Conveyor belt deviation detection method based on dual flow network
-
摘要:
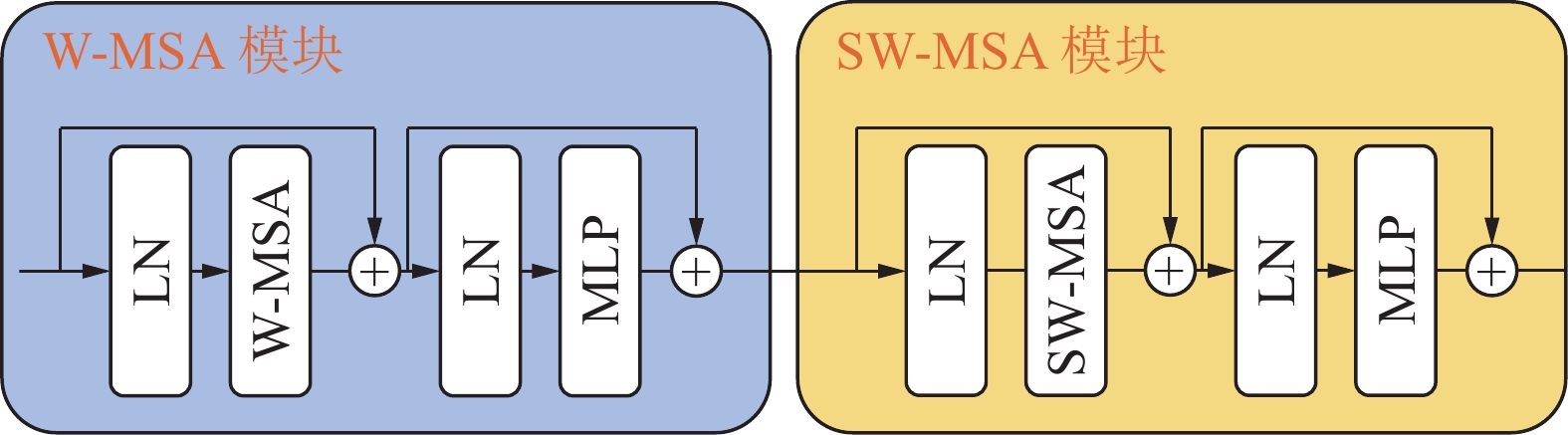
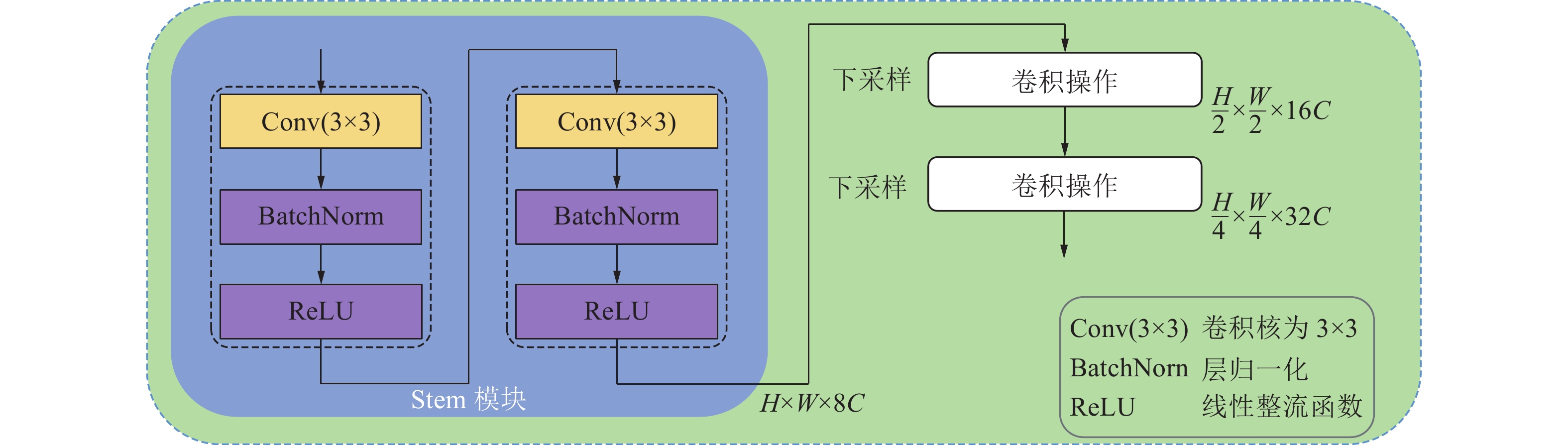
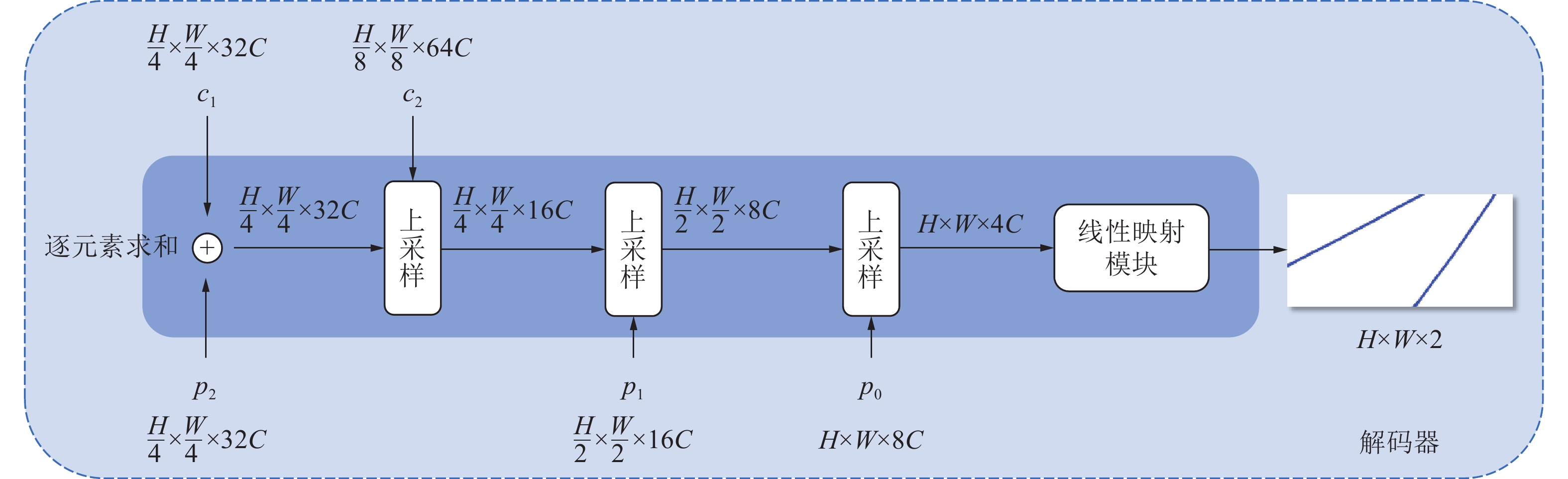
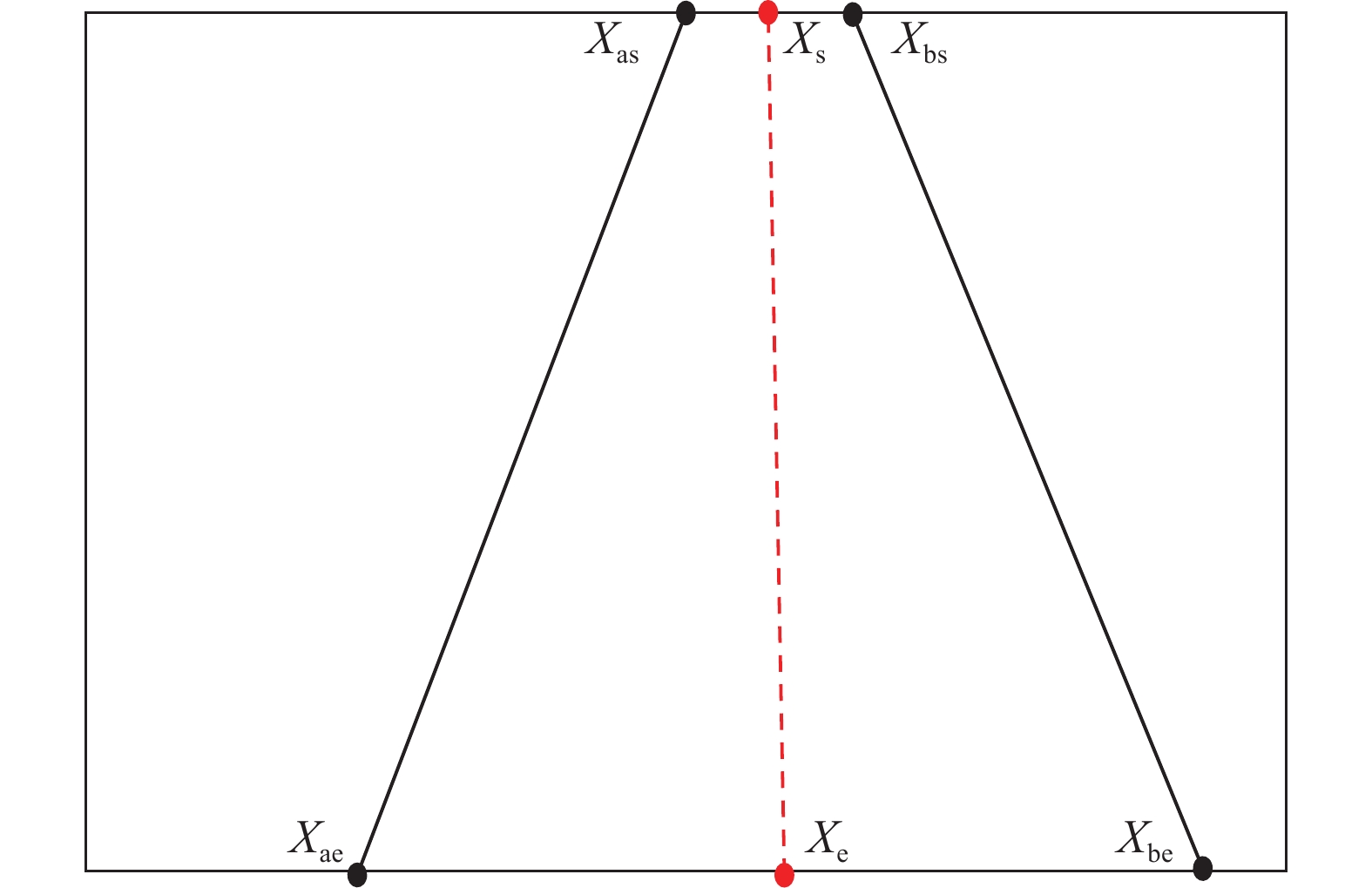
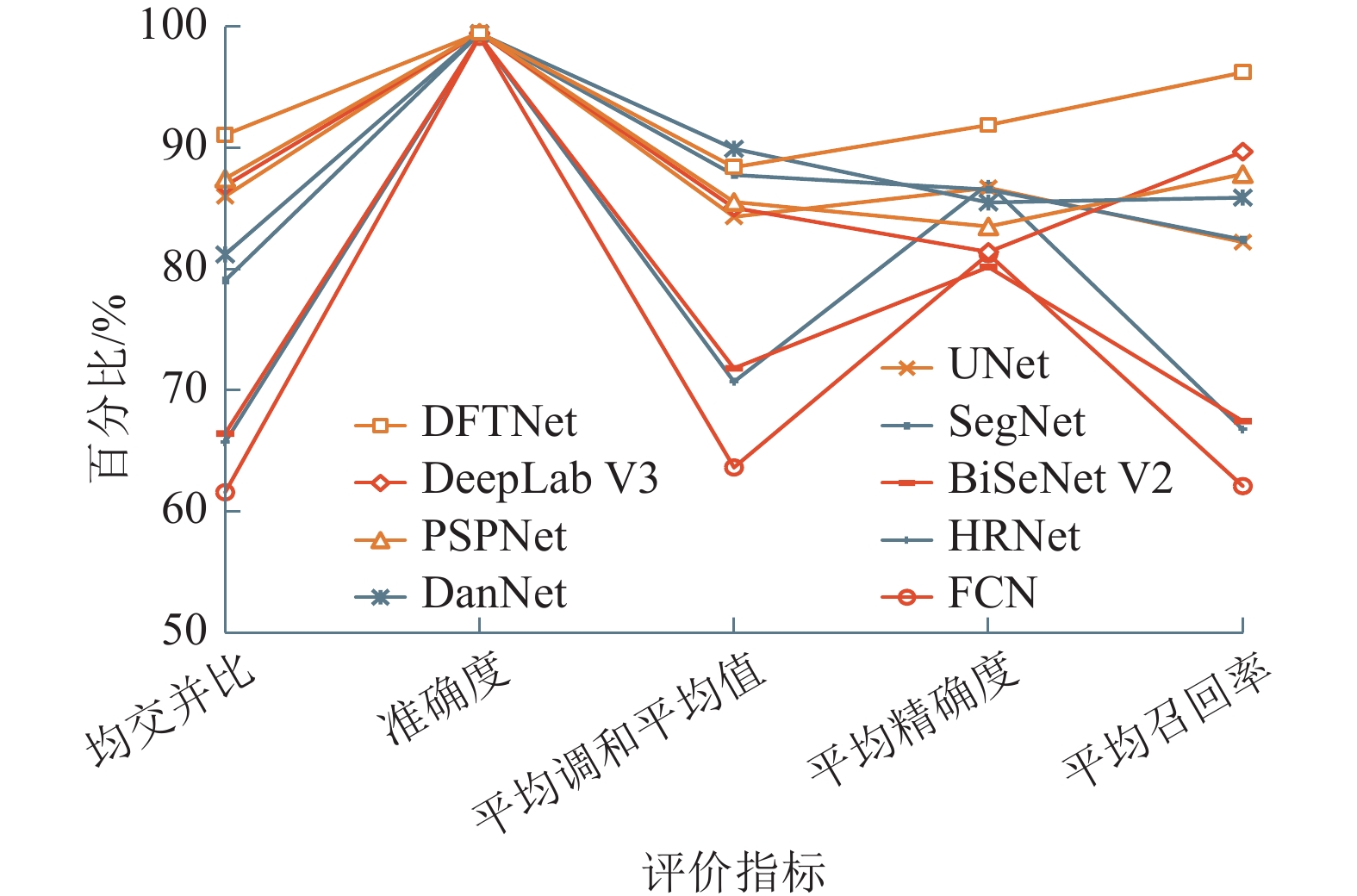
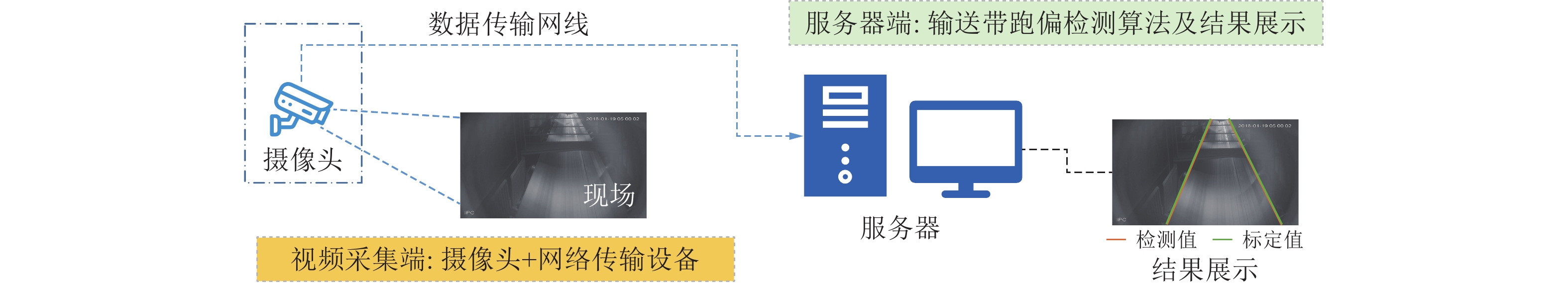
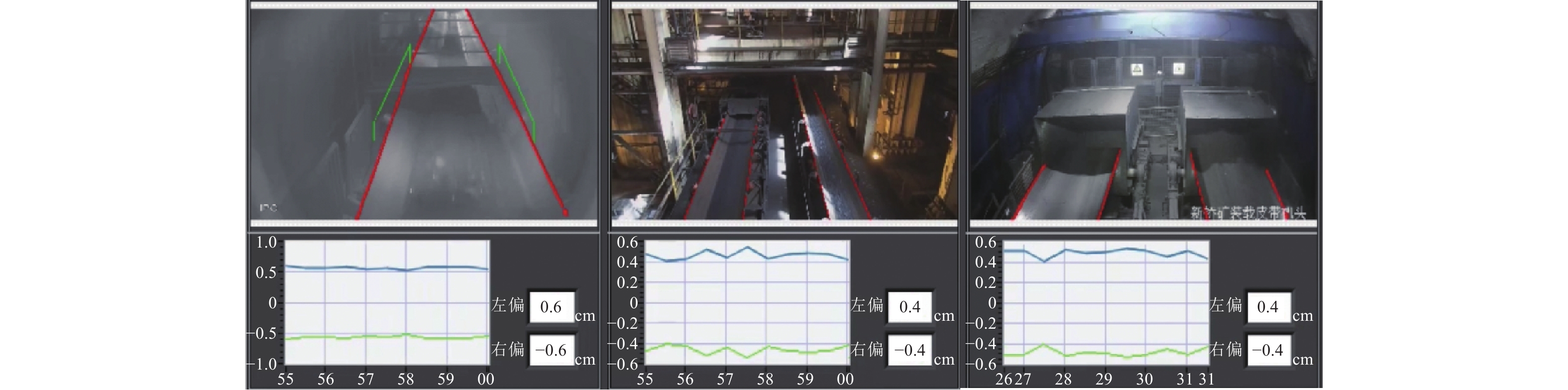
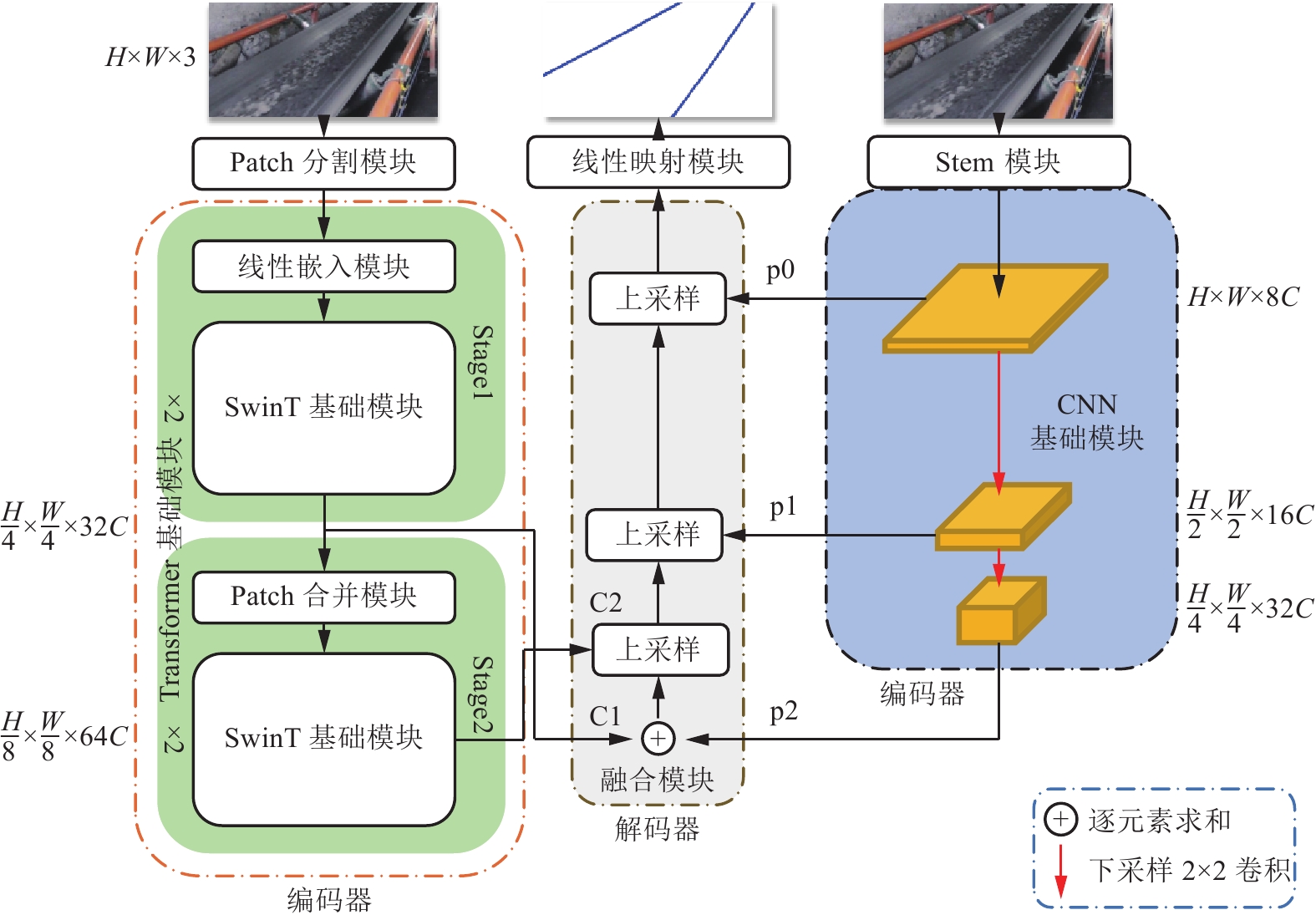
传统输送带跑偏检测方法中,接触式检测技术成本高,非接触式检测技术则精度低。随着人工智能技术的发展,虽然基于卷积神经网络的方法可以有效提高检测精度,但受限于卷积操作本身局部运算特性的限制,仍存在对长距离、全局信息感知不足等问题,很难再提升在输送带边缘检测上的精度。为解决上述问题,① 通过将传统卷积神经网络的卷积对局部特征的提取能力与Transformer结构对全局、长距离信息感知能力相结合,提出了一种全局与局部信息相互融合的双流输送带边缘检测网络模型(Dual-Flow Transformer Network,DFTNet),能够较好地提高输送带边缘检测精度并抑制输送带图像噪声和背景的干扰;② 通过设计卷积神经网络(Convolutional Neural Network,CNN)和转换器Transformer特征融合模块,形成双流编码器–解码器结构,利用结构上的巧妙设计,可以更好地融合全局上下文信息,避免了Transformer结构在大规模数据集上预训练,可以灵活调节网络结构;③ 通过从实际工业场景中所采集到多场景的运输机输送带图片,构建了包含5种不同场景下多角度、不同位置的输送带输送带数据集。研究结果表明,双流融合网络DFTNet综合性能最佳,均交并比mIou达91.08%,准确率ACC达99.48%,平均精确率mPrecision达91.88%,平均召回率mRecall达96.22%,相比纯卷积神经网络HRNet分别提升了25.36%、0.29%、17.70%与29.46%,相比全卷积神经网络(Fully Convolutional Networks,FCN)分别提升了29.5%、0.32%、24.77%与34.13%,在参数量、计算速度上均有较大提升。同时,处理图像帧率达53.07 fps,满足工业中实时性的要求,具有较大实用价值。
Abstract:Among the traditional belt edge detection methods, the contact detection technology has high cost and the non-contact detection technology has low precision. With the development of artificial intelligence technology, although the method based on convolutional neural network can effectively improve the detection accuracy, but limited by the local operation characteristics of the convolutional operation itself, there are still problems such as insufficient perception of long-distance and global information, it is difficult to improve the accuracy of the belt edge detection. In order to solve the above problems, ① by combining the traditional convolutional neural network's ability to extract local features and the Transformer structure's ability to perceive global and long-distance information, a dual-flow transformer network (DFTNet) which integrates global and local information is proposed. The edge detection network model can better improve the belt edge detection accuracy and suppress the interference of belt image noise and background; ② By designing the CNN and Transformer feature fusion modules, a dual-flow encoder-decoder structure is formed. The clever design can better integrate the global context information, avoid the pre-training of the Transformer structure on large-scale data sets and be flexibly adjusted; ③ By Through the multi-scene conveyor belt pictures collected from the actual industrial scene, a belt conveyor belt dataset containing five different scenes, various angles and different positions is constructed. Through experimental verification, the DFTNet proposed in this paper has the best comprehensive performance with mIou 91.08%, ACC 99.48%, mPrecision 91.88% and mRecall 96.22%. which are 25.36%, 0.29%, 17.70% and 29.46% respectively compared to the pure convolutional neural network HRNet, and 29.5%, 0.32%, 24.77% and 34.13% respectively compared to FCN. At the same time, the frame rate of DFTNet processing images reaches 53.07 fps, which meets the real-time requirements in the industry and has great practical value.
-
Keywords:
- belt deviation /
- edge detection /
- neural network /
- encoder-decoder /
- image segmentation
-
-
表 1 指标混淆矩阵
Table 1 Indicator confusion matrix
真实结果 预测结果 真实标签=True 真实标签=False 预测=True 真阳性TP 假阴性FP 预测=False 假阳性FN 真阴性TN 表 2 本文所制作的数据集介绍
Table 2 Introduction to the datasets produced in this paper
张 数据集 场景1 场景2 场景3 场景4 场景5 合计 训练集 744 141 135 324 132 1476 训练标签集 744 141 135 324 132 1476 测试集 186 33 36 81 33 369 测试标签集 186 33 36 81 33 369 表 3 模型深度消融试验结果
Table 3 Ablation experimental results of module deepth
网络模
型深度均交
并比/%准确
度/%平均调和
平均值/%平均精
确度/%平均召
回率/%浮点运
算量/109参数
量/106c1,c2 91.08 99.48 88.40 91.88 96.22 5.71 28.45 c1,c2,c3 87.10 99.33 85.25 89.31 90.37 7.53 45.40 c1,c2,c3,c4 86.68 99.35 84.91 88.61 90.66 9.78 45.40 表 4 输入图片尺寸消融试验结果
Table 4 Ablation experimental results of input size
输入图
片尺寸均交并比/% 准确度/% 平均调和
平均值/%平均精
确度/%平均召
回率/%64×64 88.02 91.68 88.07 90.37 95.32 128×128 89.13 96.77 88.03 90.39 95.43 256×256 91.08 99.48 88.40 91.88 96.22 512×512 88.21 90.87 87.50 91.00 94.23 表 5 模型大小消融试验结果
Table 5 Ablation experimental results of model scale
网络模
型大小均交
并比/%准确度/% 平均调和
平均值/%平均精
确度/%平均召
回率/%浮点
运算量/109参数
量/106tiny 91.08 99.48 88.40 91.88 96.22 5.71 28.45 small 90.10 98.91 87.85 89.31 96.37 6.60 49.77 base 91.25 99.35 87.21 89.61 96.16 10.78 88.40 表 6 各模型对比试验结果
Table 6 Comparing the experimental results of each model
网络
模型均交
并比/%准确
度/%平均调和
平均值/%平均精
确度/%平均召
回率/%浮点
运算量/109参数
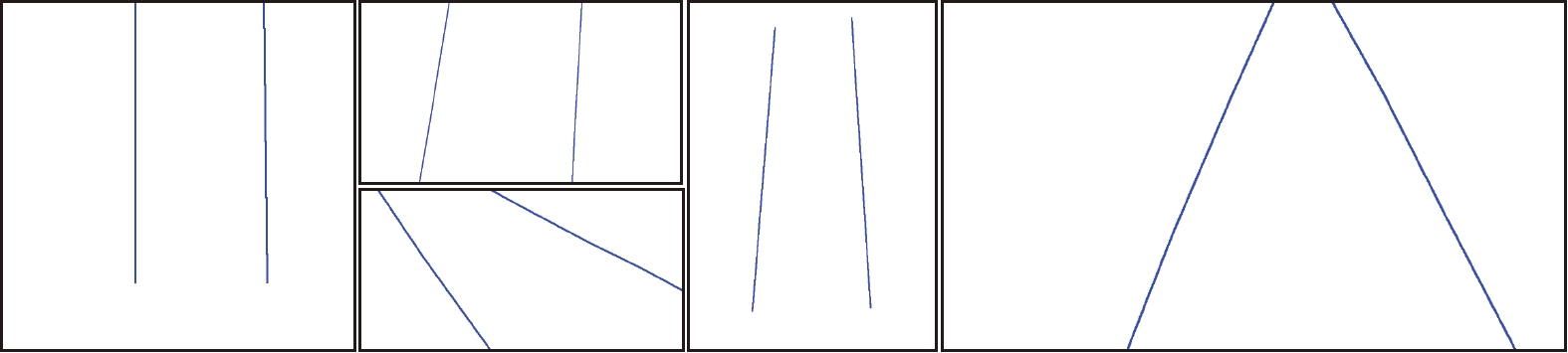
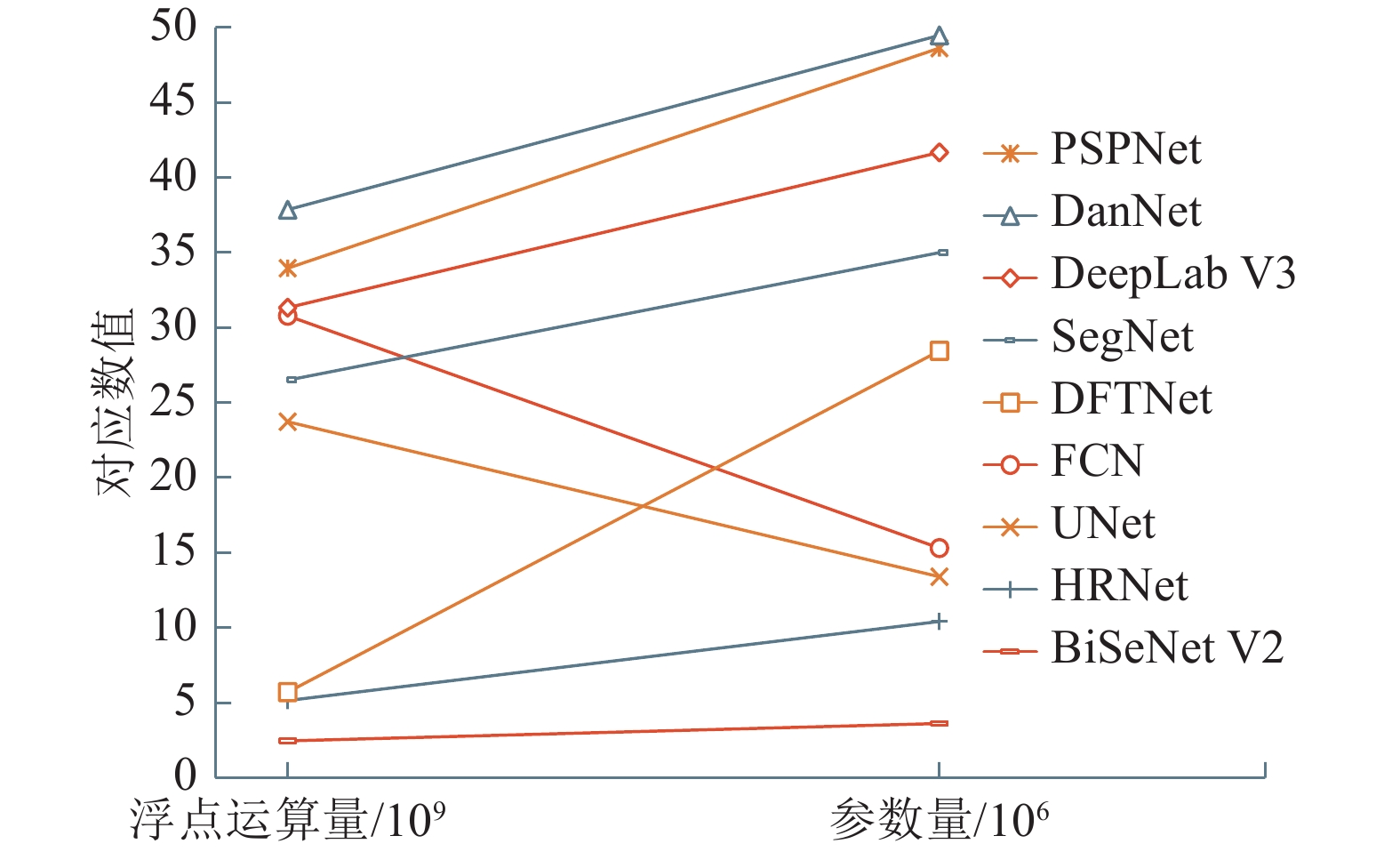
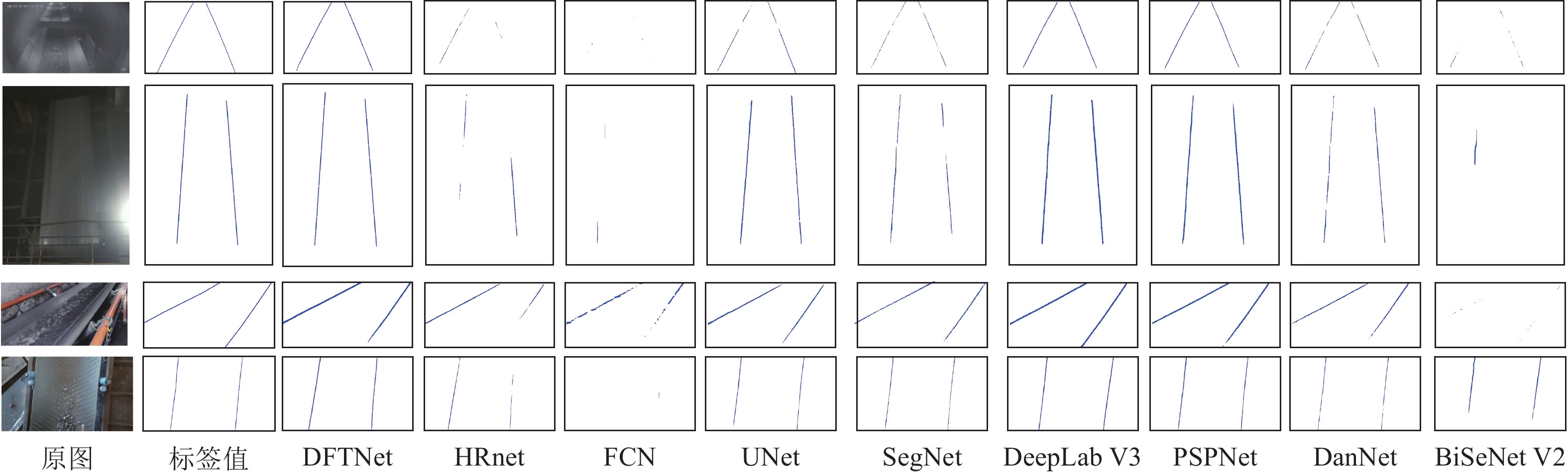
量/106HRNet 65.72 99.19 70.7 87.02 66.76 5.15 10.42 FCN 61.58 99.16 63.63 81.23 62.09 30.79 15.31 UNet 86.01 99.52 84.31 86.7 82.22 23.73 13.40 SegNet 79.06 99.41 87.76 86.55 82.42 26.50 35.00 DeepLab V3 86.87 99.44 85.05 81.41 89.68 31.33 41.68 PSPNet 87.46 99.49 85.53 83.51 87.83 33.96 48.63 DanNet 81.2 99.43 89.92 85.49 85.89 37.86 49.48 BiSeNet V2 66.43 99.22 71.81 80.16 67.45 2.46 3.62 DFTNet 91.08 99.48 88.4 91.88 96.22 5.71 28.45 -
[1] 张 佳,尹君驰,王宏等. 输送带输煤采样技术研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(9):200−206. ZHANG Jia,YIN Junchi,WANG Hong,et al. Research status and development trend of conveyor belt coal transport sampling technology[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2022,50(9):200−206.
[2] 王海军, 王洪磊. 基于参数化对数图像处理模型的光照不均匀图像的边缘检测算法[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(12):225−239. WANG Haijun, WANG Honglei. Status and prospect of intelligent key technologies of belt conveyorrStatus and prospect of intelligent key technologies of belt conveyorr[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2022,50(12):255−239.
[3] 谭 恒,张红娟,靳宝全等. 基于机器视觉的煤矿带式输送机跑偏检测方法[J]. 煤炭技术,2021,40(5):152−156. TAN Heng,ZHANG Hongjuan,JIN Baoquan,et al. Machine vision-based coal mines band-type conveyor running partial detection method[J]. Coal Technology,2021,40(5):152−156.
[4] 徐 欢,李振璧,姜媛媛等. 基于OpenCV的输送带跑偏自动检测算法研究[J]. 工矿自动化,2014,40(9):48−52. XU Huan,LI Zhenyu,JIANG Yuanyuan,et al. Research on automatic detection algorithm based on OpenCV-based conveyor belt running partial test algorithm[J]. Industry and Mining Automation,2014,40(9):48−52.
[5] 韩涛,黄友锐,张立志等. 基于图像识别的带式输送机输煤量和跑偏检测方法[J]. 工矿自动化,2020,46(4):17−22. HAN Tao,HUANG Yirui,ZHANG Lizhi,et al. The coal transmission volume and running test method based on image recognition [J]. Industry and Mining Automation,2014,40 (9):48−52.
[6] LIU Y,Wang Y,Zeng C,et al. Edge detection for conveyor belt based on the deep convolutional network[A]. Proceedings of 2018 Chinese Intelligent Systems Conference[C]. Springer,Singapore,2019:275−283.
[7] LONG J,SHELHAMER E,& DARRELL T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence,2016,39(4):474−482.
[8] CHEN L C,PAPANDREOU G,KOKKINOS I,et al. DeepLab:Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets,atrous convolution,and fully connected CRFs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2018,40(4):834−848. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2699184
[9] XIE S,TU Z. Holistically-nested edge detection[A]//Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision[C]. 2015:1395−1403.
[10] POMA X S,SAPPA A D. Improving edge detection in RGB images by adding NIR channel [A]//2018 14th International Conference on Signal-Image Technology & Internet-Based Systems (SITIS). IEEE,[C]. Las Palmas de Gran Canaria,Spain,2018:266−273.
[11] VASWANI A,SHAZEER N,PARMAR N,et al. Attention is all you need[A]//Advances in neural information processing systems[C]. Long Beach,CA,United states:MIT,2017:5998.
[12] DOSOVITSKIY A,BEYER L,KOLESNIKOV A,et al. An image is worth 16x16 words:Transformers for image recognition at scale[A]. International Conference on Learning Representations[C] Vienna:Springer,2021.
[13] TOUVRON H,CORD M,DOUZE M,et al. Training data-efficient image transformers & distillation through attention[A]//International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR[C]. 2021:10347−10357.
[14] LIU Z,LIN Y,CAO Y,et al. Swin transformer:Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows[A]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision[C]. Jeju,Korea:IEEE,2021:10012−10022.
[15] HU H,GU J,ZHANG Z,et al. Relation networks for object detection[A]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition[C]. 2018:3588−3597.
[16] HU H,ZHANG Z,XIE Z,et al. Local relation networks for image recognition[A]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision[C] 2019:3464−3473.
[17] ZHANG. Z,SABUNCU M. Generalized cross entropy loss for training deep neural networks with noisy labels[J]. Advances in neural information processing systems,2018,31:2241−2252.
[18] RONNEBERGER O,FISCHER P,BROX T. U-net:Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[A]. International Conference on Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention[C] Springer,Cham,2015:234−241.
[19] BADRINARAYANAN. V,KENDALL A,CIPOLLA R. SegNet:A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence,2017,39(12):2481−2495.
[20] ZHAO H,SHI J,QI X,et al. Pyramid scene parsing network[A]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition[C] Hawaii,2017:2881−2890.
[21] FU J,LIU J,TIAN H,et al. Dual attention network for scene segmentation [A]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition [C]. Tennessee,2019:3146−3154.
[22] YU C,GAO C,WANG J,et al. Bisenet v2:Bilateral network with guided aggregation for real-time semantic segmentation[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision,2021,129(11):3051−3068. doi: 10.1007/s11263-021-01515-2




 下载:
下载: