神南矿区煤炭绿色开采的水资源监测研究
Water resources monitoring of green coal mining in Shennan Mining Area
-
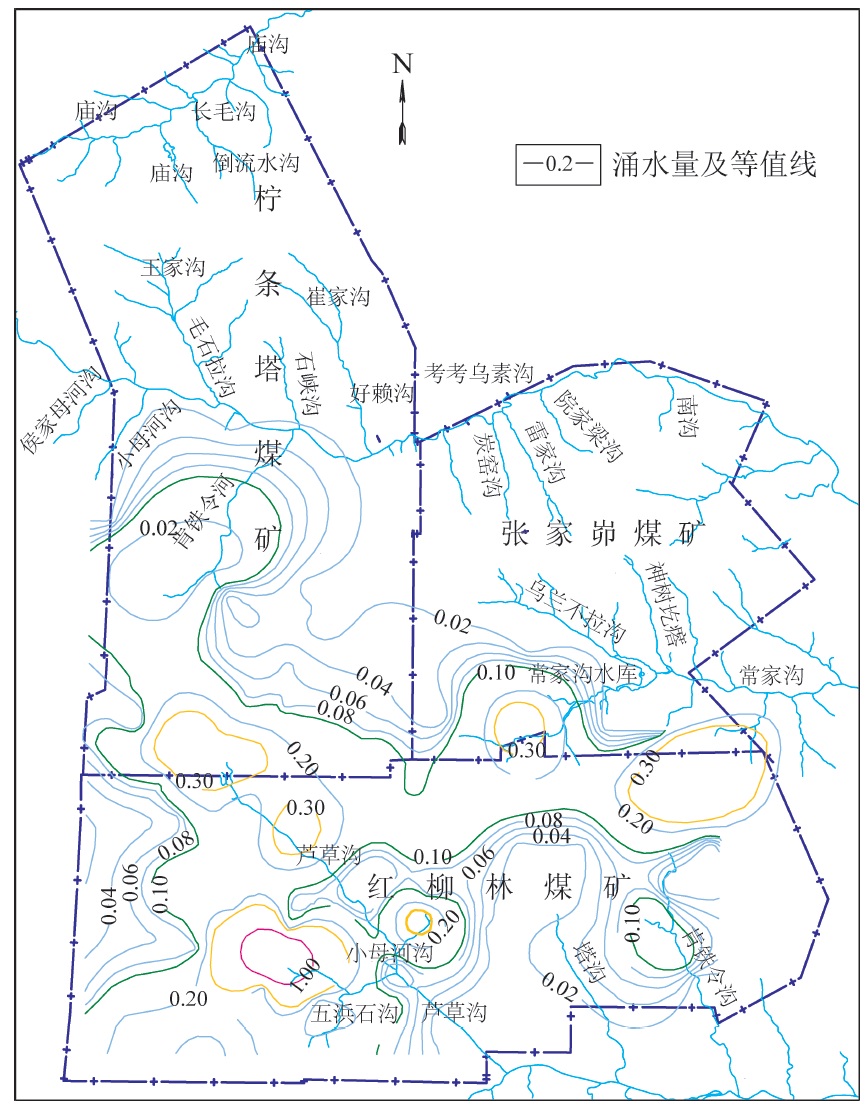
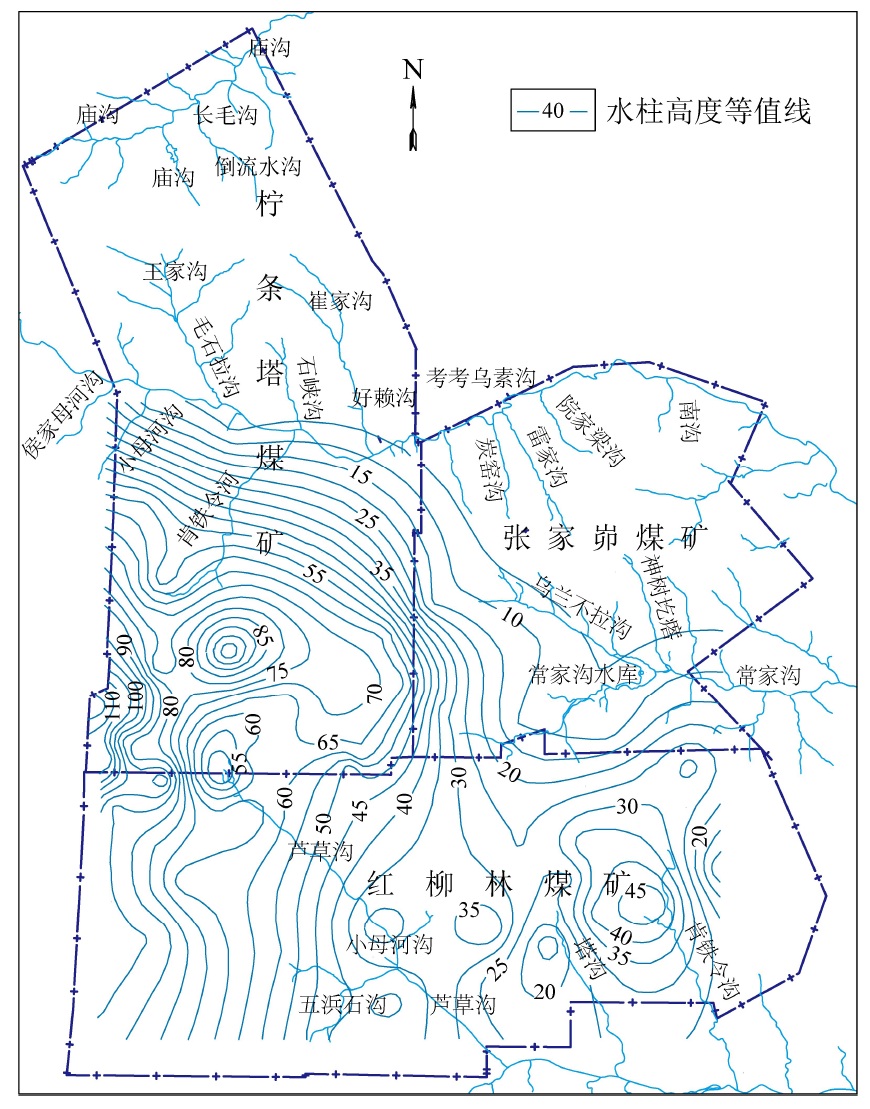
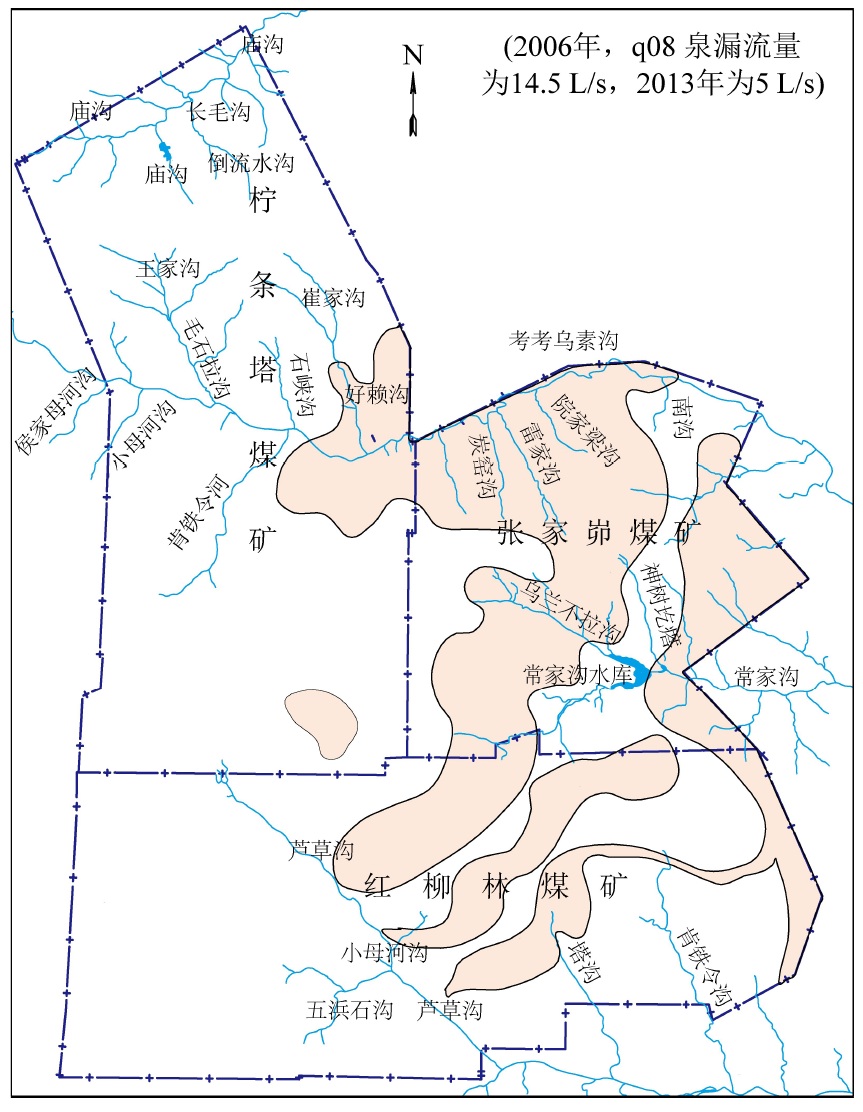
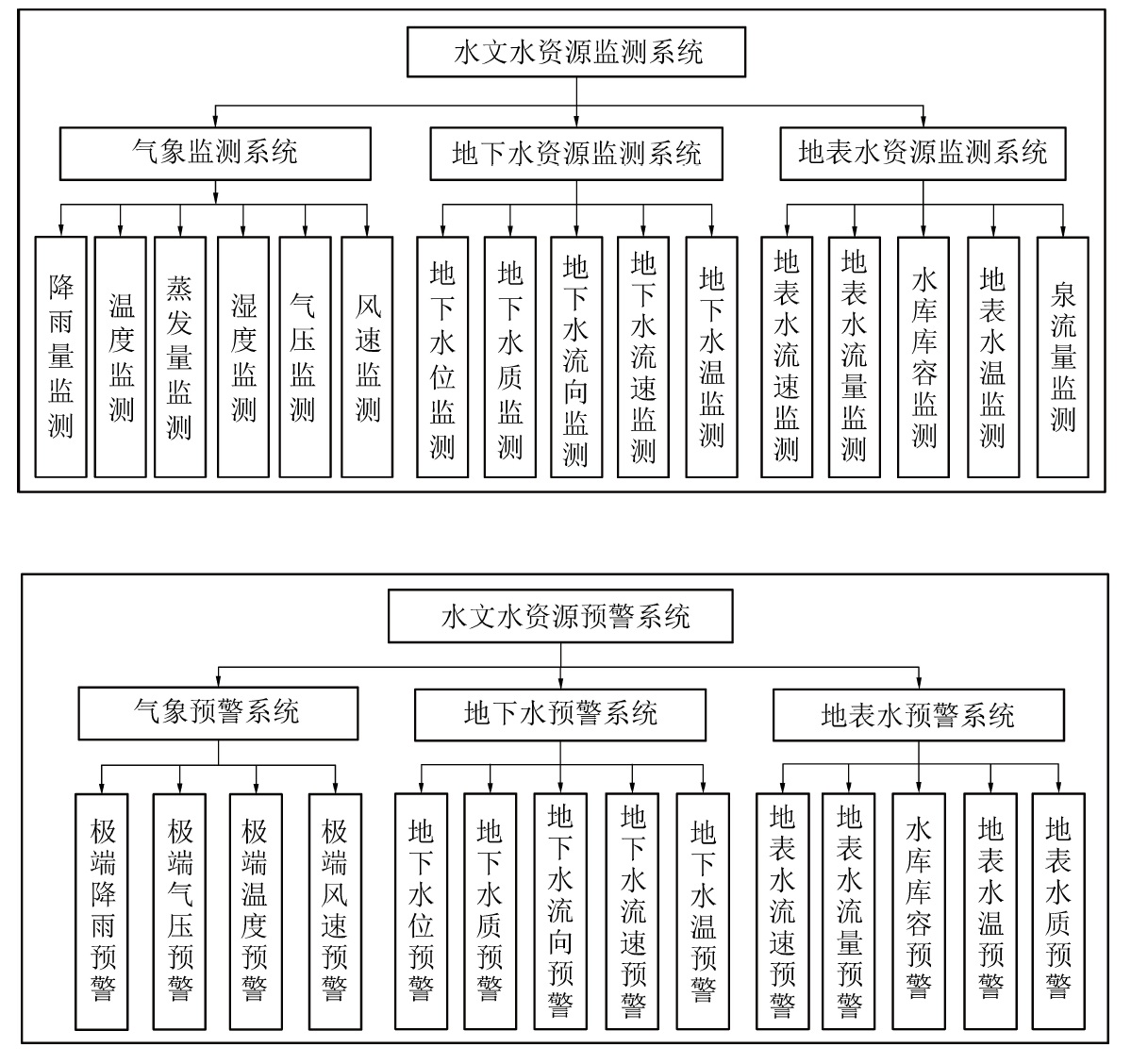
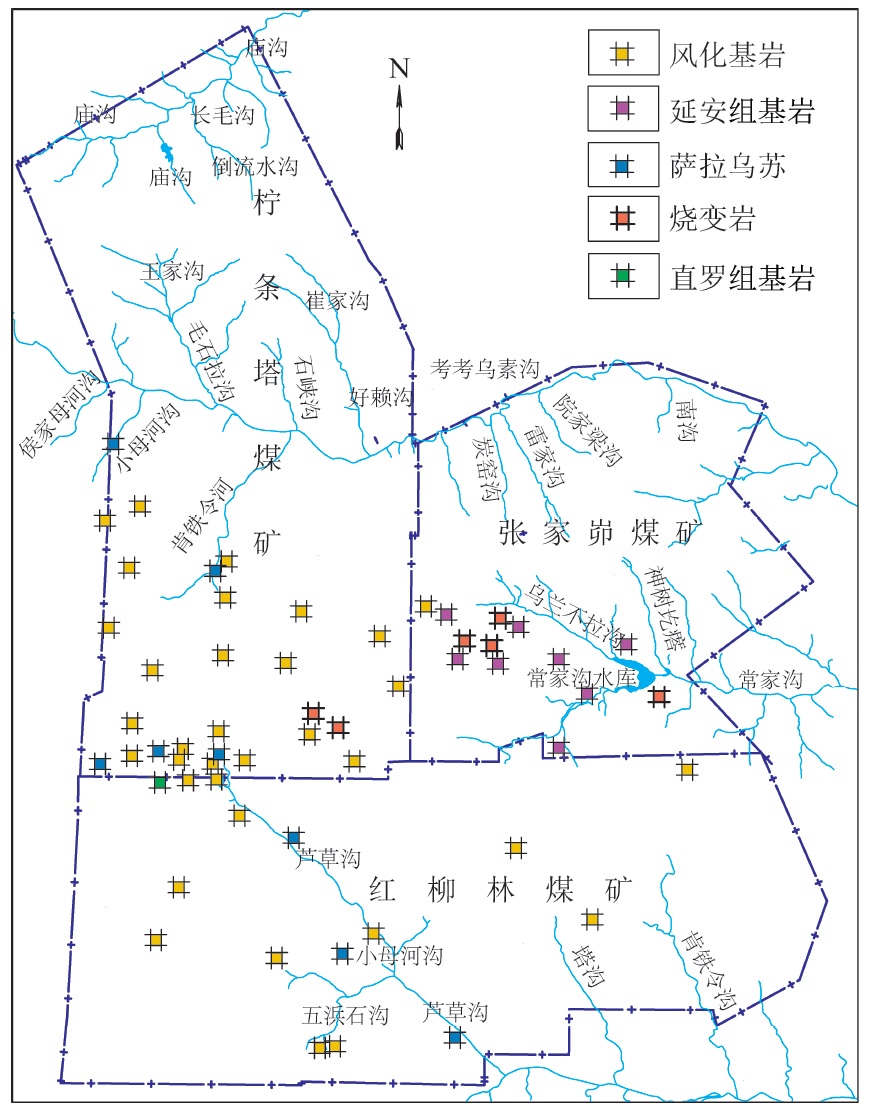
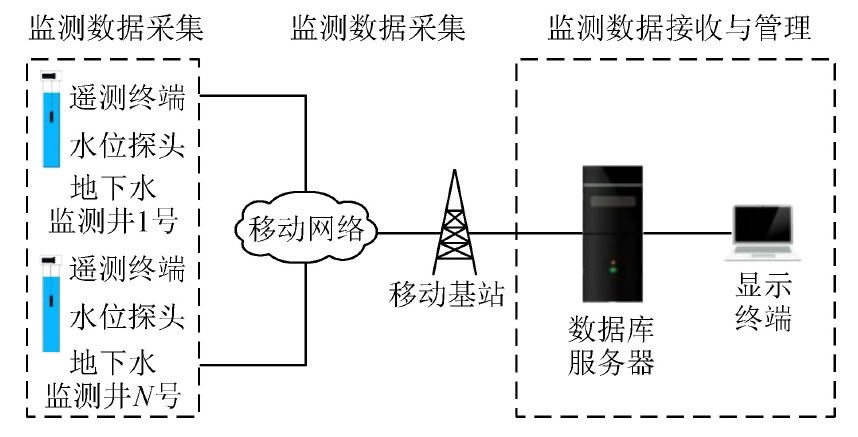
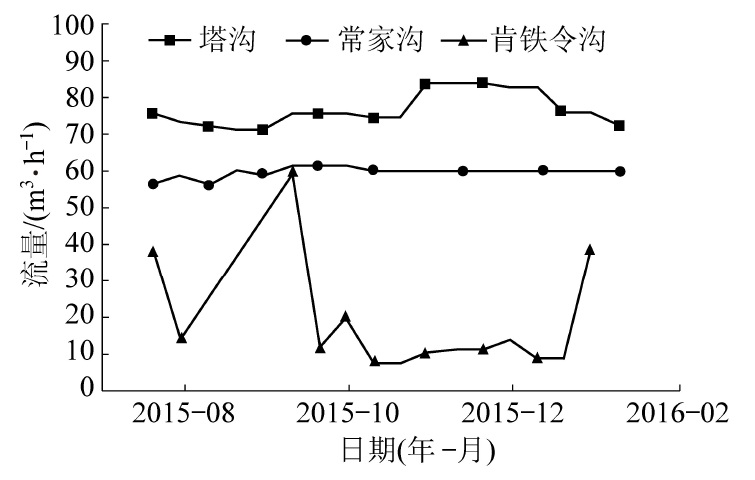
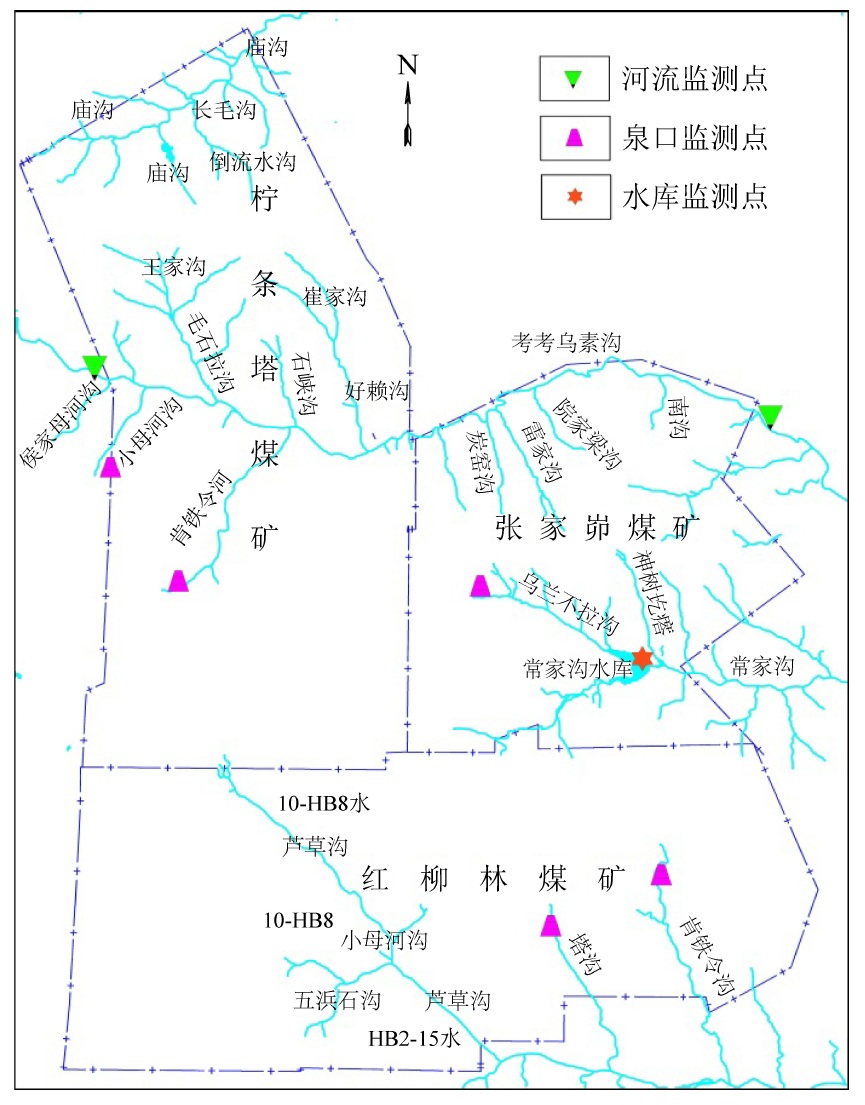
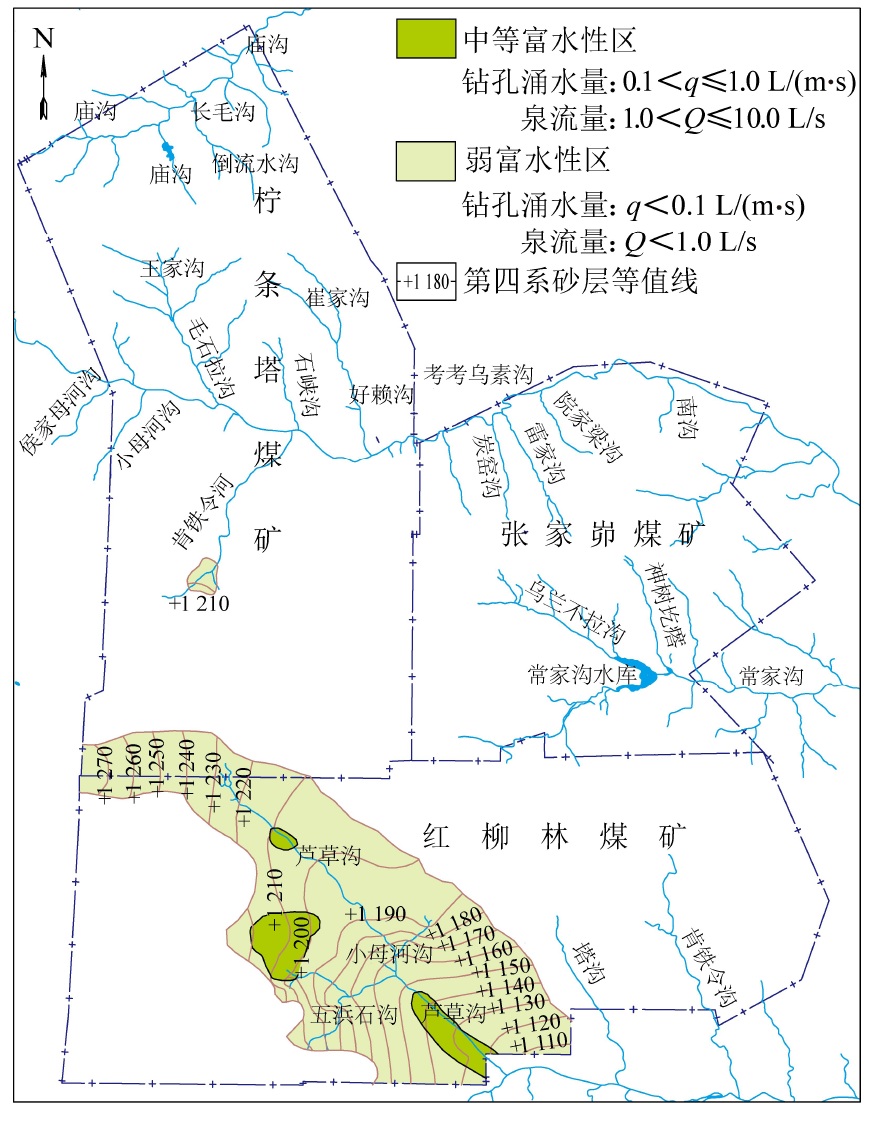
摘要: 陕北毛乌素沙地地质环境脆弱,水资源贫乏,煤炭绿色开发已经成为陕北煤炭基地可持续健康发展的必然选择,而陕北煤炭基地大规模、高强度的煤炭开采对水资源的影响程度一直是煤炭绿色开采的重要考核指标之一。为了研究陕北煤炭基地以水资源监测为核心的绿色开采监测,完善该地区水资源监测网的内容,以神南矿区柠条塔煤矿、红柳林煤矿、张家峁煤矿3座大型现代化矿井为例开展了水资源监测研究,结果表明:神南矿区内的萨拉乌苏组和风化基岩组为中强富水性含水层,烧变岩组为强富水性含水层,这3个岩组是区内的主要含水层,神南矿区针对区内不同含水层位共布置了60个监测钻孔,其中布置在萨拉乌苏组8个,烧变岩6个,风化基岩37个,直罗组基岩1个,延安组基岩8个。地下水监测数据通过自动监测系统的无线传输系统传输至数据中心,通过中心的监测管理软件实现数据的远程采集、远程实时监测。地表水监测则是在考考乌素沟上游及下游、肯铁令河、小侯家母河沟、塔沟、肯铁令沟、乌兰不拉沟及常家沟水库等地表水体各布置1个地表水监测点。通过以神南矿区60个地下水监测井、8个地表河流及泉监测点构成的水资源监测网为例,实施矿区水资源动态监控,以期为陕北煤炭基地煤炭绿色开采水资源监测提供借鉴。
-
关键词:
- 地下水监测 /
- 绿色开采 /
- 保水采煤(保水开采) /
- 烧变岩 /
- 大型煤炭基地
Abstract: The geological environment of Maowusu Sandy Land in Northern Shaanxi is fragile and the water resources are poor. Green coal development has become an inevitable choice for sustainable and healthy development of coal base in the Northern Shaanxi. The impact of large-scale and high-intensity coal mining on water resources in the Northern Shaanxi Coal Base has been one of the important assessment indicators of green coal mining. In order to study the green mining monitoring with water resources monitoring as the core in the Northern Shaanxi Coal Base and improve the content of water resources monitoring network in this area,three large-scale modern mines in the Shennan Mining Area, namely Ningtiaota Mine, Hongliulin Mine and Zhangjiamao Mine were taken, as examples to carry out the research on water resources monitoring network. The results show that the Salawusu formation and weathered bedrock formation in Shennan Mining Area are medium-strong water rich aquifer, and the Burnt rock formation is strong water rich aquifer. These three rock formations are the main aquifers in the area. A total of 60 monitoring boreholes are arranged for different aquifer levels in Shennan Mining Area, including 8 in Salawusu formation, 6 in Burnt rock formation, 37 in Weathered bedrock Formation, 1 in Zhiluo Formation and 8 in Yan’an bedrock formation. The groundwater monitoring data is transmitted to the data center through the wireless transmission system of the automatic monitoring system, and the remote collection and remote real-time monitoring of the data are realized through the monitoring management software of the center. For surface water monitoring, one surface water monitoring point is set up in the upper and lower reaches of Kaokaowusu river, Kentieling river, Xiaohoujiamu river, Tagou, Kentieling river, Wulanbula river and Changjiagou reservoir. Taking the water resources monitoring network composed of 60 groundwater monitoring wells, 8 surface rivers and springs monitoring points in Shennan Mining Area as an example, the dynamic monitoring of water resources in the mining area is implemented, so as to provide reference for the monitoring of water resources in green coal mining of the Coal Base Northern Shaanxi-
Keywords:
- water resources monitoring /
- green mining /
- water-preserved mining /
- burnt rock /
- large coal base
-
-
期刊类型引用(16)
1. 王双明,李识博,孙强,侯恩科,耿济世,师庆民,王生全,周书涛,郑鑫超. 论“碳、水、环”约束下的煤炭减损开采地质保障. 西安科技大学学报. 2025(01): 1-11 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 夏玉成,孙学阳,苗霖田,郭晨,杜荣军. 智能时代的矿井地质工作展望——矿井开采智能地质保障技术体系架构. 煤田地质与勘探. 2025(01): 64-76 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 范立民. 神府煤田勘查开发的地质科技创新与贡献. 煤田地质与勘探. 2025(03): 1-22 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 汪璐璐,谢小伟,幸茂仁,许光煜. 基于GRACE数据评估黄土高原煤炭开采对地下水储量的影响. 江西科学. 2024(02): 264-270 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王海. 隐伏火烧区烧变岩含水层水害治理技术研究. 煤田地质与勘探. 2024(05): 88-97 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 王双明,孙强,袁士豪,师庆民,侯恩科,陈凯,黄震,吴海波,武佳坤,耿济世,张玉良,黄金廷. 论煤–水–土多资源协调开发. 西北地质. 2024(05): 1-10 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 王双明,耿济世,李鹏飞,孙强,范章群,李丹. 煤炭绿色开发地质保障体系的构建. 煤田地质与勘探. 2023(01): 33-43 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 董东林,张陇强,张恩雨,傅培祺,陈宇祺,林新栋,李慧哲. 基于PSO-XGBoost的矿井突水水源快速判识模型. 煤炭科学技术. 2023(07): 72-82 .  本站查看
本站查看
9. 王义,张俊娥,程洋,陈静,王一淑,董婧,伍娟丽. 煤矿区植被-水-土响应关系研究进展分析. 干旱区资源与环境. 2023(11): 82-91 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 张瑞昭. 石圪台煤矿第四系松散含水层保水采煤方案研究. 中国煤炭. 2023(S2): 215-225 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 杨磊,杨斯亮,车晓阳. 红柳林井田烧变岩富水性分区与水害防治措施. 中国煤炭地质. 2022(02): 43-47+70 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 吴群英,胡雄武,王宏科. 陕北矿区地下水资源地面瞬变电磁法探查实践. 煤炭科学技术. 2022(05): 208-215 .  本站查看
本站查看
13. 白如鸿,刘壮,刘宁平,高兴斌,贺铜章. 榆树湾煤矿矿井涌水规律及防治水思路. 陕西煤炭. 2022(05): 144-148 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 吴立群,王建英,杨帆,郑宇航,焦养泉,荣辉,王宏科,马雄德,孙魁,陈雪永,屈伸,李金辉. 榆林地区北部侏罗纪古河道砂体与采煤涌(突)水关系分析. 煤炭学报. 2022(10): 3599-3609 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 范立民,吴群英,彭捷,迟宝锁,孙魁,王宏科,郭佐宁,宁奎斌,刘水,李成,赵小峰,田水豹,李博,陈建平,高帅,仵拨云,姬怡微,郑苗苗,杜江丽. 黄河中游大型煤炭基地地质环境监测思路和方法. 煤炭学报. 2021(05): 1417-1427 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 白如鸿,刘晋波,郑忠友,周党文,朱磊. 郭家滩煤矿无害化开采技术体系构建. 陕西煤炭. 2021(04): 200-204 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)




 下载:
下载: