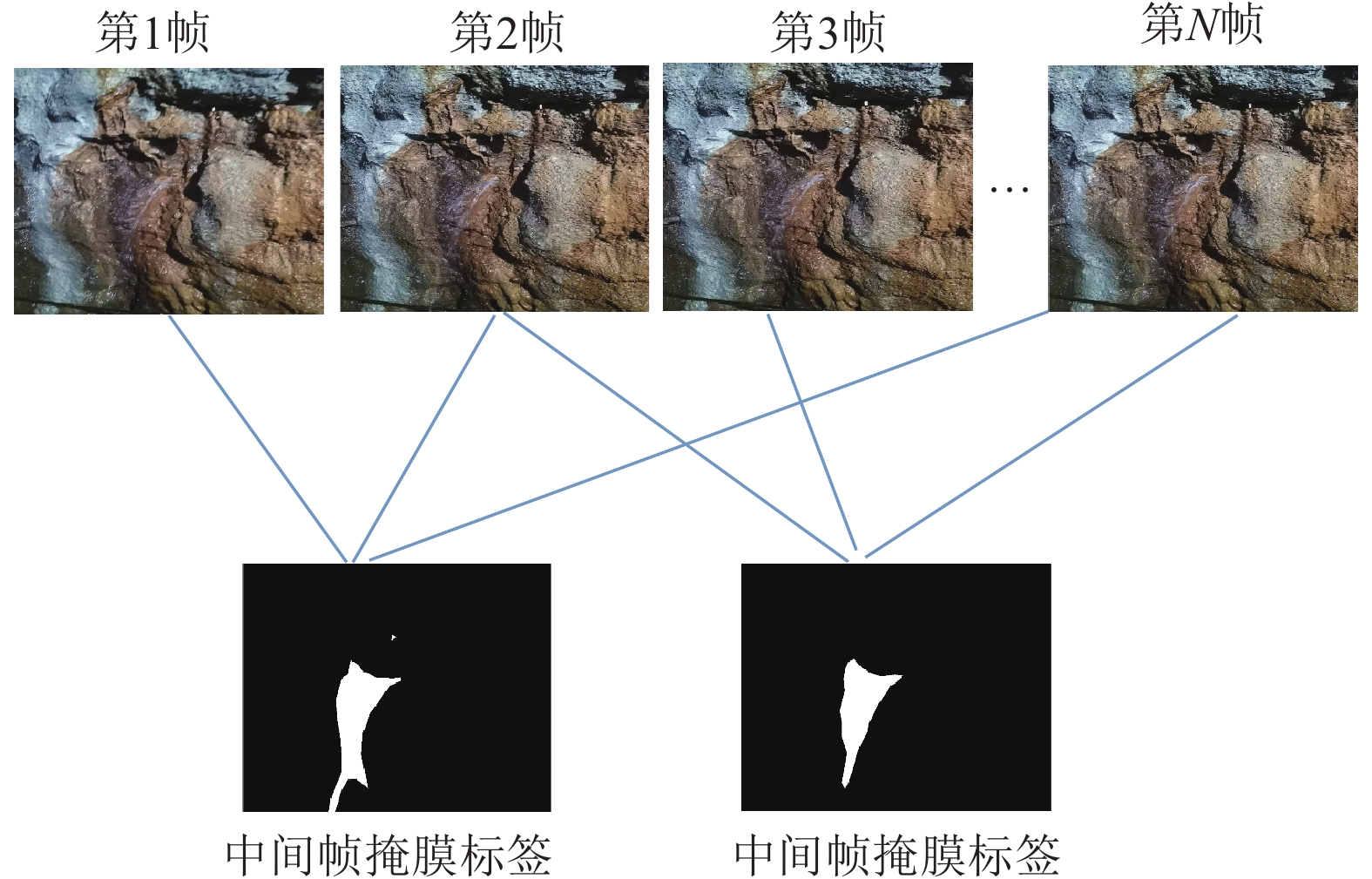
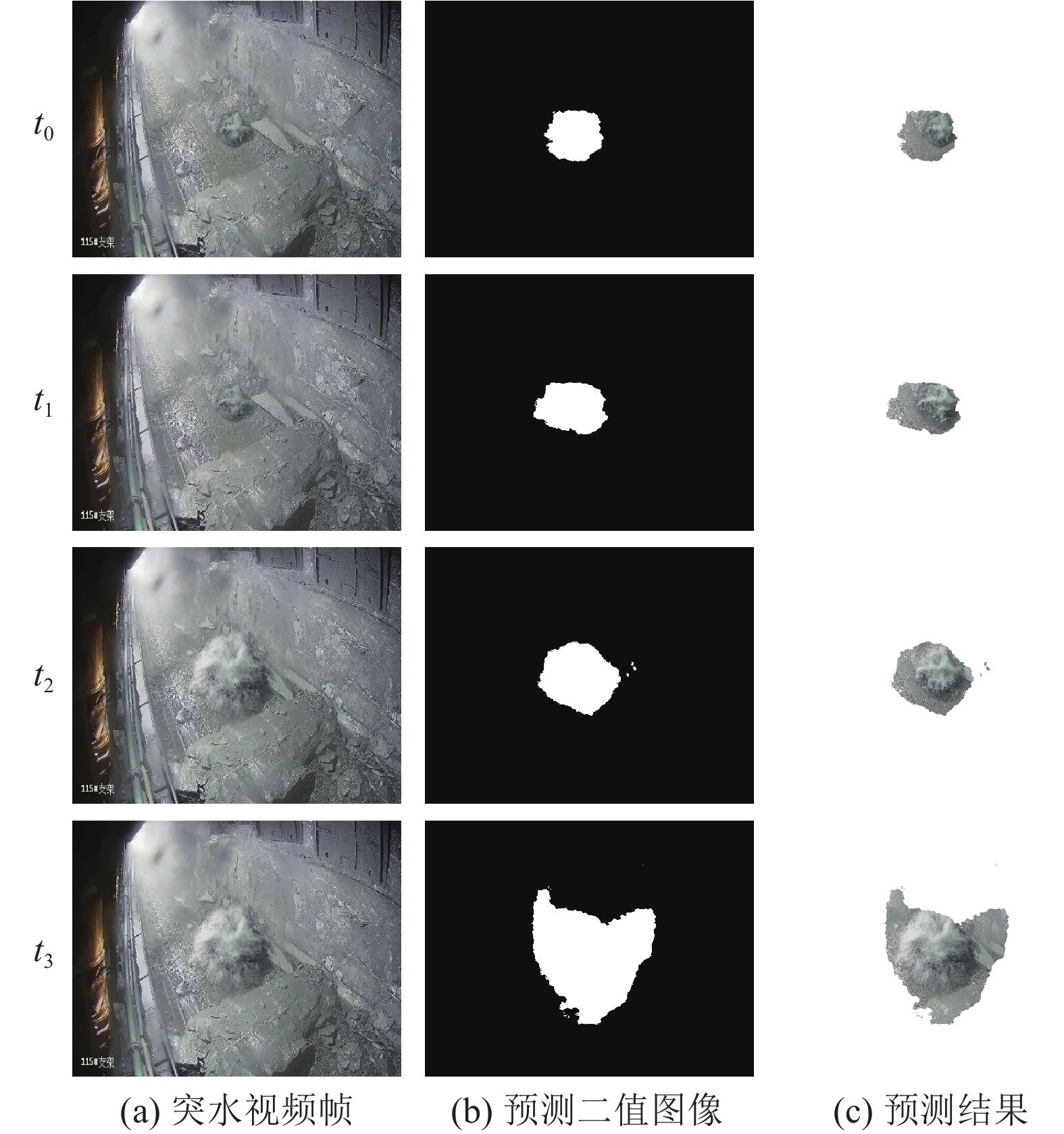
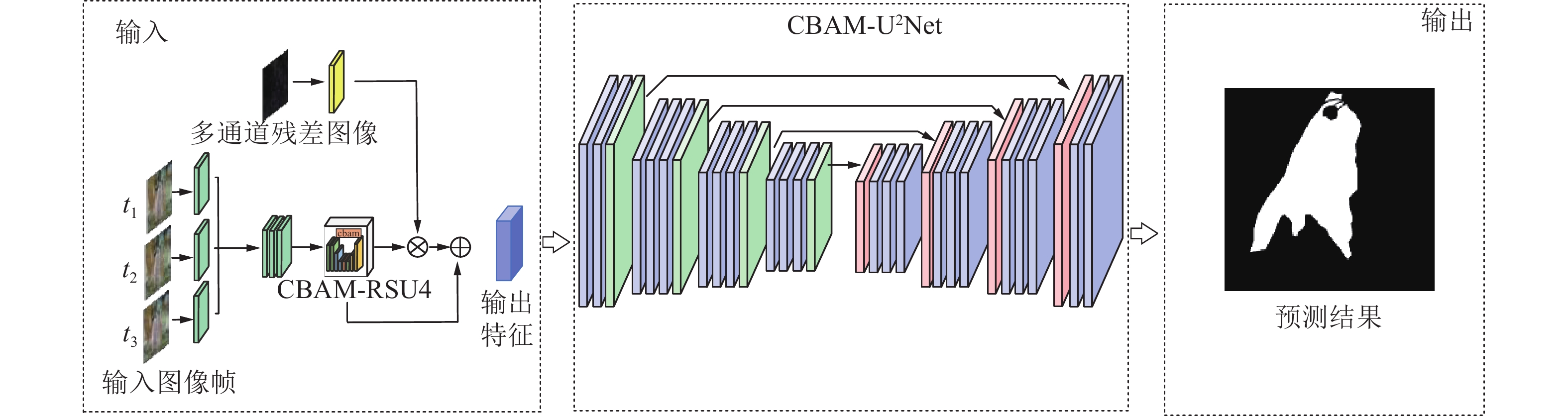
矿井涌(突)水视频识别是智能化矿井建设的关键之一,通过识别涌(突)水从无到有、从小到大的动态演变过程,有助于防止水量超出矿井排水能力并演变为水害。为此提出了一种基于多通道残差注意力机制的U2Net视频分割模型(MRAU),旨在识别涌(突)水的演变过程。首先,基于卷积注意力模块(CBAM)改进U2Net网络模型,以提高特征提取效果。通过多通道残差预处理,区分水流动态特征与静态背景,并将处理结果作为注意力机制输入模型,从而强化水流特征的学习。此外,使用中间帧掩码作为标签进行多帧融合学习,进一步提升网络对水流动态特征的识别能力。最终,通过学习不同场景下的水流特征,实现对未知场景中涌(突)水动态演变的有效识别。通过与Deeplab、LRASPP、FCN、U2Net网络模型的对比试验,选用Dice和IoU作为评价指标。试验结果表明,MRAU模型的Dice和IoU分别达到92.88%和87.51%,相比U2Net基础网络,识别结果分别提高了4.71%和7.41%。在未知的涌(突)水场景中测试时,MRAU的Dice和IoU得分分别达到了86.75%和80.23%。与其他模型相比,MRAU的识别精度最高,表明该模型在不同场景下对水流特征具有更强的泛化能力。此外,MRAU能够精准监测涌(突)水流量从小到大的演变过程。最后,通过在井下环境中模拟突水场景,进一步验证MRAU模型在实际生产中的实用性,为矿井水害监测提供了有效的技术手段。
Abstract:Mine water inrush video recognition is a key component in intelligent mine construction. By recognizing the dynamic evolution of water inrush from none to some and from small to large, it helps prevent the water volume from exceeding the mine’s drainage capacity and turning into a water hazard. Therefore, a video segmentation model based on the Multi-channel Residual Attention mechanism and U2Net (MRAU) was proposed to identify the evolution process of water inrush. First, the U2Net network model was improved based on the Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM) to enhance feature extraction. Then, through multi-channel residual preprocessing, the dynamic features of water flow were distinguished from the static background, and the processed results were input into the model as an attention mechanism to reinforce the learning of water flow features. In addition, intermediate frame masks were used as labels for multi-frame fusion learning, further enhancing the network’s ability to recognize the dynamic features of water flow. Finally, by learning the water flow features in different scenarios, the model effectively recognizes the dynamic changes of water inrush in unknown scenarios. Comparative experiments with Deeplab, LRASPP, FCN, and U2Net network models, using Dice and IoU as evaluation metrics, show that the Dice and IoU of the MRAU model reach 92.88% and 87.51%, respectively, which represents improvements of 4.71% and 7.41% over the baseline U2Net network. When tested in unknown water inrush scenarios, the MRAU model achieves Dice and IoU scores of 86.75% and 80.23%. Compared to other models, MRAU achieves the highest recognition accuracy, demonstrating stronger generalization capabilities in recognizing water flow features across different scenarios. Moreover, MRAU can accurately monitor the dynamic evolution of water inrush from small to large. Finally, simulations of water inrush scenarios in underground environments further verify the practical utility of the MRAU model in real-world production, providing an effective technical solution for mine water hazard monitoring.
-
Keywords:
- mine water inrush /
- video segmentation /
- MRAU /
- multichannel residual preprocessing /
- attention mechanism /
- U2Net
-
-
表 1 不同模型的测试性能
Table 1 Test performance of different models
项目 DeepLab LRASPP FCN U2Net MRAU 训练参数/106 42.0 3.2 35.3 44.0 44.2 训练时间/h 27.4 5.3 25.3 28.6 30.2 Dice/% 78.87 72.38 80.16 88.17 92.88 IoU/% 67.76 60.23 69.54 80.1 87.51 表 2 引入CBAM模块的对比结果
Table 2 Compares results of introducing CBAM module
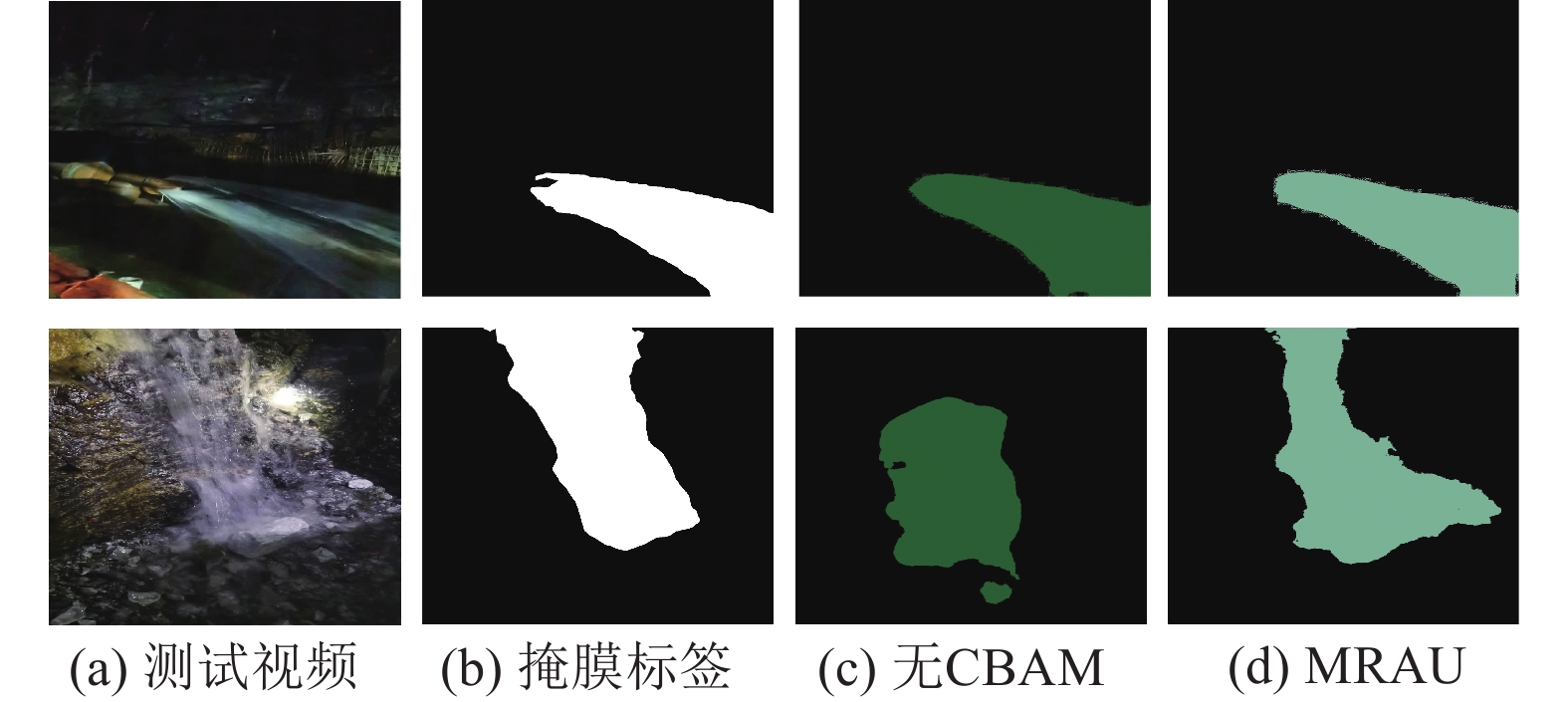
项目 未引入CBAM MRAU Dice/% 88.10 90.12 IoU/% 84.33 87.23 表 3 引入多通道残差注意力机制的模型性能
Table 3 Performance of model introducing multi-channel residual attention mechanism
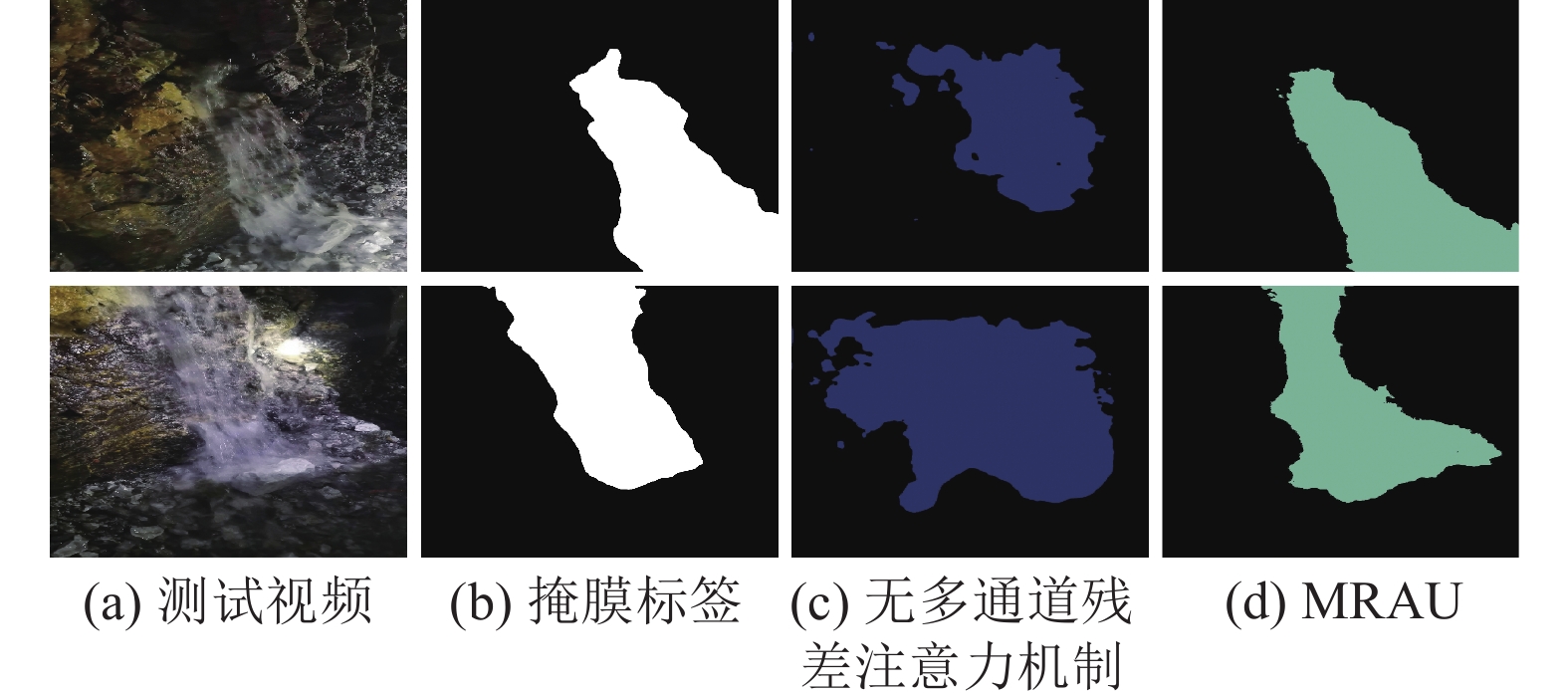
项目 无多通道残差注意力机制 MRAU Dice/% IoU/% Dice/% IoU/% 水流公共集 89.10 81.40 93.24 87.58 矿井数据集 85.68 77.81 87.44 79.9 平均值 87.39 79.61 90.34 83.74 表 4 不同输入帧数的识别结果
Table 4 Identification results of different input frame numbers
项目 1帧 3帧 5帧 7帧 Dice/% 89.50 92.88 90.67 87.38 IoU/% 81.80 87.51 83.51 79.08 表 5 不同模型的跨场景突水识别性能指标
Table 5 Performance indicators of cross-scene water inrush recognition for different models
项目 DeepLab LRASPP FCN U2Net MRAU Dice/% 76.86 81.39 78.28 82.50 86.75 IoU/% 68.97 73.07 70.49 75.67 80.23 表 6 不同视频帧中水像素个数
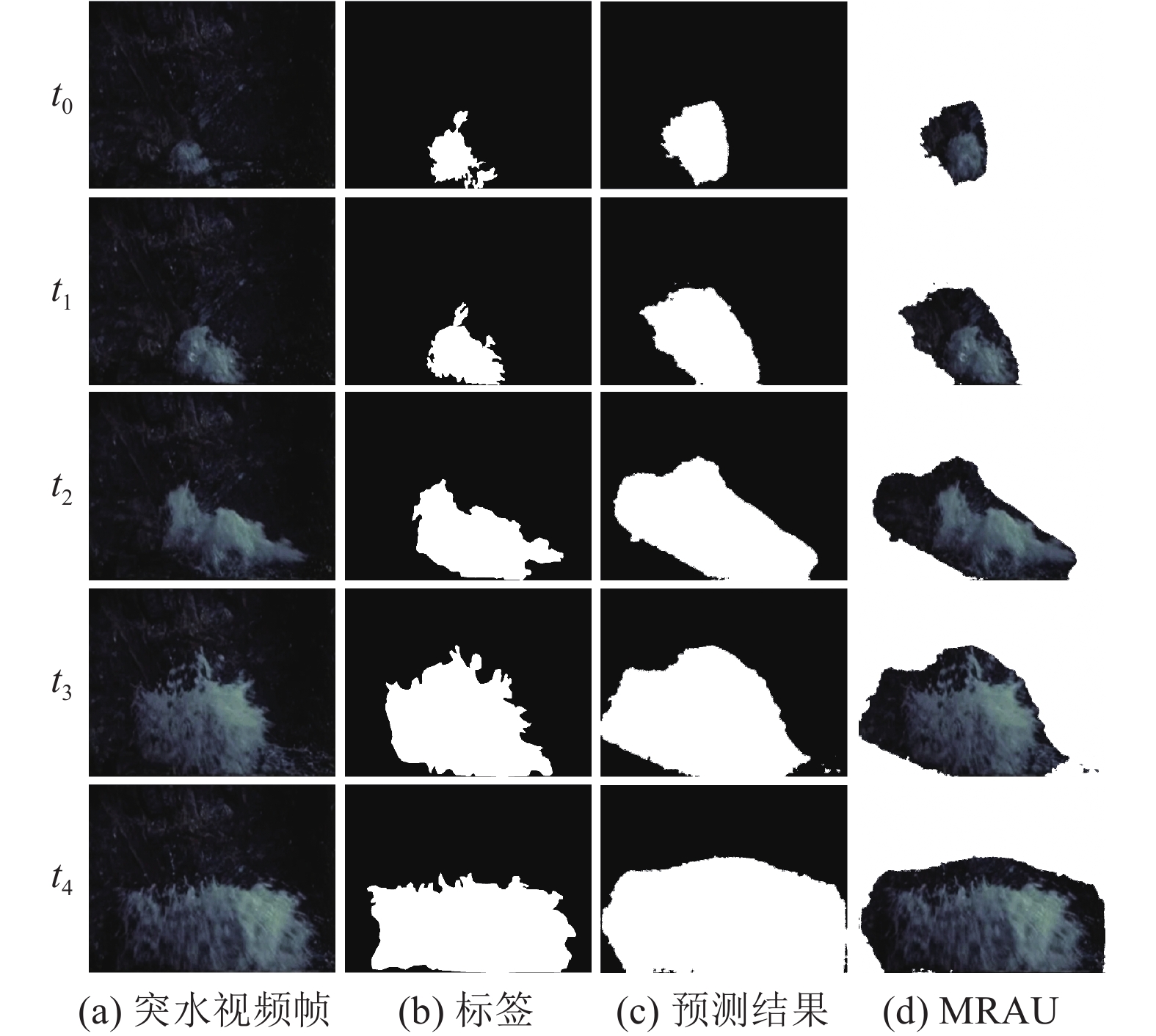
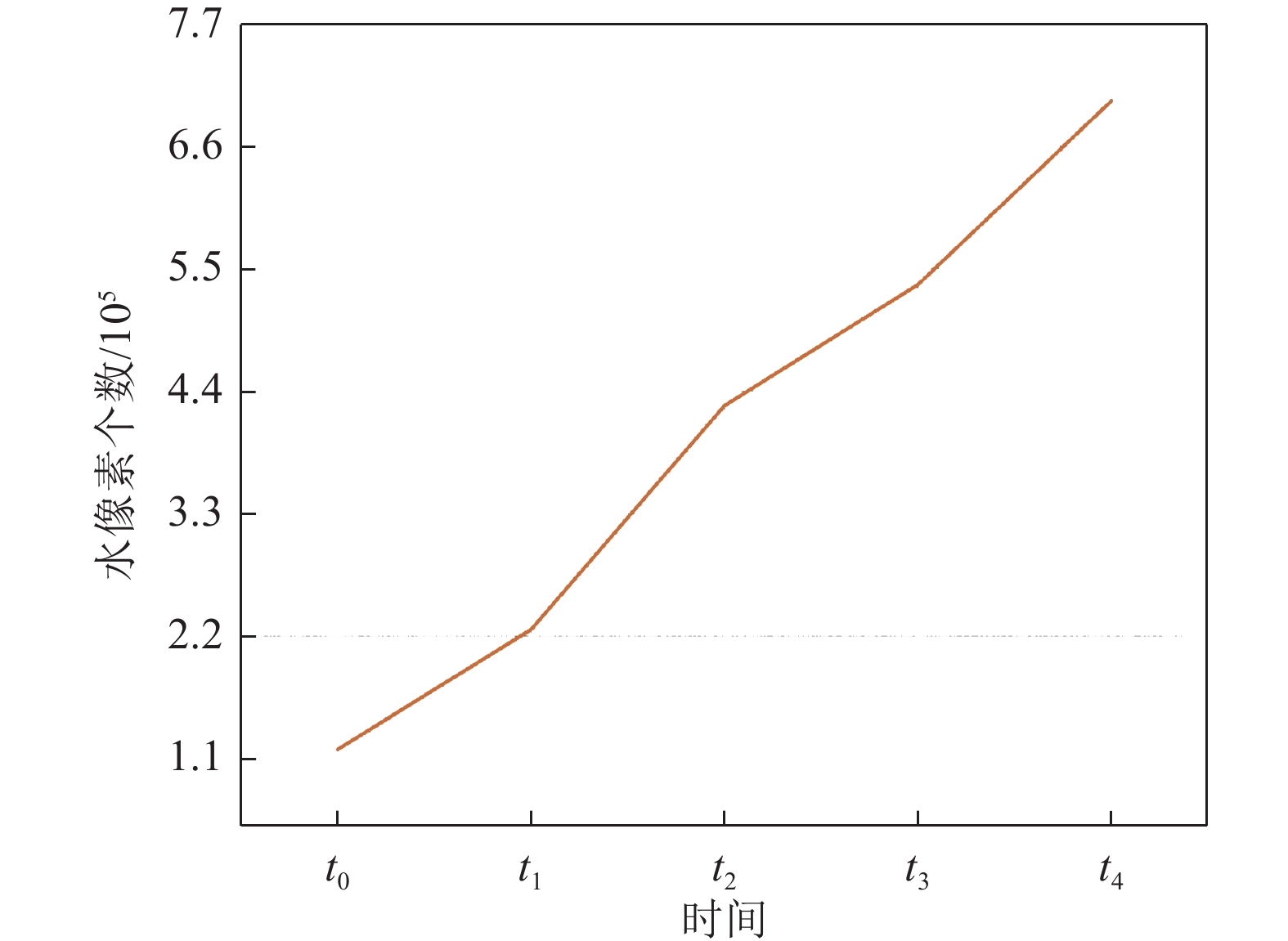
Table 6 Number of water pixels in different image frames
t1 t2 t3 t4 32 846 40 753 76 567 94 156 -
[1] 武强. 我国矿井水防控与资源化利用的研究进展、问题和展望[J]. 煤炭学报,2014,39(5):795−805. WU Qiang. Progress,problems and prospects of prevention and control technology of mine water and reutilization in China[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2014,39(5):795−805.
[2] 武强,崔芳鹏,赵苏启,等. 矿井水害类型划分及主要特征分析[J]. 煤炭学报,2013,38(4):561−565. WU Qiang,CUI Fangpeng,ZHAO Suqi,et al. Type classification and main characteristics of mine water disasters[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2013,38(4):561−565.
[3] 曾一凡,武强,赵苏启,等. 我国煤矿水害事故特征、致因与防治对策[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2023,51(7):1−14. ZENG Yifan,WU Qiang,ZHAO Suqi,et al. Characteristics,causes,and prevention measures of coal mine water hazard accidents in China[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2023,51(7):1−14.
[4] 武强,徐华,赵颖旺,等. 基于云平台的矿井水害智慧应急救援系统与应用[J]. 煤炭学报,2018,43(10):2661−2667. WU Qiang,XU Hua,ZHAO Yingwang,et al. Cloud-based smart emergency rescue system and its application in mine water disaster[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2018,43(10):2661−2667.
[5] 王学文,王孝亭,谢嘉成,等. 综采工作面XR技术发展综述:从虚拟3D可视化到数字孪生的演化[J]. 绿色矿山,2024,2(1):76−85. WANG Xuewen,WANG Xiaoting,XIE Jiacheng,et al. Review of XR technology development in fully mechanized mining faces:From 3D visualization to digital twin[J]. Journal of Green Mine,2024,2(1):76−85.
[6] 鲍久圣,张可琨,王茂森,等. 矿山数字孪生 MiDT:模型架构、关键技术及研究展望[J]. 绿色矿山,2023,1(1):166−177. BAO Jiusheng,ZHANG Kekun,WANG Maosen,et al. Mine digital twin:Model architecture,key technologies and research prospects[J]. Journal of Green Mine,2023,1(1):166−177.
[7] 闫志蕊,王宏伟,耿毅德. 基于改进DeeplabV3+和迁移学习的煤岩界面图像识别方法[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2023,51(S1):429−439. YAN Zhirui,WANG Hongwei,GENG Yide. Coal-rock interface image recognition method based on improved DeeplabV3+ and transfer learning[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2023,51(S1):429−439.
[8] 闫旭,邬建雄. 图像处理技术在无人综采系统中的应用研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(S1):269−276. YAN Xu,WU Jianxiong. Application of image processing technology in unmanned fully mechanized mining system[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2022,50(S1):269−276.
[9] 许献磊,王一丹,朱鹏桥,等. 基于高频雷达波的煤岩层位识别与追踪方法研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(7):50−58. XU Xianlei,WANG Yidan,ZHU Pengqiao,et al. Research on coal and rock horizon identification and tracking method based on high frequency radar waves[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2022,50(7):50−58.
[10] 曹现刚,李莹,王鹏,等. 煤矸石识别方法研究现状与展望[J]. 工矿自动化,2020,46(1):38−43. CAO Xiangang,LI Ying,WANG Peng,et al. Research status of coal-gangue identification method and its prospect[J]. Industry and Mine Automation,2020,46(1):38−43.
[11] 饶中钰,吴景涛,李明. 煤矸石图像分类方法[J]. 工矿自动化,2020,46(3):69−73. RAO Zhongyu,WU Jingtao,LI Ming. Coal-gangue image classification method[J]. Industry and Mine Automation,2020,46(3):69−73.
[12] 沈宁,窦东阳,杨程,等. 基于机器视觉的煤矸石多工况识别研究[J]. 煤炭工程,2019,51(1):120−125. SHEN Ning,DOU Dongyang,YANG Cheng,et al. Research on multi-condition identification of gangue based on machine vision[J]. Coal Engineering,2019,51(1):120−125.
[13] 杨春雨,袁晓光. 煤矿井下巷道变形巡检视频异常检测方法[J]. 工矿自动化,2021,47(2):13−17. YANG Chunyu,YUAN Xiaoguang. Anomaly detection method of inspection video for coal mine underground roadway deformation[J]. Journal of Mine Automation,2021,47(2):13−17.
[14] 王昱栋,代伟,马小平. 基于机器视觉的锚杆异常快速检测方法[J]. 工矿自动化,2021,47(4):13−18. WANG Yudong,DAI Wei,MA Xiaoping. Rapid detection method of bolt abnormality based on machine vision[J]. Journal of Mine Automation,2021,47(4):13−18.
[15] 付燕,李瑶,严斌斌. 一种煤矿井下视频图像增强算法[J]. 工矿自动化,2018,44(7):80−83. FU Yan,LI Yao,YAN Binbin. An underground video image enhancement algorithm[J]. Industry and Mine Automation,2018,44(7):80−83.
[16] 王震威,冯瑾,卢兆林. 基于耦合偏微分方程的煤矿图像去噪算法[J]. 工矿自动化,2013,39(10):81−85. doi: 10.7526/j.issn.1671-251X.2013.10.021 WANG Zhenwei,FENG Jin,LU Zhaolin. Denoising algorithm for coal mine image based on coupled partial differential equations[J]. Journal of Mine Automation,2013,39(10):81−85. doi: 10.7526/j.issn.1671-251X.2013.10.021
[17] 孙继平,江静. 基于PURE-LET的激光光斑图像快速去噪算法[J]. 煤炭学报,2013,38(9):1710−1714. SUN Jiping,JIANG Jing. PURE-LET-based fast denoising algorithm for laser spot imagery[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2013,38(9):1710−1714.
[18] 田丰,陈婷婷,刘晓佩. 基于自适应光照估计的Retinex-Net矿井图像增强算法研究[J/OL]. 煤炭科学技术,2024:1−16 [2024−06−30]. DOI: 10.12438/cst.2024-0561. Tian Feng,Chen Tingting,Liu Xiaopei. Research on Retinex-Net mine image enhancement algorithm based on adaptive illumination estimation [J/OL]. Coal Science and Technology,2024:1−16. [2024−06−30]. DOI: 10.12438/cst.2024-0561.
[19] YU C D,LUO H Z,FAN Y W,et al. A cascaded convolutional neural network for two-phase flow PIV of an object entering water[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement,2021,71:5002410.
[20] MANGALRAJ M,MOHANTY A,SINGH S. Salient object detection using water flow approach and image boundary contrast map[C]//2021 International Conference on Computing,Communication,and Intelligent Systems (ICCCIS). Greater Noida:IEEE,2021:161−166.
[21] KHAN M N,ANWAR S. Robust weed recognition through color based image segmentation and convolution neural network based classification[C]//ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition,Salt Lake City:American Society of Mechanical Engineers,2019:V004T05A045.
[22] SANGHYUN W,JONGCHAN P,JOON-YOUNG L,et al. CBAM:Convolutional block attention module[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV),2018:3−19.
[23] QIN X B,ZHANG Z C,HUANG C Y,et al. U2-Net:Going deeper with nested U-structure for salient object detection[J]. Pattern Recognition,2020,106:107404. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2020.107404
[24] RONNEBERGER O,FISCHER P,BROX T. U-net:Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]//Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention–MICCAI 2015:18th international conference. Munich:Springer International Publishing,2015:234−241.




 下载:
下载: